Unlocking Performance: A Guide to Disabling Power Throttling in Windows 10
Related Articles: Unlocking Performance: A Guide to Disabling Power Throttling in Windows 10
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unlocking Performance: A Guide to Disabling Power Throttling in Windows 10. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unlocking Performance: A Guide to Disabling Power Throttling in Windows 10

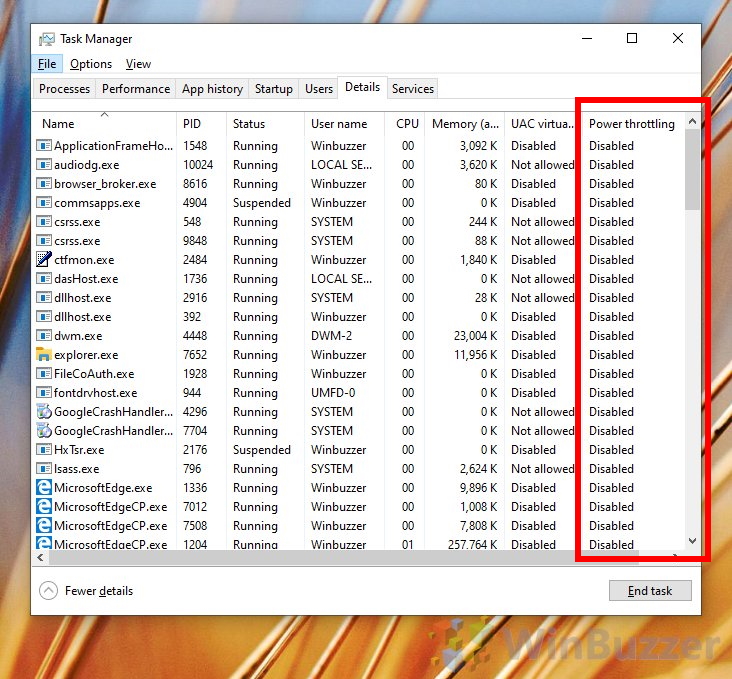
Power throttling, a feature designed to conserve battery life and reduce heat generation, can sometimes hinder the performance of your Windows 10 device. While its intent is to optimize power consumption, it can also lead to noticeable slowdowns, particularly during demanding tasks like gaming, video editing, or resource-intensive software applications. This article provides a comprehensive guide on how to disable power throttling in Windows 10, offering a clear understanding of the process and its potential benefits.
Understanding Power Throttling
Power throttling is a mechanism employed by operating systems and hardware components to manage power consumption. It dynamically adjusts the processor’s clock speed and voltage, reducing performance when idle or under low-demand scenarios. This is particularly relevant for laptops and other mobile devices where battery life is a primary concern.
However, for users who prioritize performance over battery life, power throttling can be a hindrance. By limiting the processor’s capabilities, it can lead to:
- Reduced frame rates in games: Power throttling can significantly impact gaming performance, resulting in stuttering and lower frame rates.
- Slower application responsiveness: Resource-intensive applications, such as video editing software or 3D modeling tools, may experience delays and sluggishness.
- Increased loading times: Applications and games may take longer to load or launch due to the reduced processing power.
Methods to Disable Power Throttling
There are several methods to disable power throttling in Windows 10. Each method targets a different aspect of power management, allowing users to tailor their approach based on their specific needs.
1. Modifying Power Plan Settings
Windows 10 offers several built-in power plans, each designed for a specific purpose. The "High Performance" plan prioritizes performance over battery life, potentially reducing the impact of power throttling.
- Navigate to Power Options: Open the Control Panel and select "Power Options."
- Choose "High Performance" Plan: Select the "High Performance" power plan from the available options.
- Adjust Power Plan Settings (Optional): You can further adjust the power plan settings by clicking on "Change plan settings." This allows you to modify specific power-related options, such as the screen brightness and sleep settings.
2. Using the Command Prompt
The Command Prompt offers a more direct way to disable power throttling. This method involves modifying the power settings through a specific command.
- Open the Command Prompt: Search for "cmd" in the Windows search bar and run the Command Prompt as an administrator.
-
Execute the Command: Type the following command and press Enter:
powercfg -setacvalueindex SCHEME_CURRENT 54533251-82be-4824-96c1-47b60b740d00 1This command sets the processor’s minimum performance state to 100%, effectively disabling power throttling.
3. Utilizing the Registry Editor
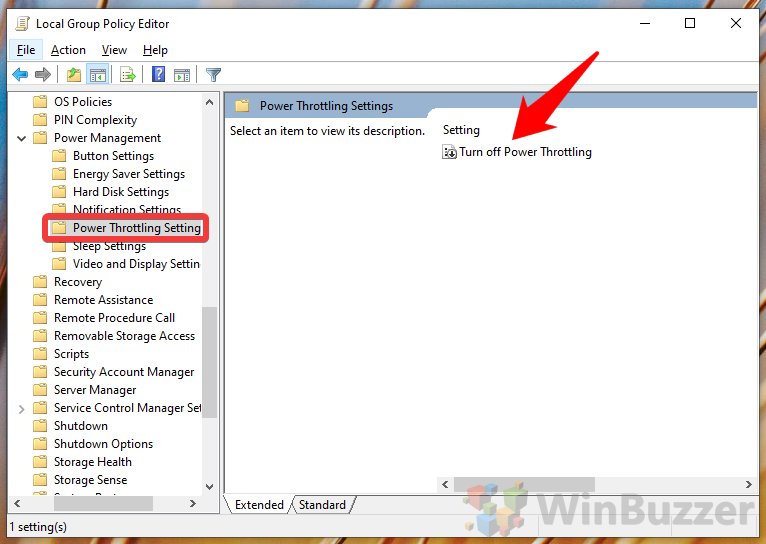
The Registry Editor allows for fine-grained control over system settings, including power management. By modifying specific registry keys, you can disable power throttling at a deeper level.
- Open Registry Editor: Press Windows key + R, type "regedit" and press Enter.
-
Navigate to the Power Management Key: Navigate to the following registry key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlPower - Create a New Value: Right-click in the right pane and select "New" > "DWORD (32-bit) Value."
- Name the Value: Name the new value "ProcessorMinimumState."
- Set Value Data: Double-click the newly created value and set the "Value data" to "1."
4. Using Third-Party Software
Several third-party applications are designed to manage and optimize system performance, including the ability to disable power throttling. These tools often offer user-friendly interfaces and advanced features for customizing power management settings.
