Troubleshooting Windows 10 Boot Issues: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Troubleshooting Windows 10 Boot Issues: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Troubleshooting Windows 10 Boot Issues: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Troubleshooting Windows 10 Boot Issues: A Comprehensive Guide

Encountering a Windows 10 boot failure can be a frustrating experience, leaving users unable to access their data and applications. The inability to boot into the operating system can stem from various causes, ranging from minor software glitches to hardware malfunctions. This guide provides a comprehensive approach to diagnosing and resolving common Windows 10 boot problems, empowering users to regain access to their systems.
Understanding the Importance of Boot Processes
Before delving into troubleshooting steps, it is crucial to understand the fundamental processes involved in the Windows 10 boot sequence. When a computer powers on, the BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) takes control, initializing hardware components and loading the operating system from the designated storage device (typically a hard drive or SSD).
The boot process involves several key stages:
- POST (Power-On Self-Test): The BIOS performs a series of hardware checks, ensuring components like RAM, hard drive, and keyboard function correctly.
- Boot Device Selection: The BIOS identifies the boot device (e.g., hard drive) and loads the boot sector.
- Boot Loader Execution: The boot loader, a small program responsible for loading the operating system, is executed.
- Operating System Kernel Loading: The boot loader loads the Windows 10 kernel, the core of the operating system.
- System Startup: The operating system initializes drivers, loads services, and prepares the user interface, culminating in the familiar desktop environment.
Any disruption or error in these steps can prevent the system from booting successfully.
Common Causes of Windows 10 Boot Failures
Identifying the root cause of a boot failure is crucial for selecting the appropriate troubleshooting method. Some common culprits include:
- Hardware Issues: Faulty hard drives, RAM modules, or other hardware components can disrupt the boot process.
- Software Conflicts: Corrupted system files, incompatible drivers, or malware infections can cause boot errors.
- Incorrect Boot Settings: Changes to BIOS settings, such as the boot order or boot mode, can lead to boot failures.
- Power Supply Problems: An unstable power supply can cause intermittent boot issues.
- Boot Sector Damage: The boot sector, containing critical boot information, can be corrupted due to hardware failures, virus attacks, or improper shutdowns.
Troubleshooting Steps: A Systematic Approach
Addressing Windows 10 boot issues requires a methodical approach, starting with simple solutions and progressing to more advanced techniques.
1. Basic Troubleshooting:
- Restart the Computer: A simple restart can resolve temporary glitches or software conflicts.
- Check for Loose Connections: Ensure all cables, including power cables, data cables, and RAM modules, are securely connected.
- Verify Hardware Components: Visually inspect hardware components for any signs of damage or loose connections.
-
Run a System Scan: Use the built-in Windows 10 System File Checker (SFC) tool to scan for and repair corrupted system files:
- Open Command Prompt as administrator.
- Type
sfc /scannowand press Enter.
- Update Drivers: Outdated or incompatible drivers can cause boot issues. Update drivers through Windows Update or the manufacturer’s website.
2. Advanced Troubleshooting:
- Access the BIOS: Access the BIOS setup by pressing the designated key (usually F2, F10, or Delete) during the boot process. Check boot settings, such as the boot order and boot mode (UEFI or Legacy). Ensure the correct boot device is selected.
