Unraveling the Time of the Last Reboot: A Comprehensive Guide to Windows 10 System Information
Related Articles: Unraveling the Time of the Last Reboot: A Comprehensive Guide to Windows 10 System Information
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Time of the Last Reboot: A Comprehensive Guide to Windows 10 System Information. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unraveling the Time of the Last Reboot: A Comprehensive Guide to Windows 10 System Information
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unraveling the Time of the Last Reboot: A Comprehensive Guide to Windows 10 System Information
- 3.1 The Power of Knowing: Why Understanding the Last Reboot Time Matters
- 3.2 Exploring the Avenues: Methods to Retrieve the Last Reboot Time
- 3.3 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 3.4 Tips for Finding the Last Reboot Time
- 3.5 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Unraveling the Time of the Last Reboot: A Comprehensive Guide to Windows 10 System Information

Understanding when your Windows 10 computer last rebooted can be invaluable for troubleshooting various issues, analyzing system performance, and even detecting potential security threats. The last reboot time serves as a crucial timestamp, providing insights into the system’s recent activity and helping pinpoint the root cause of problems. This article delves into the various methods to retrieve this information, catering to both novice and experienced users.
The Power of Knowing: Why Understanding the Last Reboot Time Matters
The last reboot timestamp holds significance for several reasons:
-
Troubleshooting Issues: When encountering software malfunctions, driver conflicts, or system instability, knowing the last reboot time can be a starting point for investigations. Did the issue arise after the last reboot? Did a recent update or installation precede the reboot? The answers can guide troubleshooting efforts.
-
Security Investigations: A sudden or unexpected reboot might indicate a potential security breach or malicious activity. By knowing the last reboot time, security analysts can trace back potential threats, analyze system logs, and identify suspicious activity.
-
Performance Monitoring: Frequent reboots can point to hardware or software issues that affect system stability and performance. Understanding the reboot frequency helps in identifying potential bottlenecks or resource-intensive applications.
-
System Audit: Regularly tracking the last reboot time can assist in maintaining a comprehensive system audit log, providing valuable information about system changes and activity.
Exploring the Avenues: Methods to Retrieve the Last Reboot Time
Several methods exist to determine the last reboot time in Windows 10. Each approach offers a unique perspective and level of detail, allowing users to choose the most suitable method based on their needs and technical expertise.
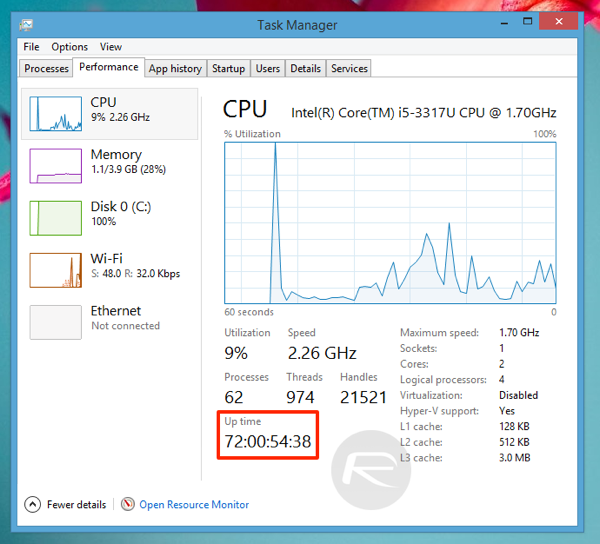
1. The Task Manager: A Quick and Easy Overview
The Task Manager, a readily accessible tool within Windows 10, offers a quick glimpse into the last reboot time.
- Access the Task Manager: Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc or right-click the taskbar and select Task Manager.
- Navigate to the Performance Tab: Select the Performance tab.
- Locate the Uptime Information: Under the CPU section, you will find the system’s uptime, which indicates the time elapsed since the last reboot.
2. The Event Viewer: A Detailed Chronicle of System Events
The Event Viewer, a powerful tool for monitoring and analyzing system events, provides a comprehensive log of system activity, including reboot timestamps.
- Open the Event Viewer: Search for "Event Viewer" in the Windows search bar and open the application.
- Navigate to System Logs: Expand Windows Logs and select System.
- Filter for System Events: Use the Filter Current Log option to search for events with the ID 6006 or 6008. These events correspond to system shutdown and startup respectively.
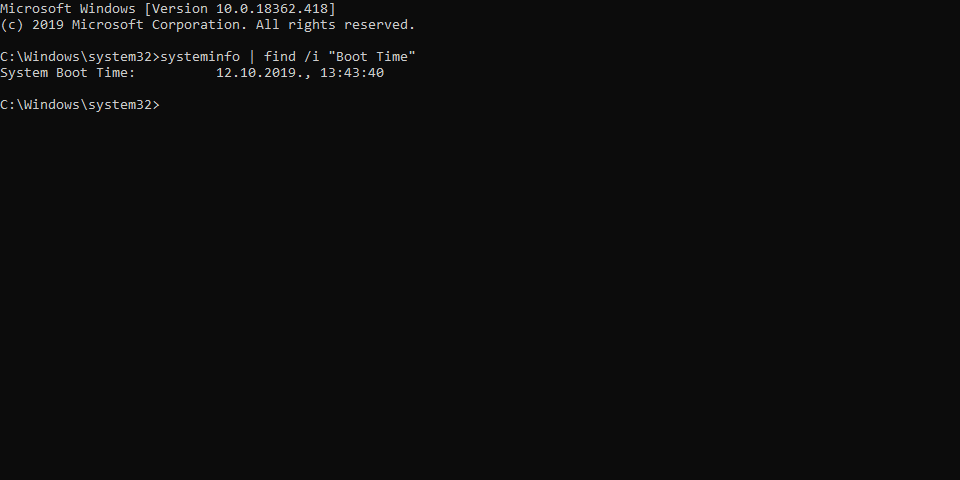
3. The Command Prompt: A Versatile Command-Line Tool
The Command Prompt offers a powerful command-line interface for interacting with the operating system. It provides access to various system information, including the last reboot time.
