Unveiling Patterns: A Guide to Effective Trend Visualization
Related Articles: Unveiling Patterns: A Guide to Effective Trend Visualization
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling Patterns: A Guide to Effective Trend Visualization. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling Patterns: A Guide to Effective Trend Visualization
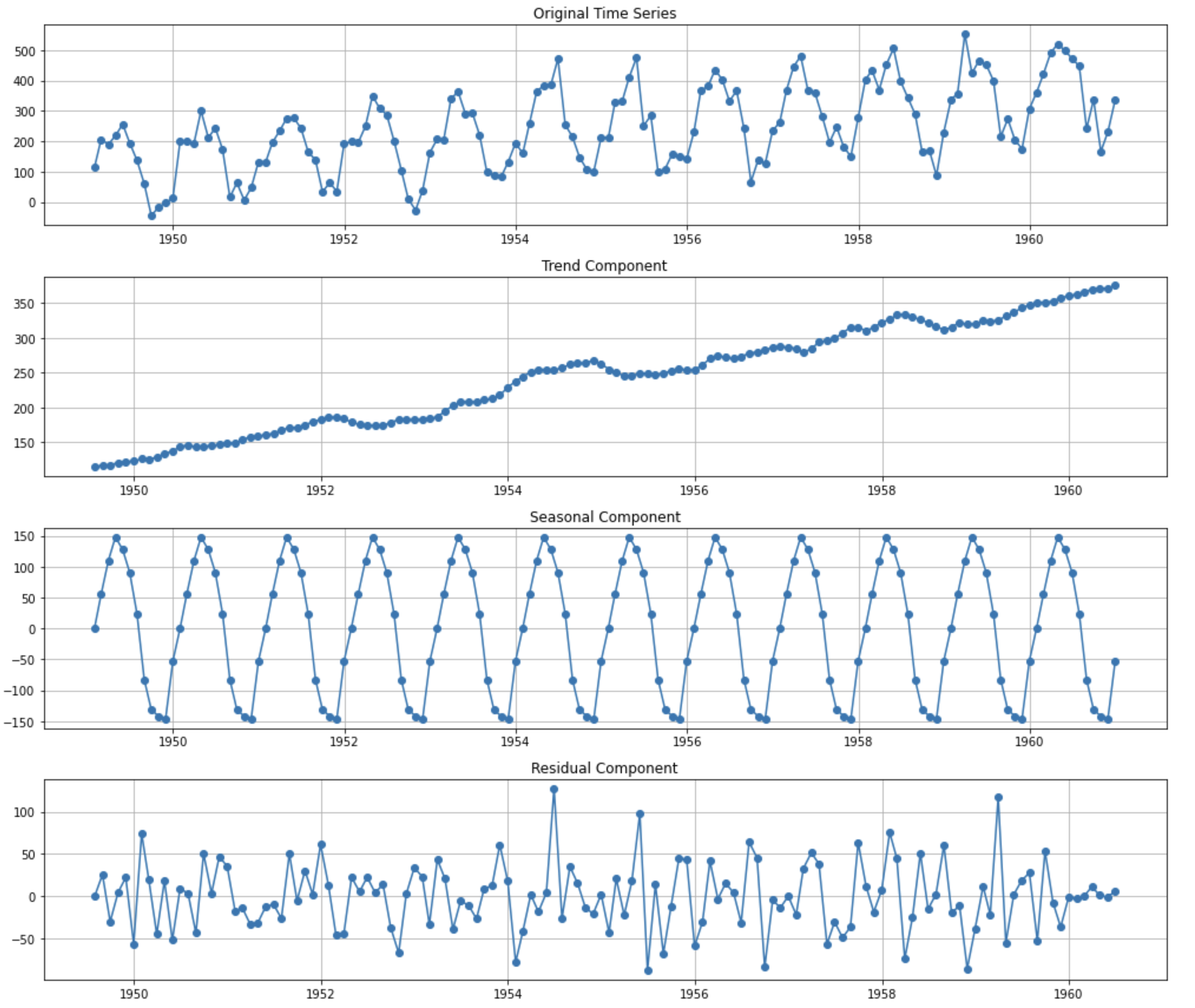
Trends, the subtle shifts and pronounced surges in data, hold the key to understanding the present and predicting the future. Whether it’s market behavior, social sentiment, or scientific research, identifying and showcasing these patterns is crucial for informed decision-making. This comprehensive guide explores the various methods for displaying trends, highlighting their strengths and applications, and ultimately empowering you to communicate insights effectively.
Understanding the Power of Visual Representation
Trends are often hidden within vast datasets, requiring specialized tools and techniques to extract meaningful information. While raw data can be overwhelming, visual representations offer a clear and concise way to communicate patterns and insights. The human brain is inherently visual, making charts and graphs more accessible and impactful than long tables of numbers.
