Unlocking Windows 10’s Potential: A Comprehensive Guide to Group Policy Editor
Related Articles: Unlocking Windows 10’s Potential: A Comprehensive Guide to Group Policy Editor
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unlocking Windows 10’s Potential: A Comprehensive Guide to Group Policy Editor. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unlocking Windows 10’s Potential: A Comprehensive Guide to Group Policy Editor
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unlocking Windows 10’s Potential: A Comprehensive Guide to Group Policy Editor
- 3.1 Understanding the Group Policy Editor
- 3.2 Navigating the Group Policy Editor
- 3.3 Applying and Managing Policies
- 3.4 Practical Examples of Group Policy Editor Applications
- 3.5 FAQs Regarding the Group Policy Editor
- 3.6 Tips for Effective Use of the Group Policy Editor
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Unlocking Windows 10’s Potential: A Comprehensive Guide to Group Policy Editor

The Group Policy Editor, accessed through the gpedit.msc command, provides a powerful tool for Windows 10 administrators to manage and configure various aspects of the operating system. It allows for granular control over user settings, security configurations, and system behavior, empowering users to tailor Windows 10 to meet specific needs and enhance security. This comprehensive guide will explore the Group Policy Editor’s functionalities, its benefits, and how to utilize it effectively.
Understanding the Group Policy Editor
The Group Policy Editor is a hierarchical framework that organizes policies into distinct categories, including User Configuration and Computer Configuration. These categories contain settings that affect user accounts and the system itself, respectively. Each policy setting can be configured to apply to specific user groups, computers, or organizational units. This granular control allows administrators to manage policies effectively within complex IT environments.
Key Benefits of Utilizing the Group Policy Editor:
- Centralized Management: The Group Policy Editor facilitates centralized management of system settings, ensuring consistency and uniformity across a network. This simplifies the process of applying configuration changes to multiple computers, eliminating the need for manual adjustments on each device.
- Enhanced Security: By leveraging the Group Policy Editor, administrators can implement robust security measures, such as password complexity requirements, account lockout policies, and restrictions on software installation. This helps to mitigate security risks and protect sensitive data.
- User Experience Customization: The Group Policy Editor empowers administrators to tailor the user experience by controlling features like the Start menu, taskbar, and desktop background. This allows for the creation of customized environments that cater to specific user roles or preferences.
- Streamlined Software Deployment: The Group Policy Editor facilitates the deployment of software applications and updates across an organization. Administrators can define software installation policies, ensure automatic updates, and manage application usage.
- Improved Performance and Stability: By configuring system settings through the Group Policy Editor, administrators can optimize performance, enhance stability, and reduce resource consumption. This leads to a smoother user experience and improved system efficiency.
Navigating the Group Policy Editor
Upon launching gpedit.msc, users are presented with a hierarchical structure that organizes policies into categories. The left pane displays the policy categories, while the right pane showcases the available settings within each category.
Exploring the Key Categories:
- User Configuration: This category contains settings that directly affect user accounts, including user rights, application settings, and desktop customization options.
- Computer Configuration: This category governs system-wide settings, including network configuration, security policies, and software installation preferences.
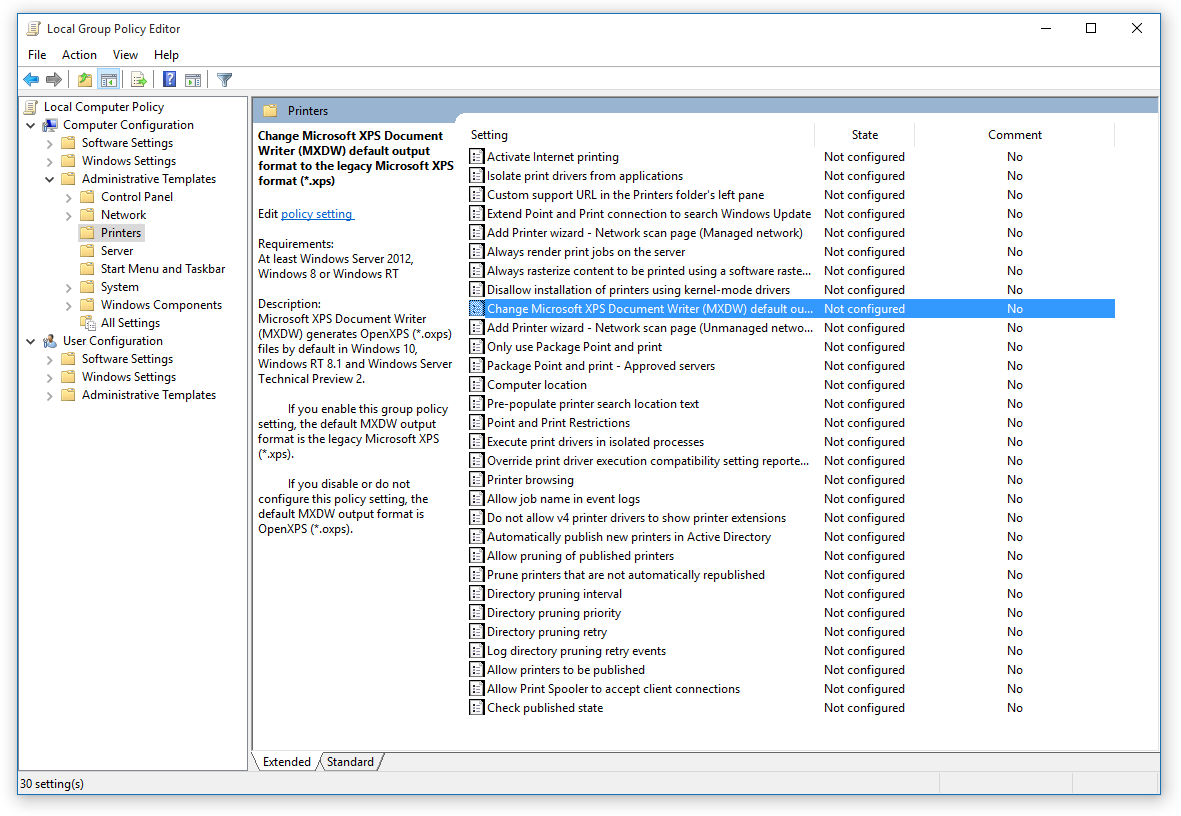
- Administrative Templates: This category provides access to pre-defined templates that offer a comprehensive set of policy settings for specific applications and system components.
