Understanding and Managing Fast Startup in Windows 10
Related Articles: Understanding and Managing Fast Startup in Windows 10
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding and Managing Fast Startup in Windows 10. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding and Managing Fast Startup in Windows 10
Fast startup, a feature introduced in Windows 8, aims to accelerate the boot process by leveraging a hybrid shutdown approach. This method combines elements of a traditional shutdown with a hibernation state, enabling Windows to resume quickly from a state of partial shutdown. While Fast Startup generally offers a noticeable performance boost, its functionality might not be desirable in certain scenarios, leading users to seek methods to disable it. This article provides a comprehensive guide to understanding Fast Startup, its implications, and the steps involved in disabling it in Windows 10.
Understanding the Mechanics of Fast Startup
To grasp the rationale behind Fast Startup and its potential drawbacks, it’s crucial to understand its underlying mechanism. When you initiate a "shutdown" with Fast Startup enabled, Windows does not fully shut down. Instead, it performs the following steps:
- Active Applications and User Sessions are Closed: Similar to a traditional shutdown, open applications and user sessions are closed.
- System Files and Kernel State are Saved: The current state of the operating system, including system files and the kernel, is saved to a hibernation file (hiberfil.sys). This file stores the system’s memory contents, allowing for a faster restart.
- Power Consumption Minimized: The computer enters a low-power state, consuming minimal energy.
Upon restarting, Windows does not need to go through the full boot process. Instead, it retrieves the saved system state from the hibernation file, significantly reducing the boot time.
Potential Drawbacks of Fast Startup
While Fast Startup offers a convenient speed boost, it also presents certain potential drawbacks:
- Increased Boot Time in Specific Scenarios: While Fast Startup generally accelerates boot times, scenarios involving hardware changes, driver updates, or system updates might necessitate a full boot cycle, negating the speed advantage.
- Compatibility Issues with Certain Software: Some applications or utilities, particularly those relying on specific boot-time operations, might experience compatibility issues with Fast Startup.
- Larger Hibernation File: Fast Startup creates a larger hibernation file (hiberfil.sys), consuming more disk space compared to a traditional shutdown. This can be a concern for users with limited storage capacity.
- Potential for System Corruption: In rare cases, issues with the hibernation file could lead to system corruption, necessitating a system repair or recovery.
Disabling Fast Startup in Windows 10
If the potential drawbacks of Fast Startup outweigh its speed benefits for your specific needs, you can disable it by following these steps:
- Access Control Panel: Open the Control Panel by searching for it in the Windows search bar.
- Navigate to Power Options: Click on "Hardware and Sound," followed by "Power Options."
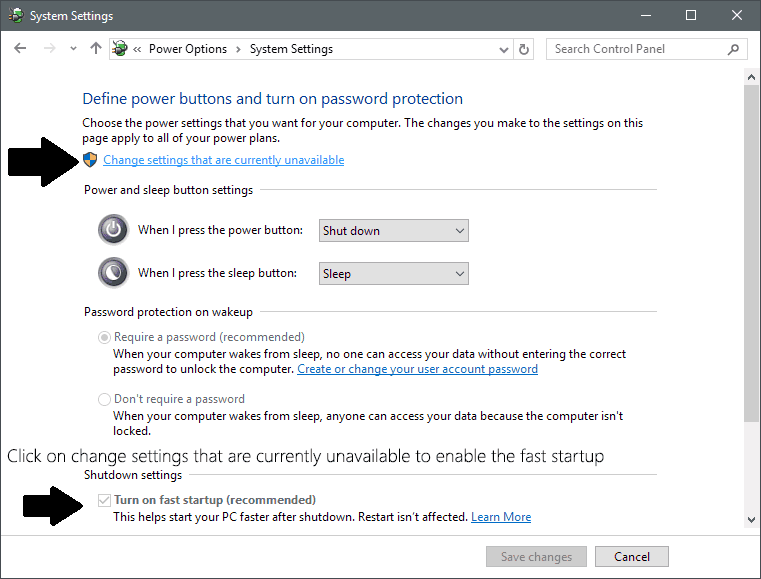
- Select "Choose What the Power Buttons Do": In the left-hand menu, click on "Choose what the power buttons do."