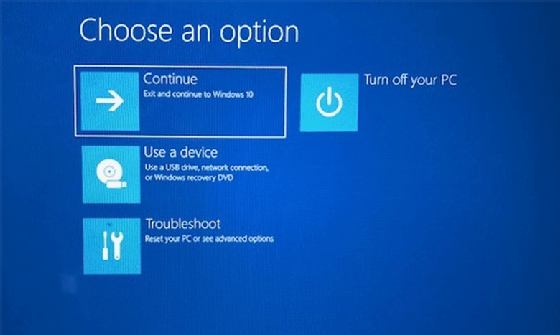
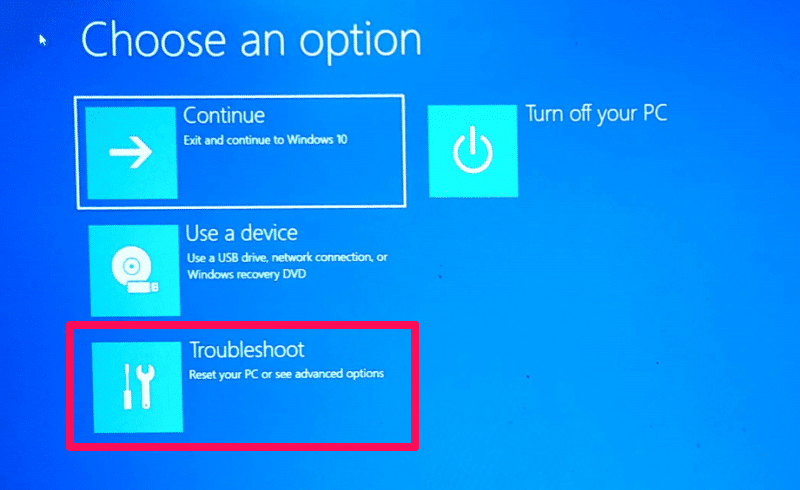
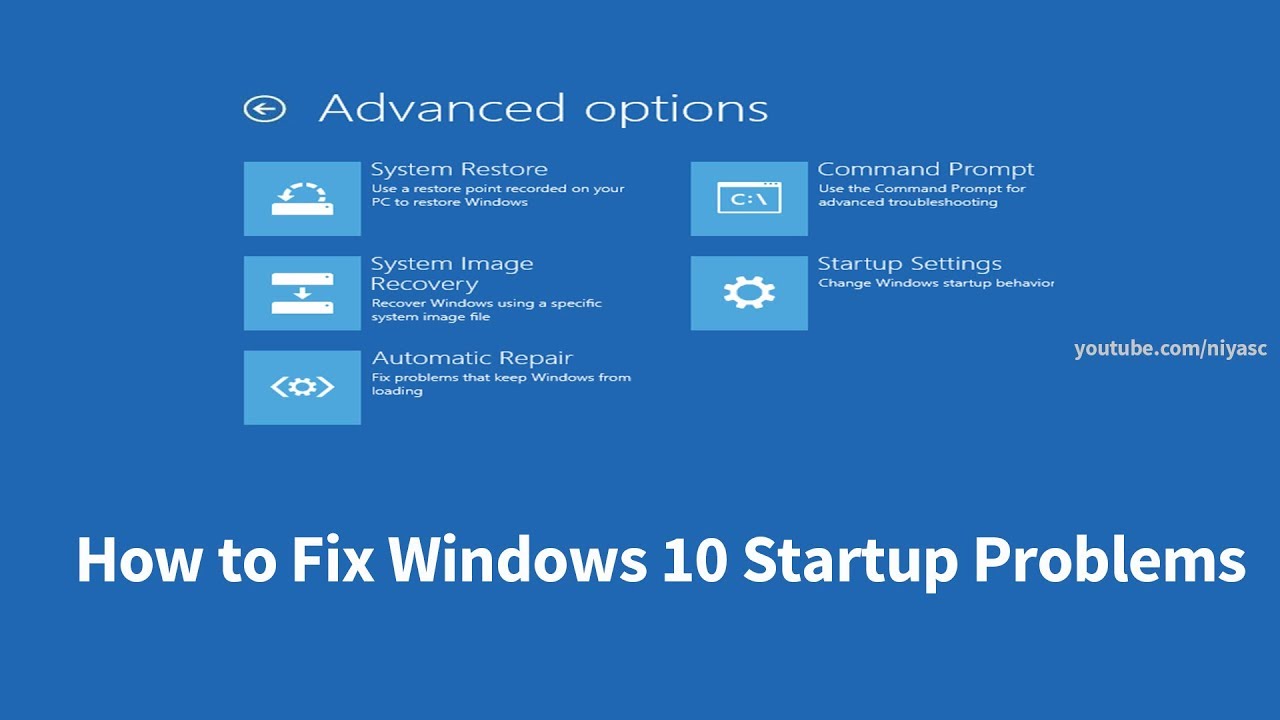
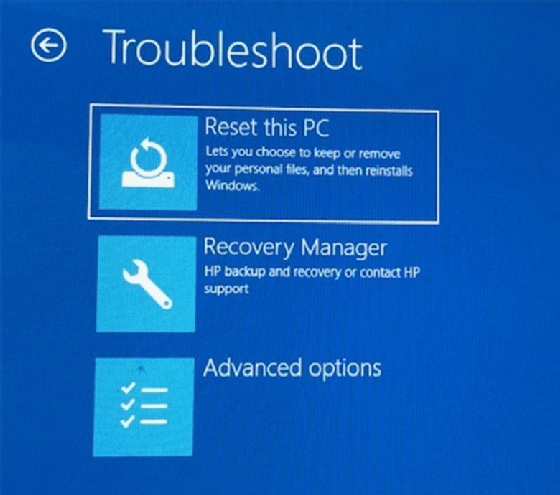
- Use the Windows 10 Recovery Environment: Access the Recovery Environment by restarting the computer and pressing Shift+F8 during startup. This environment provides options for repairing boot issues, resetting the system, or reinstalling Windows.
