Understanding Your System’s Memory: A Guide to RAM in Windows 11
Related Articles: Understanding Your System’s Memory: A Guide to RAM in Windows 11
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding Your System’s Memory: A Guide to RAM in Windows 11. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Your System’s Memory: A Guide to RAM in Windows 11

In the realm of personal computing, understanding your system’s memory, often referred to as RAM (Random Access Memory), is crucial for optimizing performance and troubleshooting potential issues. This guide delves into the intricacies of RAM in Windows 11, exploring how to determine the installed memory, its significance, and how to leverage this knowledge for a smoother user experience.
The Crucial Role of RAM
RAM acts as the short-term memory of your computer, holding the data and instructions that your processor needs to access quickly. Imagine it as a temporary workspace where your computer actively juggles information while running programs and tasks. The more RAM you have, the more programs and data your computer can handle simultaneously without experiencing slowdowns.
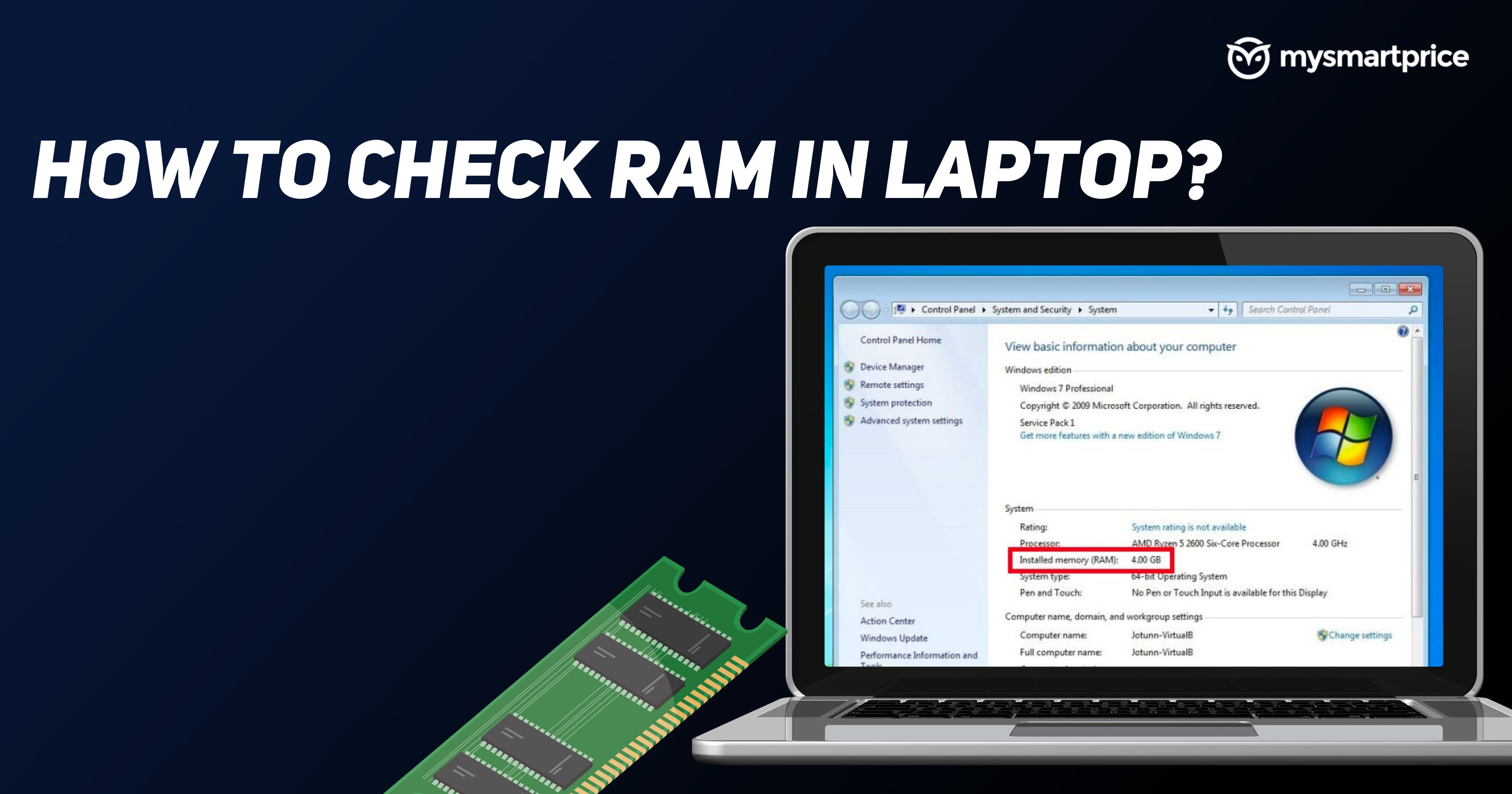
Determining Installed Memory: A Step-by-Step Guide
Several methods allow you to uncover the amount of RAM installed in your Windows 11 system. Here’s a breakdown of the most common and straightforward approaches:
1. Using the Windows Settings App:
- Navigate to Settings by pressing Windows key + I.