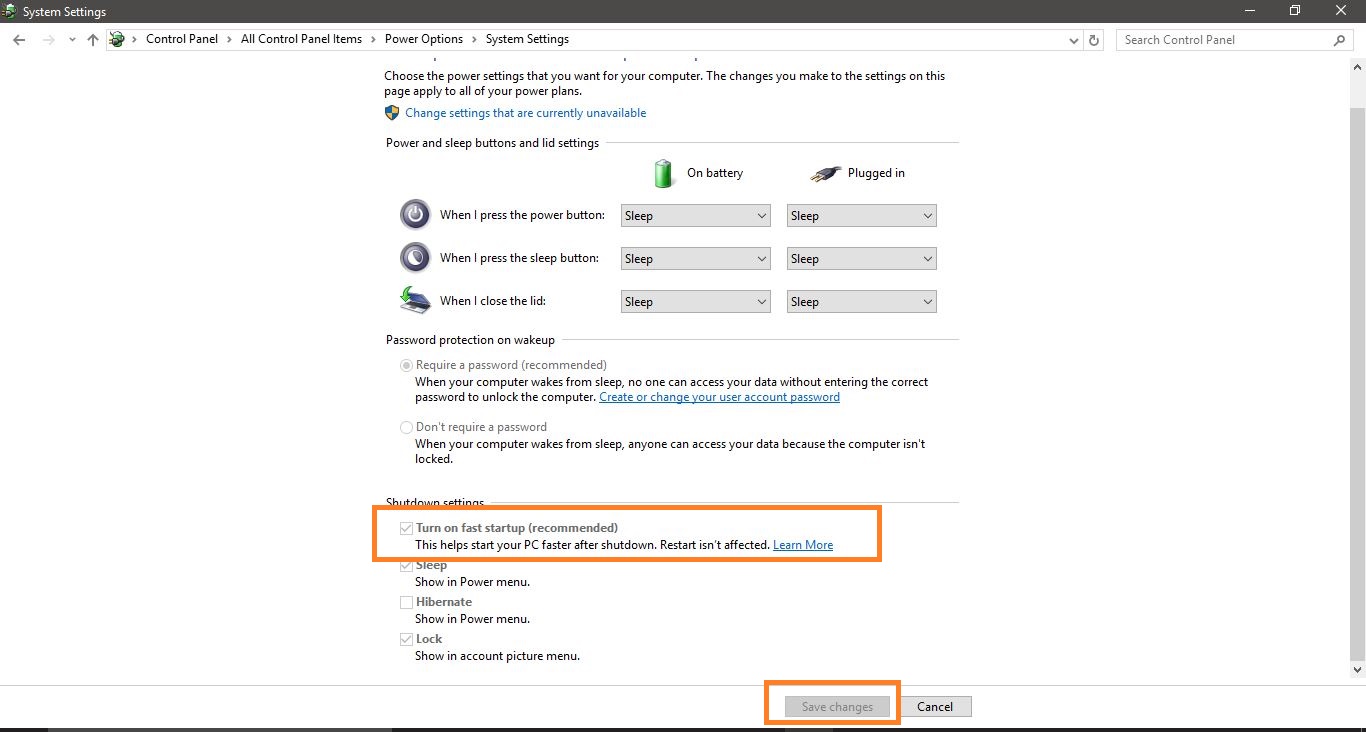
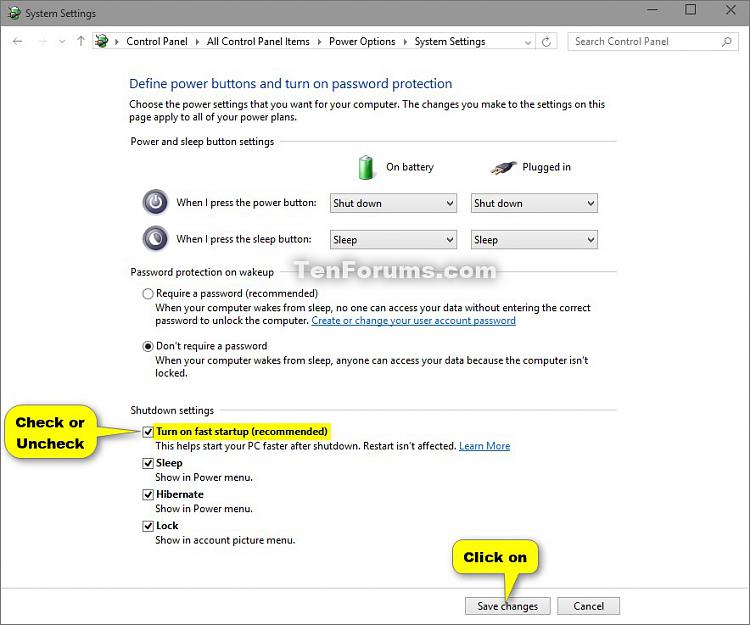
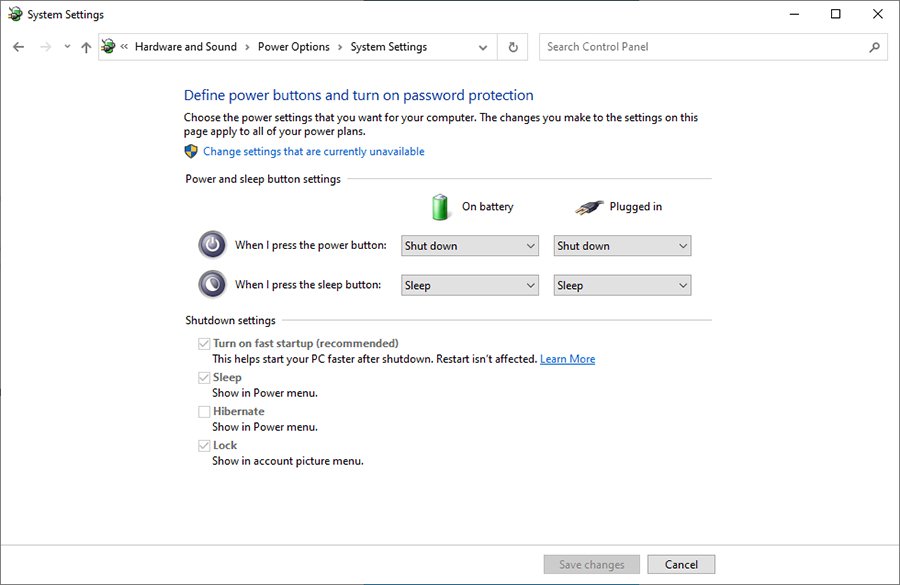
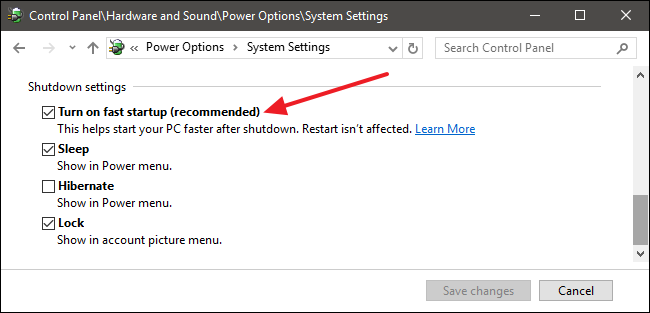
- Disable Fast Startup: Click on the link "Change settings that are currently unavailable." Under "Shutdown settings," uncheck the box labeled "Turn on fast startup (recommended)."
- Save Changes: Click "Save changes" to apply the modifications.
Alternative Approaches to Speed Up Windows Boot Time
If you decide to disable Fast Startup, consider implementing these alternative approaches to improve your Windows boot time:
- Optimize Startup Programs: Disable unnecessary startup programs by navigating to "Task Manager" (Ctrl+Shift+Esc) and accessing the "Startup" tab.
- Defragment Hard Drive: Regularly defragment your hard drive to improve file access speeds.
- Upgrade to a Solid-State Drive (SSD): SSDs offer significantly faster read and write speeds compared to traditional hard drives, drastically reducing boot times.
- Disable Unnecessary Services: Identify and disable unnecessary background services through the "Services" window (services.msc) to reduce system load during boot.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Is Fast Startup Necessary for Windows 10 to Function Correctly?
No, Fast Startup is an optional feature. Windows 10 will function correctly even with Fast Startup disabled.
2. Can I Disable Fast Startup Temporarily?
While there’s no option to temporarily disable Fast Startup, you can always re-enable it if you find it necessary for specific situations.
