Unlocking Performance: A Guide to Disabling Throttling in Windows 10
Related Articles: Unlocking Performance: A Guide to Disabling Throttling in Windows 10
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unlocking Performance: A Guide to Disabling Throttling in Windows 10. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unlocking Performance: A Guide to Disabling Throttling in Windows 10

Windows 10, while a robust operating system, employs various mechanisms to manage system resources and ensure stability. One such mechanism is throttling, a process that limits the performance of hardware components, often the CPU, to prevent overheating and potential damage. While this is a valuable feature for safeguarding hardware, it can also negatively impact the user experience, particularly for demanding applications like gaming, video editing, or intensive software development.
This article provides a comprehensive guide to understanding throttling in Windows 10 and explores methods to disable it, empowering users to unlock the full potential of their systems.
Understanding Throttling in Windows 10
Throttling is a dynamic process, meaning its intensity varies based on factors like system temperature, workload, and power settings. Windows 10 utilizes a combination of hardware and software components to monitor and regulate performance.
- Thermal Throttling: When the CPU reaches a predefined temperature threshold, the system automatically reduces its clock speed and performance to prevent overheating. This is a critical mechanism for protecting the processor from damage.
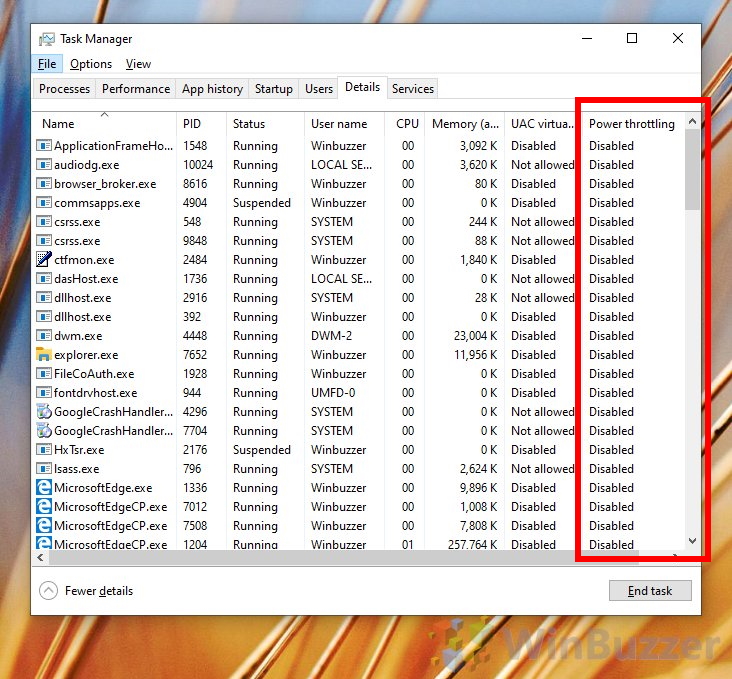
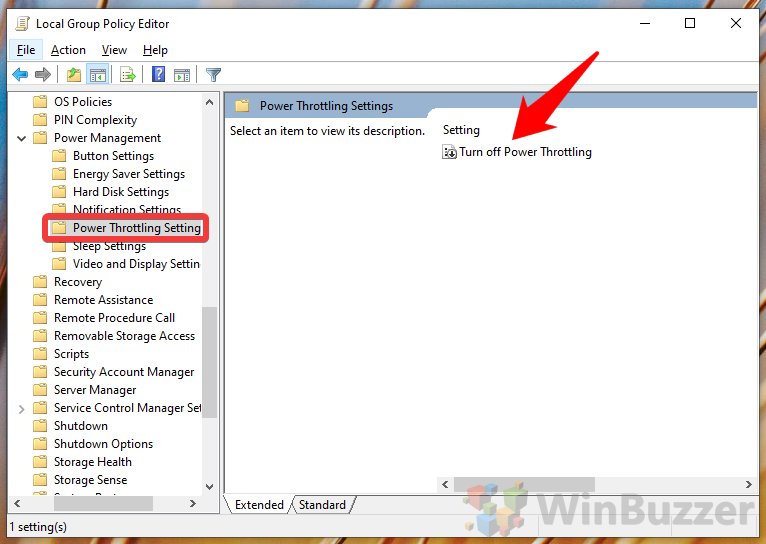
- Power Throttling: Windows 10 incorporates power management settings that can throttle performance to conserve battery life on laptops and mobile devices.