- Open the Command Prompt: Search for "cmd" in the Windows search bar and run as administrator.
-
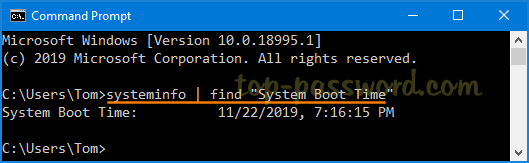
Utilize the "systeminfo" Command: Execute the command
systeminfoand scroll through the output. The "System Up Time" field displays the time since the last reboot.
4. The PowerShell: A Scripting Language for Advanced Users
PowerShell, a scripting language built into Windows 10, provides more advanced methods for retrieving system information.
- Open PowerShell: Search for "powershell" in the Windows search bar and run as administrator.
-
Use the "Get-EventLog" Cmdlet: Execute the following command:
Get-EventLog -LogName System -InstanceId 6006 | Select-Object -Property TimeCreatedThis command retrieves the time of the last shutdown event.
5. Third-Party Tools: Specialized Solutions for Specific Needs
Numerous third-party tools offer specialized features for analyzing system information, including the last reboot time. These tools often provide graphical interfaces, advanced filtering options, and integration with other system monitoring tools.
- Process Explorer: This tool from Microsoft offers detailed information about running processes and system resources, including the last reboot time.
- Sysinternals Suite: This collection of tools from Microsoft includes utilities like Bootmon and EventLog that provide in-depth system analysis, including reboot timestamps.
6. The BIOS/UEFI Settings: A Peek into the System’s Boot Process
The BIOS/UEFI settings, accessible during system startup, may contain information about the last boot time.
- Access the BIOS/UEFI: Restart the computer and press the appropriate key (usually F2, F10, or Del) to enter the BIOS/UEFI setup.
- Search for Boot Information: Navigate through the BIOS/UEFI menus to find a section related to boot information or system logs.
7. The System Logs: A Detailed Record of System Activity
Windows 10 maintains detailed system logs that record various system events, including reboots. These logs can be accessed using the Event Viewer or through specialized system analysis tools.
- Event Viewer: The Event Viewer provides access to system logs, including the "System" log, which records events related to system startup and shutdown.
- System Analysis Tools: Several third-party tools offer advanced features for analyzing system logs, providing detailed information about system events and reboot timestamps.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: How often should I reboot my computer?
A: While there is no hard and fast rule, regular reboots are generally recommended for maintaining system stability and performance. A weekly reboot is often considered a good practice, although you may need to reboot more frequently if you encounter specific issues.
Q: Can I reset the last reboot time?
A: While you cannot directly reset the last reboot time, restarting your computer will update the timestamp to the current time.
Q: What if the last reboot time information is missing or inaccurate?
A: If you suspect that the last reboot time is missing or inaccurate, you can try the following:
- Check the system logs: The Event Viewer may contain more detailed information about system events, including reboots.
- Use a third-party tool: Specialized system analysis tools may provide more accurate or detailed information about system events.
- Contact your computer manufacturer: If you are unable to find the information yourself, you can contact your computer manufacturer for assistance.
Q: Is there a way to automatically record the last reboot time?
A: You can configure Windows 10 to automatically record system events, including reboots, in the Event Viewer. This provides a detailed log of system activity.
Q: What are the best practices for system maintenance and rebooting?
A: To ensure optimal system performance and stability, consider these best practices:
- Regularly reboot your computer: A weekly reboot is generally recommended to clear system resources and update system files.
- Install updates promptly: Install software and driver updates as they become available to maintain system security and performance.
- Run a system scan regularly: Use a system scan tool to check for malware and other threats.
- Clean your computer regularly: Remove unnecessary files and programs to free up disk space and improve performance.
- Monitor system performance: Use system monitoring tools to track resource usage and identify potential bottlenecks.
Tips for Finding the Last Reboot Time
- Utilize multiple methods: Use different methods to verify the last reboot time and ensure accuracy.
- Consult system logs: The Event Viewer provides detailed system logs that can help pinpoint the last reboot time.
- Consider third-party tools: Specialized tools offer advanced features for analyzing system information, including reboot timestamps.
- Check the BIOS/UEFI settings: The BIOS/UEFI settings may contain information about the last boot time.
- Be aware of system events: Keep track of recent system events, such as software installations, updates, or security scans, as these can affect the last reboot time.
Conclusion
Determining the last reboot time in Windows 10 is a valuable skill for troubleshooting issues, analyzing system performance, and enhancing security. This article has presented a comprehensive guide to various methods for retrieving this information, catering to users of varying technical expertise. Understanding the last reboot time empowers users to diagnose problems, monitor system health, and maintain a secure and stable computing environment. By leveraging the techniques outlined in this article, users can confidently navigate the intricacies of their Windows 10 systems and effectively address any challenges that arise.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Time of the Last Reboot: A Comprehensive Guide to Windows 10 System Information. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!