- Boot into Safe Mode: Safe Mode starts Windows with minimal drivers and services, allowing you to troubleshoot boot issues. Access Safe Mode by pressing F8 during startup or through the Recovery Environment.
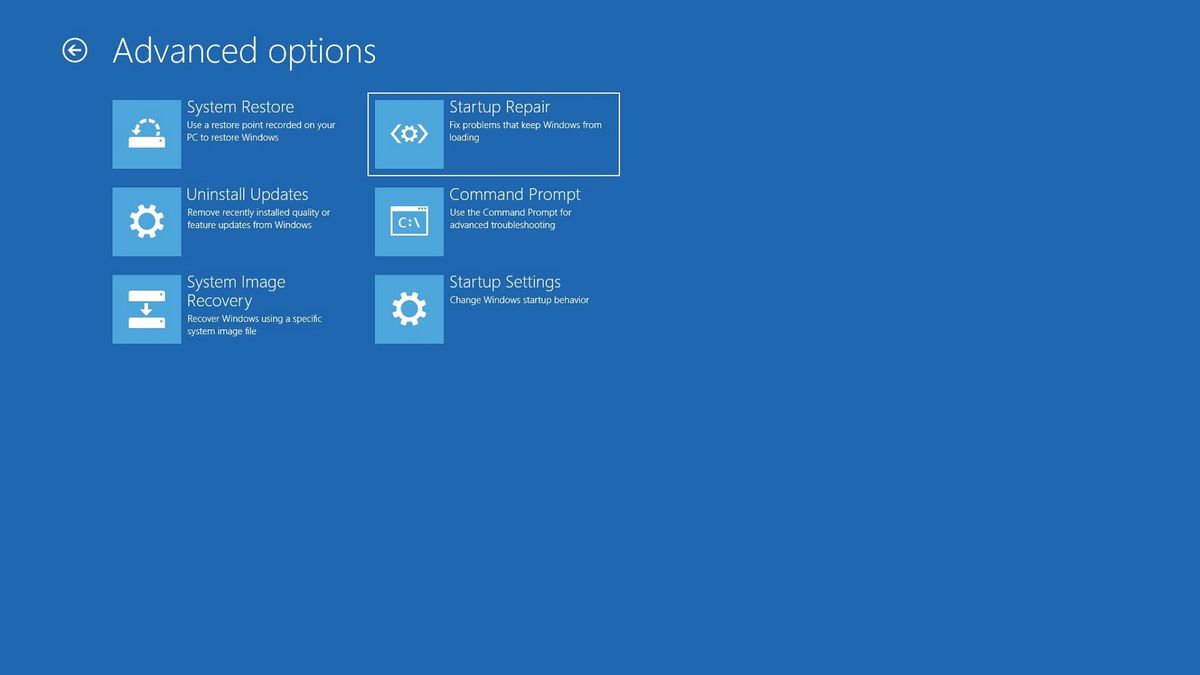
- Run a Startup Repair: The Startup Repair tool attempts to identify and fix boot problems. Access it through the Recovery Environment.