- Select System from the left-hand menu.
- Click on About on the right-hand pane.
- Under Device specifications, you will find the Installed RAM information.
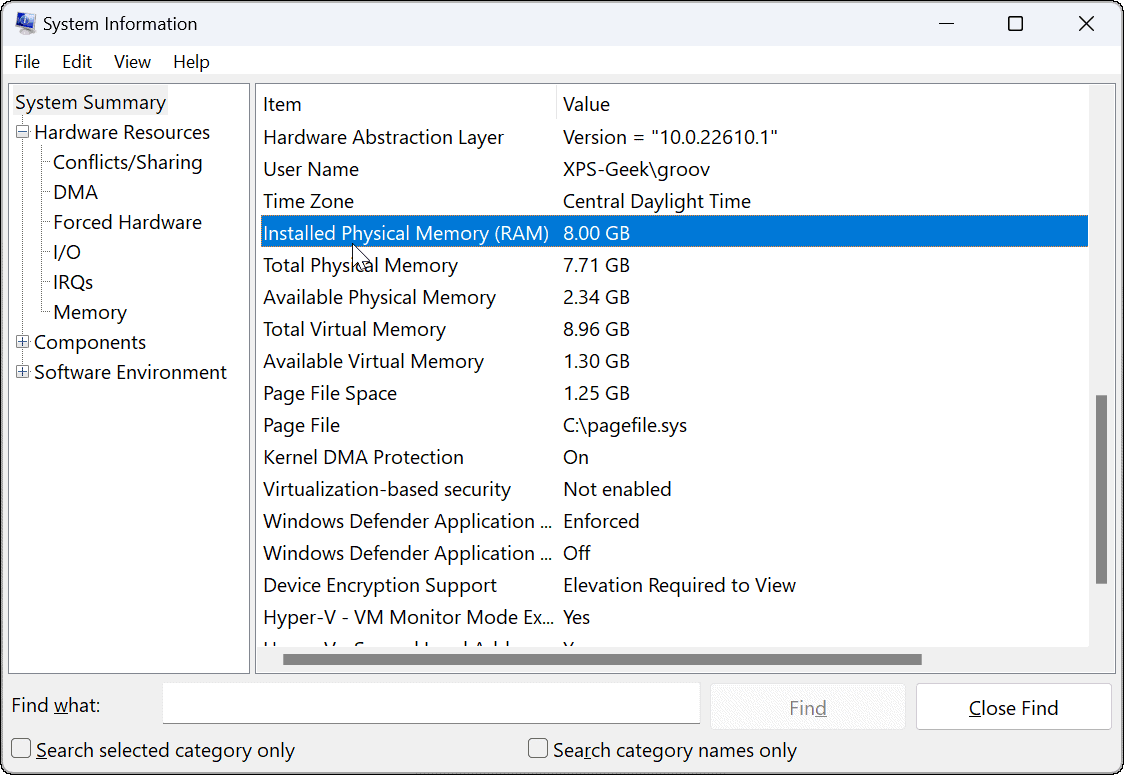
2. Utilizing the System Information Tool:
- Press Windows key + R to open the Run dialog box.