- Install a Performance Optimization Tool: Consider using reputable software like Intel XTU (for Intel processors) or AMD Ryzen Master (for AMD processors).
- Configure Power Settings: Within the software, locate the power management settings and disable power throttling or adjust the processor’s performance limits.
5. Utilizing BIOS Settings
The BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) is a firmware that controls the hardware components of your computer. Some BIOS settings allow you to disable power throttling at a hardware level.
- Access the BIOS: Restart your computer and press the designated key (usually Delete or F2) to enter the BIOS setup.
- Locate Power Management Settings: Navigate to the "Power Management" or "Advanced" settings section.
- Disable Power Throttling: Locate the option to disable power throttling or adjust the processor’s performance settings. The specific options and their names may vary depending on the BIOS manufacturer.
Benefits of Disabling Power Throttling
Disabling power throttling can offer significant advantages for users who prioritize performance:
- Enhanced Gaming Performance: Games can run smoother with higher frame rates and reduced stuttering, providing a more enjoyable gaming experience.
- Increased Application Responsiveness: Resource-intensive applications can operate more efficiently, leading to faster processing times and improved productivity.
- Faster Loading Times: Applications and games may launch and load significantly faster due to the increased processing power.
Considerations and Potential Drawbacks
While disabling power throttling can improve performance, it’s important to be aware of potential drawbacks:
- Increased Power Consumption: Disabling power throttling can lead to higher power consumption, which may result in a shorter battery life on laptops and other mobile devices.
- Higher Heat Generation: The processor will operate at a higher frequency and voltage, generating more heat. This could lead to thermal throttling, where the processor automatically reduces performance to prevent overheating.
- Potential System Instability: In some cases, disabling power throttling might lead to system instability or unexpected crashes.
FAQs
Q: Will disabling power throttling damage my hardware?
A: Disabling power throttling itself does not damage hardware. However, the increased heat generation could potentially lead to premature wear and tear if not properly managed.
Q: Is disabling power throttling necessary for all users?
A: No, disabling power throttling is not necessary for all users. If you prioritize battery life or rarely use demanding applications, it may not be beneficial.
Q: Can I disable power throttling for specific applications?
A: Some power management tools allow you to configure power settings for specific applications. This allows you to disable power throttling only for the applications that require it.
Q: How can I monitor the temperature of my processor?
A: You can use system monitoring tools like HWMonitor or CPU-Z to track the temperature of your processor. This allows you to ensure that it is not overheating.
Tips
- Monitor Processor Temperature: Regularly monitor your processor’s temperature to ensure it is not exceeding safe operating limits.
- Use a Cooling Pad: Consider using a cooling pad for your laptop to help dissipate heat and prevent thermal throttling.
- Consider a Dedicated Graphics Card: For demanding gaming or graphics-intensive tasks, a dedicated graphics card can alleviate the workload on the processor and reduce the need for power throttling.
Conclusion
Disabling power throttling in Windows 10 can offer significant performance improvements, particularly for users who engage in demanding tasks like gaming, video editing, or running resource-intensive applications. However, it’s essential to weigh the benefits against the potential drawbacks, such as increased power consumption and heat generation. By carefully considering your needs and utilizing the appropriate methods, you can unlock the full potential of your Windows 10 device while maintaining system stability and hardware longevity.



![]()


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unlocking Performance: A Guide to Disabling Power Throttling in Windows 10. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!