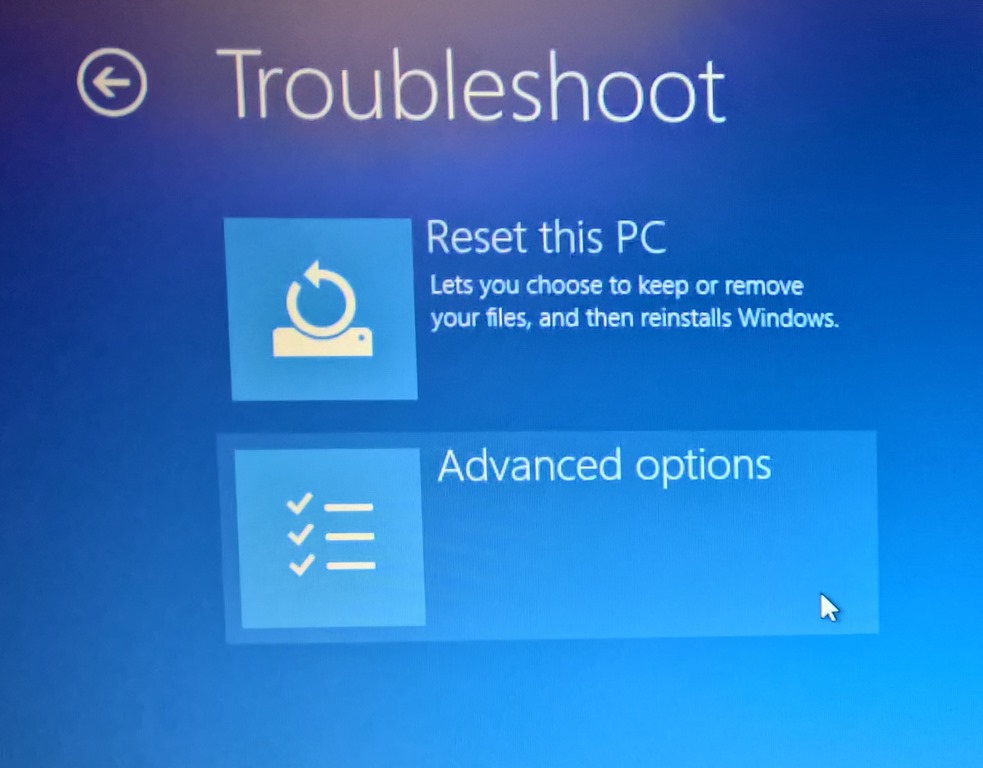
- Perform a System Restore: If the problem occurred recently, a system restore can revert the system to a previous working state. Access System Restore through the Recovery Environment or Control Panel.
3. Reinstallation or Repair
If the above steps fail to resolve the boot issue, consider the following options:
- Reinstall Windows 10: Reinstalling Windows 10 can resolve software conflicts or corrupted system files. Back up important data before proceeding.
- Repair Windows 10: Use the Windows 10 installation media to repair the operating system without deleting your data.
4. Hardware Diagnostics
If boot issues persist despite troubleshooting software issues, consider hardware problems.
- Run Memory Diagnostics: Test RAM modules for errors using the built-in Windows Memory Diagnostic tool.
- Check Hard Drive Health: Use a hard drive diagnostic tool to check for errors or drive failures.
- Replace Faulty Components: If hardware components are identified as faulty, replace them with compatible replacements.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
1. How do I access the BIOS setup?
The key to access the BIOS setup varies depending on the computer manufacturer. Consult the user manual or search online for your specific model. Common keys include F2, F10, or Delete.
2. What is the difference between UEFI and Legacy boot modes?
UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) is a modern boot standard that offers faster boot times and improved security. Legacy BIOS is the older standard. Ensure the boot mode in the BIOS settings matches the requirements of your operating system.
3. What are the signs of a corrupted boot sector?
A corrupted boot sector often manifests as a black screen with no error messages or a message indicating that the operating system cannot be found.
4. Can I recover data from a hard drive that is not booting?
Yes, you can attempt to recover data using data recovery software or a professional data recovery service.
5. What if the problem is related to the power supply?
A faulty power supply can cause intermittent boot issues or complete system failures. Consider testing the power supply or replacing it if necessary.
Tips for Preventing Boot Issues
- Regularly update Windows: Windows updates include security patches and bug fixes that can improve system stability.
- Back up your data: Regularly back up important data to an external hard drive or cloud storage service.
- Avoid installing untrusted software: Be cautious when downloading and installing software from unknown sources, as they can contain malware or viruses.
- Monitor system health: Use system monitoring tools to keep track of hardware temperatures and other system metrics.
Conclusion
Troubleshooting Windows 10 boot issues requires a systematic and methodical approach, starting with basic checks and progressing to more advanced techniques. By understanding the common causes of boot failures and following the steps outlined in this guide, users can effectively diagnose and resolve boot problems, restoring their systems to a functional state. Remember, a proactive approach to system maintenance, including regular updates, backups, and security measures, can significantly reduce the likelihood of encountering boot failures in the future.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Troubleshooting Windows 10 Boot Issues: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!