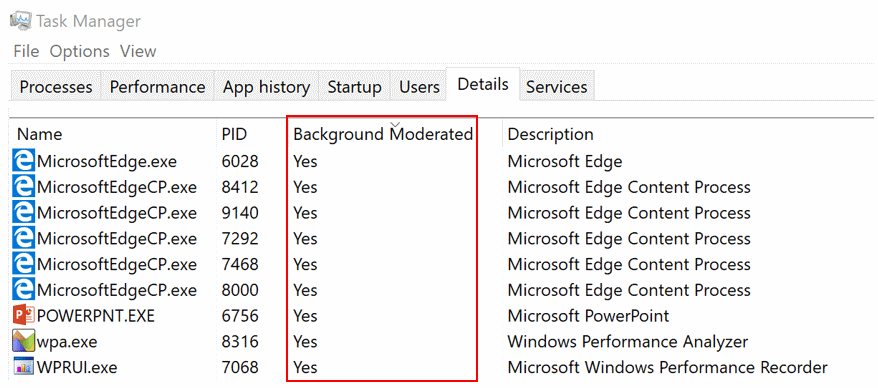
- Background Throttling: This feature prioritizes active applications and restricts the background activity of less critical processes, optimizing system responsiveness.
The Impact of Throttling on Performance
While throttling aims to protect hardware and optimize power consumption, it can have a noticeable impact on performance:
- Reduced Frame Rates: In gaming, throttling can lead to stuttering, frame drops, and an overall decrease in visual fidelity, impacting the user’s gaming experience.
- Slower Application Response: Throttling can slow down demanding applications like video editing software, graphic design tools, and complex simulations, affecting productivity.
- Increased Latency: For tasks requiring real-time responsiveness, such as online gaming or video conferencing, throttling can introduce delays and lag, impacting the user’s experience.
Disabling Throttling: A Cautious Approach
Disabling throttling should be approached with caution, as it can potentially lead to hardware damage if not done correctly. It’s crucial to understand the risks and potential consequences before proceeding.
Methods for Disabling Throttling
Several methods can be employed to disable throttling in Windows 10. These methods vary in complexity and effectiveness, and the appropriate approach depends on the user’s specific needs and technical expertise.
1. Modifying Power Settings
Windows 10 offers a range of power management options that can influence throttling behavior. To modify these settings:
- Open Control Panel: Navigate to "Control Panel" by searching in the Windows search bar.
- Select Power Options: Click on "Power Options" to access the power management settings.
- Choose a Power Plan: Select a power plan that suits your needs. "High Performance" typically offers the least throttling, while "Balanced" and "Power Saver" prioritize power efficiency and may involve more throttling.
- Adjust Advanced Settings: Click on "Change Plan Settings" and then "Change Advanced Power Settings" to access more granular options.
- Configure Power Management: Within the advanced settings, locate "Processor Power Management" and adjust the "Maximum Processor State" and "Minimum Processor State" to control the CPU’s performance range.
2. Utilizing BIOS Settings
The BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) is a low-level software that manages the hardware components of a computer. Some BIOS settings can influence throttling behavior:
- Access BIOS: Restart your computer and press the designated key (usually Delete or F2) during the boot process to enter the BIOS setup.
- Locate Power Management: Navigate through the BIOS menu to find the "Power Management" or "Advanced Settings" section.