Choosing the Right Visual Tool
The choice of visualization depends on the specific trend you wish to display and the audience you are targeting. Here are some common and effective methods:
1. Line Charts:
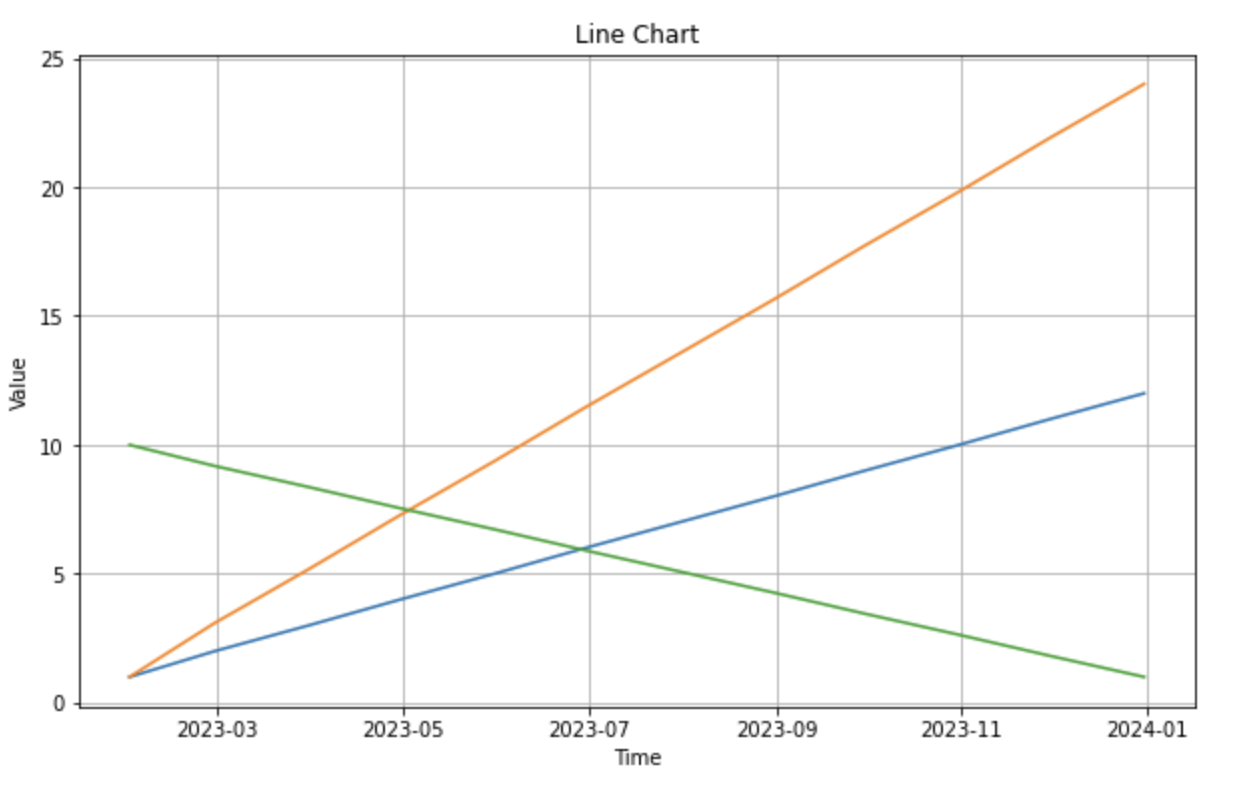
Line charts excel at showcasing trends over time. They are particularly useful for displaying continuous data, such as sales figures, website traffic, or temperature fluctuations. The slope of the line indicates the direction and magnitude of the trend.
2. Bar Charts:
Bar charts are ideal for comparing discrete categories or data points at specific intervals. They are particularly effective for visualizing changes over time, highlighting differences between groups, or comparing performance metrics.
3. Scatter Plots:
Scatter plots are used to visualize the relationship between two variables. By plotting data points on a two-dimensional graph, one can identify potential correlations and trends.
4. Area Charts:
Area charts are similar to line charts, but they fill the space beneath the line, highlighting the cumulative effect of the trend over time. They are particularly effective for visualizing growth or decline in a specific area.
5. Heat Maps:
Heat maps use color gradients to represent data density or intensity. They are ideal for visualizing complex datasets with multiple variables, allowing for the identification of clusters and patterns.
6. Maps:
Maps are powerful tools for visualizing geographical trends. They can display the distribution of data across regions, highlighting areas of high concentration or growth.