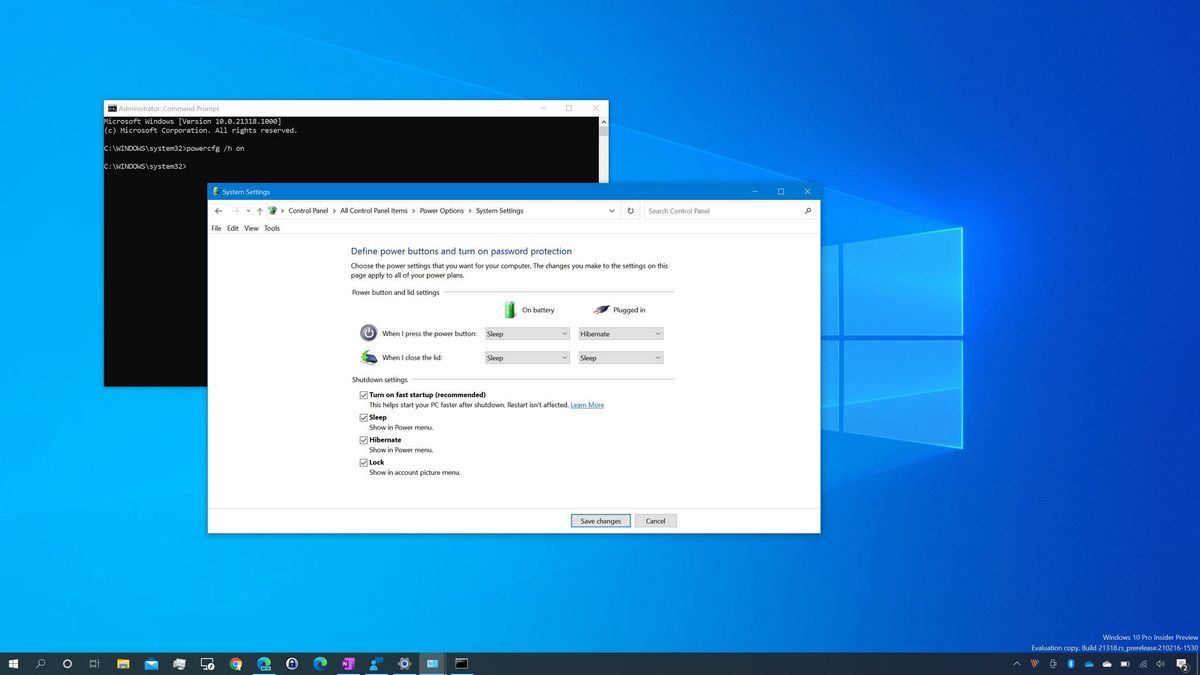
3. Can I Delete the Hibernation File (hiberfil.sys)?
You can delete the hibernation file by running the command "powercfg -h off" in an elevated command prompt. However, this will disable hibernation and Fast Startup, and you will need to re-enable them if desired.
4. Does Disabling Fast Startup Affect Battery Life?
Disabling Fast Startup might have a minor impact on battery life, as the system will need to go through a full boot process instead of resuming from a hibernation state. However, the difference is usually minimal.
5. Is Disabling Fast Startup Recommended for All Users?
Disabling Fast Startup is not universally recommended. If you experience compatibility issues with certain software or require a full boot cycle for specific tasks, disabling Fast Startup might be beneficial. However, for most users, the speed benefits of Fast Startup outweigh the potential drawbacks.
Tips for Managing Fast Startup
- Monitor System Behavior: Carefully observe your system’s behavior after disabling Fast Startup. If you encounter any unexpected issues or performance degradation, consider re-enabling the feature.
- Prioritize System Stability: If you are experiencing frequent system crashes or instability, temporarily disabling Fast Startup might help identify and resolve underlying issues.
- Backup Important Data: Before making any significant changes to your system settings, it’s always advisable to back up your important data to prevent data loss.
- Consult Online Resources: For more in-depth information and troubleshooting tips related to Fast Startup, refer to official Microsoft documentation and reputable online resources.
Conclusion
Fast Startup is a valuable feature in Windows 10, offering a significant performance boost for most users. However, understanding its underlying mechanisms and potential drawbacks is crucial for informed decision-making. If you encounter compatibility issues, prioritize system stability, or have limited storage space, disabling Fast Startup might be the best course of action. By following the steps outlined in this article, you can effectively manage Fast Startup and optimize your Windows 10 experience based on your specific needs and preferences. Remember to carefully assess your system’s behavior after making any changes and consult online resources for further guidance if necessary.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding and Managing Fast Startup in Windows 10. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!