Applying and Managing Policies
Once a policy setting is configured, it can be applied to specific user groups, computers, or organizational units. This allows for targeted policy implementation based on user roles or network structure. Policies can be applied through the Group Policy Object (GPO) editor, which allows administrators to link policies to specific Active Directory objects.
Managing Policy Settings:
- Enabled/Disabled: Policy settings can be enabled or disabled, enabling administrators to activate or deactivate specific configurations based on their needs.
- Configured: Settings can be configured to specific values, allowing for customized configuration options.
- Not Configured: This option leaves the setting at its default value, allowing for flexibility and avoiding unnecessary intervention.
Practical Examples of Group Policy Editor Applications
1. Restricting User Access to Specific Applications:
Administrators can use the Group Policy Editor to restrict user access to specific applications. This is particularly useful in environments where users need to access only specific software for their tasks. By setting up an appropriate policy, administrators can prevent users from running unauthorized applications, enhancing security and productivity.
2. Enforcing Strong Password Policies:
The Group Policy Editor allows administrators to enforce strong password policies, requiring users to create passwords that meet specific criteria. This can include minimum password length, complexity requirements, and password expiry policies. By implementing these policies, administrators can mitigate the risk of unauthorized access and protect sensitive data.
3. Configuring Network Settings:
The Group Policy Editor provides granular control over network settings, allowing administrators to configure network access, firewall rules, and proxy settings. This ensures consistent network connectivity and security across the organization.
4. Managing Software Updates:
Administrators can leverage the Group Policy Editor to manage software updates, ensuring timely updates across the network. This includes configuring automatic updates, scheduling update times, and controlling update delivery methods.
5. Customizing the User Interface:
The Group Policy Editor allows for customization of the user interface, including the Start menu, taskbar, and desktop background. This enables administrators to create a consistent and user-friendly environment that meets the organization’s specific needs.
FAQs Regarding the Group Policy Editor
1. What are the prerequisites for using the Group Policy Editor?
The Group Policy Editor is available in Windows 10 Professional, Enterprise, and Education editions. It is not available in Windows 10 Home edition.
2. How do I access the Group Policy Editor?
The Group Policy Editor can be accessed by typing gpedit.msc in the Windows search bar and pressing Enter.
3. Can I use the Group Policy Editor to manage user accounts?
While the Group Policy Editor does not directly manage user accounts, it can be used to configure policies that affect user accounts, such as password complexity requirements and account lockout policies.
4. Is the Group Policy Editor compatible with Active Directory?
Yes, the Group Policy Editor is fully compatible with Active Directory, allowing administrators to manage policies across a network of computers.
5. What are the potential risks associated with using the Group Policy Editor?
Misconfigured Group Policy settings can lead to system instability or security vulnerabilities. It is crucial to understand the impact of policy changes before implementing them.
Tips for Effective Use of the Group Policy Editor
- Start with a Backup: Before making any significant changes to Group Policy settings, create a backup of the existing policies to ensure a recovery point in case of errors.
- Test Thoroughly: Always test policy changes in a test environment before deploying them to production systems. This minimizes the risk of unexpected issues.
- Document Policy Changes: Maintain detailed documentation of all Group Policy changes, including the purpose, impact, and date of implementation. This helps with troubleshooting and future policy management.
- Use the Administrative Templates: Leverage the pre-defined Administrative Templates to streamline policy configuration and ensure consistent settings across the organization.
- Stay Updated: Regularly review and update Group Policy settings to ensure they are aligned with evolving security best practices and organizational needs.
Conclusion
The Group Policy Editor is a powerful tool for Windows 10 administrators, offering a wide range of functionalities for managing and configuring various aspects of the operating system. By leveraging the Group Policy Editor, administrators can enhance security, customize the user experience, streamline software deployment, and improve system performance. With careful planning, thorough testing, and a clear understanding of the impact of policy changes, the Group Policy Editor can be a valuable asset for any Windows 10 environment.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/how-to-use-policy-editor-win10-9ecfa903131742b2a3f67946af33ed2e.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/configuration-743d451063574baf980aa51d865dd37c.jpg)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unlocking Windows 10’s Potential: A Comprehensive Guide to Group Policy Editor. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!