- Type msinfo32 and press Enter.
- In the System Information window, navigate to System Summary.
- Locate the Installed Physical Memory (RAM) entry to view the total memory installed.
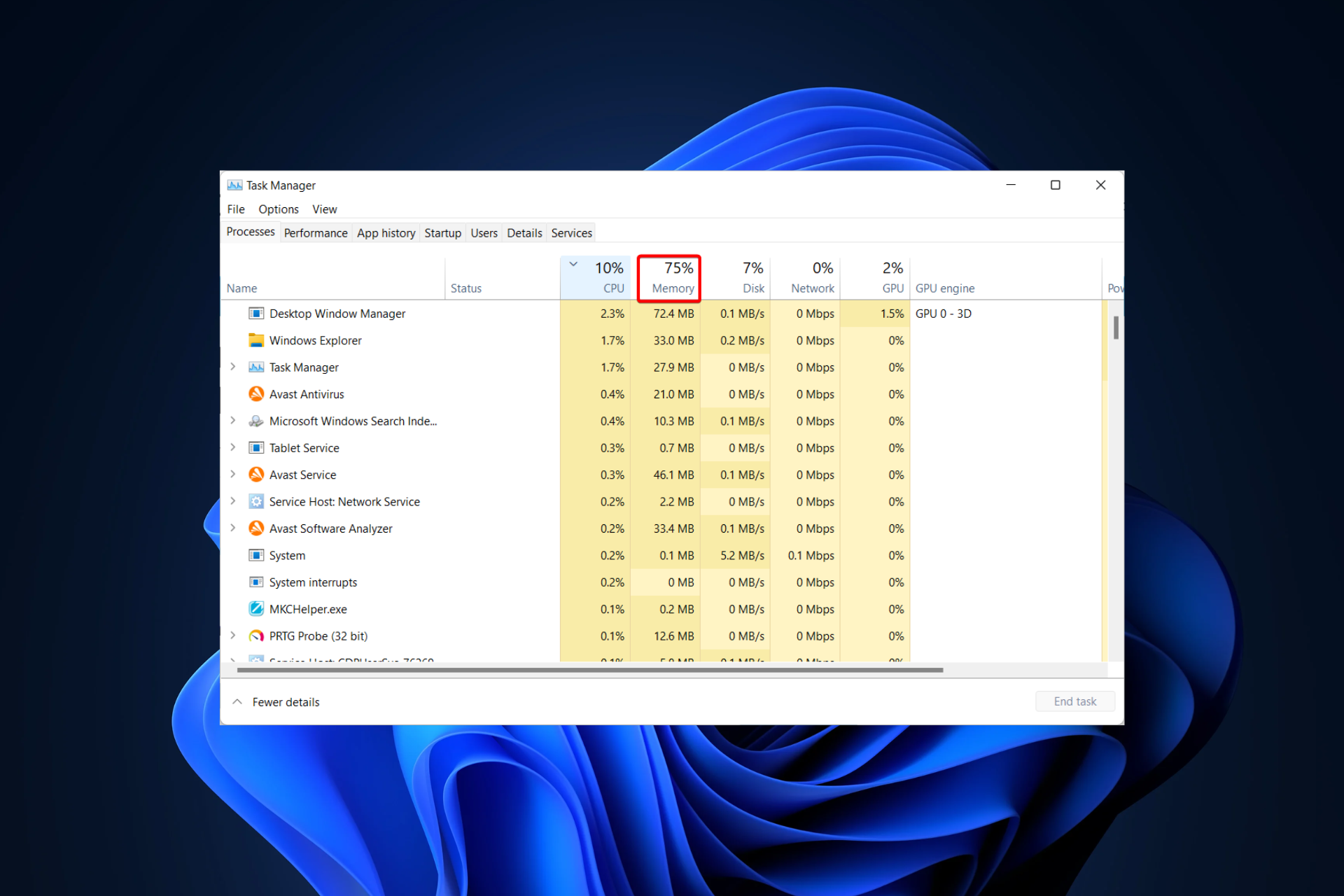
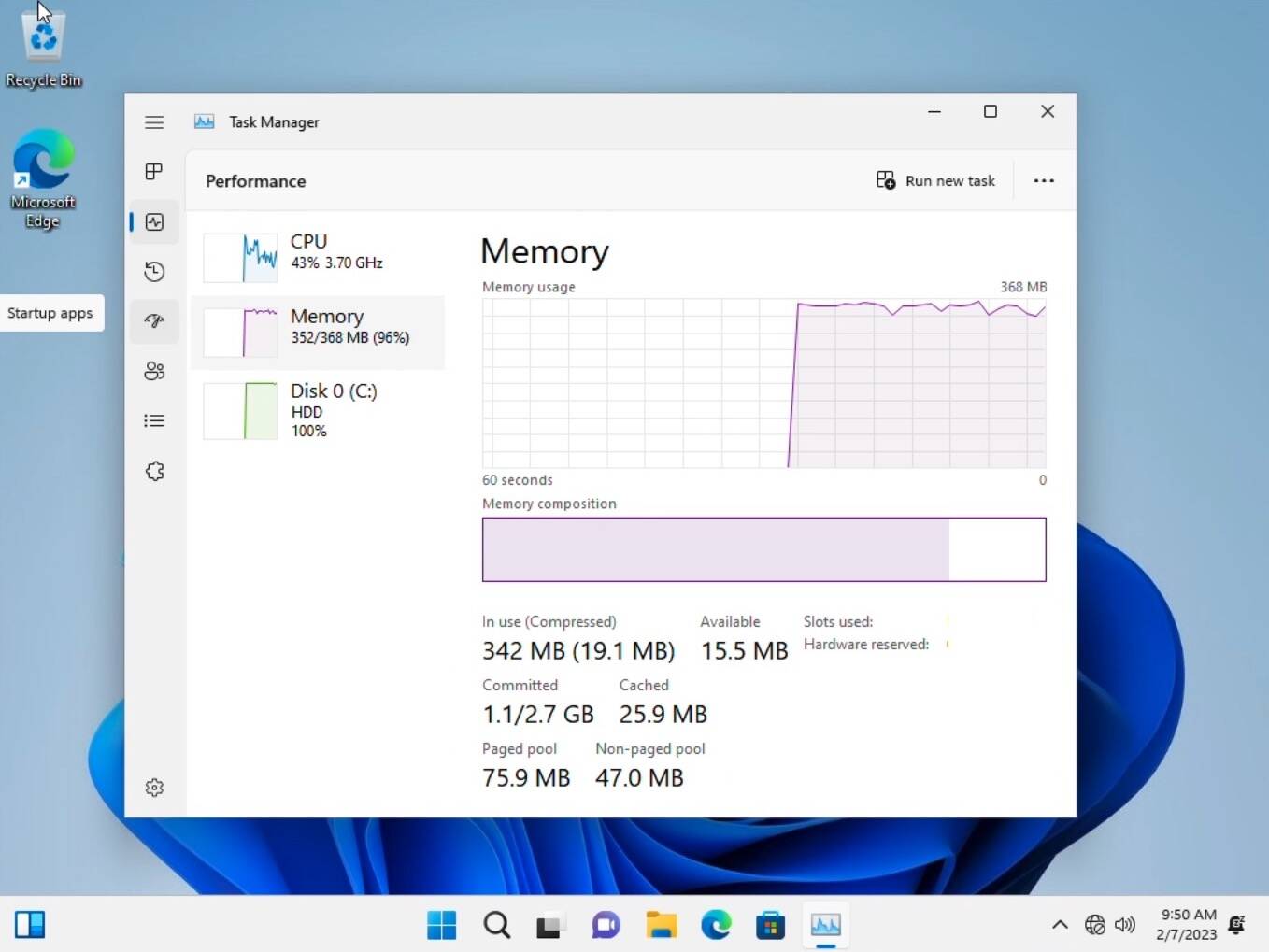
3. Employing Task Manager:
- Right-click on the Taskbar and select Task Manager.