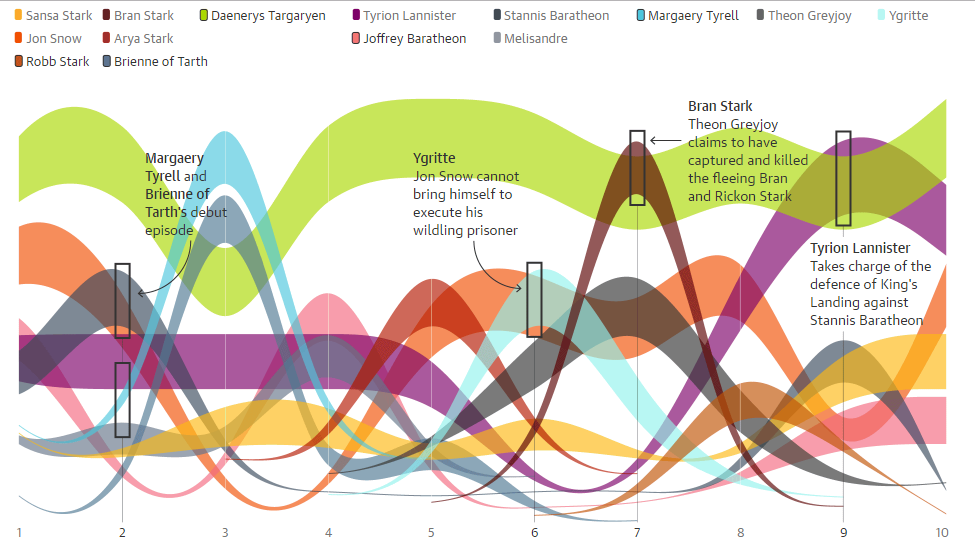
7. Infographics:
Infographics combine visual elements with textual information to present complex data in a clear and engaging manner. They are particularly effective for communicating trends to a broad audience, simplifying complex information into easily digestible visuals.
8. Interactive Dashboards:
Interactive dashboards offer a dynamic and engaging way to explore trends. Users can filter, sort, and manipulate data in real-time, gaining deeper insights and discovering hidden patterns.
Beyond Basic Visualization: Adding Depth and Context
While the above tools provide a foundation for trend visualization, adding context and depth can significantly enhance their impact. Consider these techniques:
1. Annotations:
Annotations, such as labels, arrows, and notes, can be added to highlight specific data points, explain trends, or provide further context. They help the viewer understand the story behind the data.
2. Comparisons:
Comparing trends across different groups, time periods, or variables can reveal valuable insights. This can be achieved through side-by-side comparisons, stacked charts, or the use of different colors or patterns.
3. Trend Lines:
Trend lines can be added to charts to highlight the overall direction of the data. They can be linear, exponential, or logarithmic, depending on the nature of the trend.
4. Data Storytelling:
Beyond the visualization itself, the story you tell around the data is crucial. Contextualize the trends, explain their significance, and highlight key takeaways.
5. Interactive Elements:
Interactive elements, such as tooltips, filters, and zoom functions, can empower viewers to explore the data further and gain a deeper understanding of the trends.
FAQs
1. What are the best practices for choosing a visualization method?
The best visualization method depends on the type of data, the message you want to convey, and the target audience. Consider the following factors:
- Data Type: Continuous data is best displayed with line charts or area charts, while discrete data is better suited for bar charts or scatter plots.
- Message: If you want to highlight growth or decline, use area charts or bar charts. If you want to show relationships between variables, use scatter plots.
- Audience: Consider the level of technical expertise of your audience when choosing a visualization method. Keep it simple and easy to understand for a general audience.
2. How can I make my visualizations more engaging?
- Use clear and concise labels and titles.
- Choose colors and fonts that are visually appealing and easy to read.
- Limit the amount of information on each chart.
- Use interactive elements to encourage exploration.
- Tell a story with the data, highlighting key insights and takeaways.
3. What are some common pitfalls to avoid when displaying trends?
- Overcrowding the chart with too much information.
- Using misleading scales or axes.
- Choosing inappropriate visualization methods for the data.
- Failing to provide context or explanation.
Tips
- Start with a clear understanding of the data and the message you want to convey.
- Experiment with different visualization methods to find the best fit for your data and audience.
- Use color and design elements to enhance the visual impact of your visualizations.
- Always provide context and explanation for your visualizations.
- Test your visualizations with different audiences to ensure they are effective and understandable.
Conclusion
Visualizing trends is not merely about creating aesthetically pleasing charts; it’s about communicating complex information in a clear, concise, and engaging manner. By mastering the art of trend visualization, you can unlock the power of data, revealing hidden patterns, and driving informed decision-making. Choose the right tools, add context and depth, and tell a compelling story with your data. This will not only enhance your understanding of the trends but also empower you to communicate insights effectively, influencing stakeholders and shaping the future.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling Patterns: A Guide to Effective Trend Visualization. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