- Adjust CPU Settings: Look for options related to CPU power management, such as "CPU Throttling" or "Thermal Protection." Disable these options or adjust the temperature thresholds to reduce throttling.
3. Using Third-Party Software
Various third-party software applications are designed to manage and optimize system performance, including throttling control. These tools offer a user-friendly interface and often provide more granular control over throttling settings compared to the built-in Windows options.
- Research Reputable Software: Choose a reputable software provider with a positive track record and user reviews.
- Install and Configure: Download and install the software, following the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Customize Throttling Settings: Use the software’s interface to adjust throttling settings, potentially including the ability to disable throttling entirely.
4. Overclocking the CPU
Overclocking involves increasing the CPU’s clock speed, potentially allowing for higher performance. However, overclocking should only be attempted by experienced users as it can lead to instability and hardware damage if not done correctly.
- Research Overclocking Techniques: Understand the risks and potential consequences of overclocking before attempting it.
- Use a Reliable Overclocking Tool: Choose a reputable overclocking software application designed for your specific hardware.
- Monitor System Temperature: Carefully monitor the CPU temperature during overclocking to avoid overheating.
5. Ensuring Proper Cooling
Adequate cooling is essential for preventing overheating and throttling. This involves ensuring proper airflow, clean fans, and sufficient heat dissipation:
- Clean System Components: Regularly clean the computer’s internal components, including fans, heatsinks, and air vents, to prevent dust buildup and improve airflow.
- Use a High-Quality Cooler: Consider upgrading to a more powerful CPU cooler, especially if the stock cooler is insufficient for your needs.
- Ensure Proper Airflow: Ensure adequate airflow within the computer case by strategically positioning components and fans.
The Importance of a Balanced Approach
While disabling throttling can unlock higher performance, it’s crucial to strike a balance between performance and hardware longevity. Excessive overclocking or disabling all throttling mechanisms can lead to overheating and potential damage to the CPU or other components.
Tips for Optimizing Performance
- Monitor System Temperature: Regularly monitor the CPU temperature using system monitoring tools to identify potential overheating issues.
- Adjust Power Settings: Experiment with different power plans and advanced power settings to find the optimal balance between performance and power consumption.
- Keep Drivers Up-to-Date: Regularly update device drivers, particularly for the CPU and motherboard, to ensure optimal performance and compatibility.
- Optimize Background Processes: Minimize unnecessary background processes and services to reduce system load and improve performance.
- Consider Hardware Upgrades: If performance limitations persist, consider upgrading hardware components, such as the CPU, RAM, or storage, to enhance overall system performance.
FAQs
1. Is Disabling Throttling Safe?
Disabling throttling can be safe if done correctly and with an understanding of the potential risks. However, it can lead to hardware damage if the CPU overheats due to excessive workload.
2. Will Disabling Throttling Improve Gaming Performance?
Disabling throttling can potentially improve gaming performance, but the impact varies depending on the game, system configuration, and other factors.
3. Can I Disable Throttling Permanently?
Disabling throttling permanently may be possible through BIOS settings or third-party software, but it’s recommended to carefully consider the potential risks and consequences.
4. What Happens If I Disable Throttling on a Laptop?
Disabling throttling on a laptop can lead to faster performance but may result in reduced battery life due to increased power consumption.
5. How Can I Monitor CPU Temperature?
Several system monitoring tools, like HWMonitor, CPU-Z, or Task Manager, can provide real-time CPU temperature readings.
Conclusion
Disabling throttling in Windows 10 can unlock higher performance and enhance user experience for demanding tasks. However, it’s crucial to approach this process cautiously and understand the potential risks and consequences. By carefully considering the methods, tips, and FAQs presented in this guide, users can optimize their systems while ensuring hardware longevity. Ultimately, the decision to disable throttling should be based on individual needs, system configuration, and a balanced approach to performance and hardware protection.


![]()

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unlocking Performance: A Guide to Disabling Throttling in Windows 10. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!