- Click on the Performance tab.
- In the Memory section, you will find the Total Installed RAM information.
4. Checking the BIOS or UEFI:
- Restart your computer and press the designated key (usually Delete, F2, or F12) to enter the BIOS or UEFI setup menu.
- Navigate to the System Information or Main section.
- Locate the Memory or RAM entry to view the total installed memory.
The Importance of Knowing Your RAM Capacity
Understanding your system’s RAM capacity offers several advantages:
- Performance Optimization: Knowing your RAM allows you to assess whether it’s sufficient for your needs. If you frequently encounter slowdowns or lag, upgrading your RAM might be a viable solution.
- Troubleshooting Issues: If your computer is experiencing frequent crashes or freezes, insufficient RAM could be a contributing factor. Identifying the installed memory helps pinpoint the problem and potentially resolve it.
- Program Compatibility: Some programs have minimum RAM requirements. Knowing your system’s RAM capacity helps determine whether your computer can run specific software effectively.
- Upgrade Planning: If you’re considering upgrading your computer’s hardware, knowing your current RAM capacity assists in planning future upgrades.
Understanding Memory Specifications
Beyond the total amount of RAM, several other specifications are essential for understanding your system’s memory capabilities:
- Speed (MHz): This indicates how quickly data can be accessed from the RAM modules. Higher speeds generally translate to faster performance.
- Type (DDR4, DDR5): Different generations of RAM technologies offer varying speeds and power consumption. DDR5 is the latest generation, offering faster speeds and lower power consumption compared to DDR4.
- Capacity (GB): This refers to the total amount of memory installed in your system. Higher capacities allow for more programs and data to be held in RAM simultaneously.
- Channels: RAM modules can operate in single or dual-channel configurations. Dual-channel configurations generally provide better performance, especially in memory-intensive tasks.
Tips for Optimizing RAM Usage
- Close Unused Programs: Regularly close programs you’re not actively using to free up RAM.
- Disable Unnecessary Startup Programs: Minimize the number of programs that launch automatically at startup to reduce the initial RAM usage.
- Use a Memory Optimizer: Consider using a memory optimizer tool to help manage and optimize RAM usage. However, be cautious as some tools may have performance overhead.
- Consider Upgrading: If your RAM capacity is consistently insufficient, upgrading to a higher capacity might be necessary.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
Q: Can I add more RAM to my Windows 11 system?
A: Yes, most computers allow you to add more RAM. However, you need to ensure the new RAM modules are compatible with your motherboard and existing RAM configuration.
Q: What happens if I have too much RAM?
A: While excessive RAM won’t harm your computer, it’s generally an unnecessary expense. Windows 11 can utilize a maximum of 128GB of RAM, and most users will not require this amount.
Q: How do I know what type of RAM my computer supports?
A: You can consult your motherboard’s manual or use a system information tool like CPU-Z or Speccy to identify the supported RAM type and specifications.
Conclusion
Understanding the RAM installed in your Windows 11 system is crucial for optimizing performance, troubleshooting issues, and planning future upgrades. By utilizing the methods outlined above, you can easily determine your system’s RAM capacity and specifications. Armed with this knowledge, you can make informed decisions about your computer’s performance and ensure a smooth and efficient user experience. Remember, regular monitoring and optimizing your RAM usage can significantly impact your overall computing experience.

![How To Fix High RAM/Memory Usage on Windows 11 [Complete Guide] - YouTube](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/rnAOFqBKXwM/maxresdefault.jpg)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Your System’s Memory: A Guide to RAM in Windows 11. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!