The Missing Speed Boost: Understanding the Absence of Fast Startup in Windows 11
Related Articles: The Missing Speed Boost: Understanding the Absence of Fast Startup in Windows 11
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Missing Speed Boost: Understanding the Absence of Fast Startup in Windows 11. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Missing Speed Boost: Understanding the Absence of Fast Startup in Windows 11
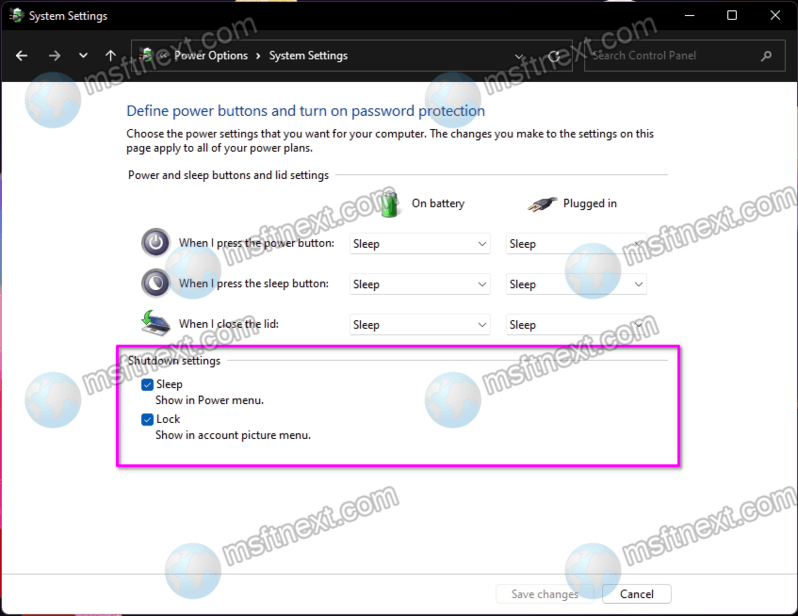
Windows 11, heralded for its refined interface and enhanced performance, has unfortunately left some users puzzled by the absence of a familiar feature: Fast Startup. This seemingly innocuous omission has generated considerable confusion and frustration, particularly among those who have grown accustomed to its speed-enhancing benefits. This article delves into the reasons behind this change, the implications for user experience, and the potential solutions available.
The Essence of Fast Startup:
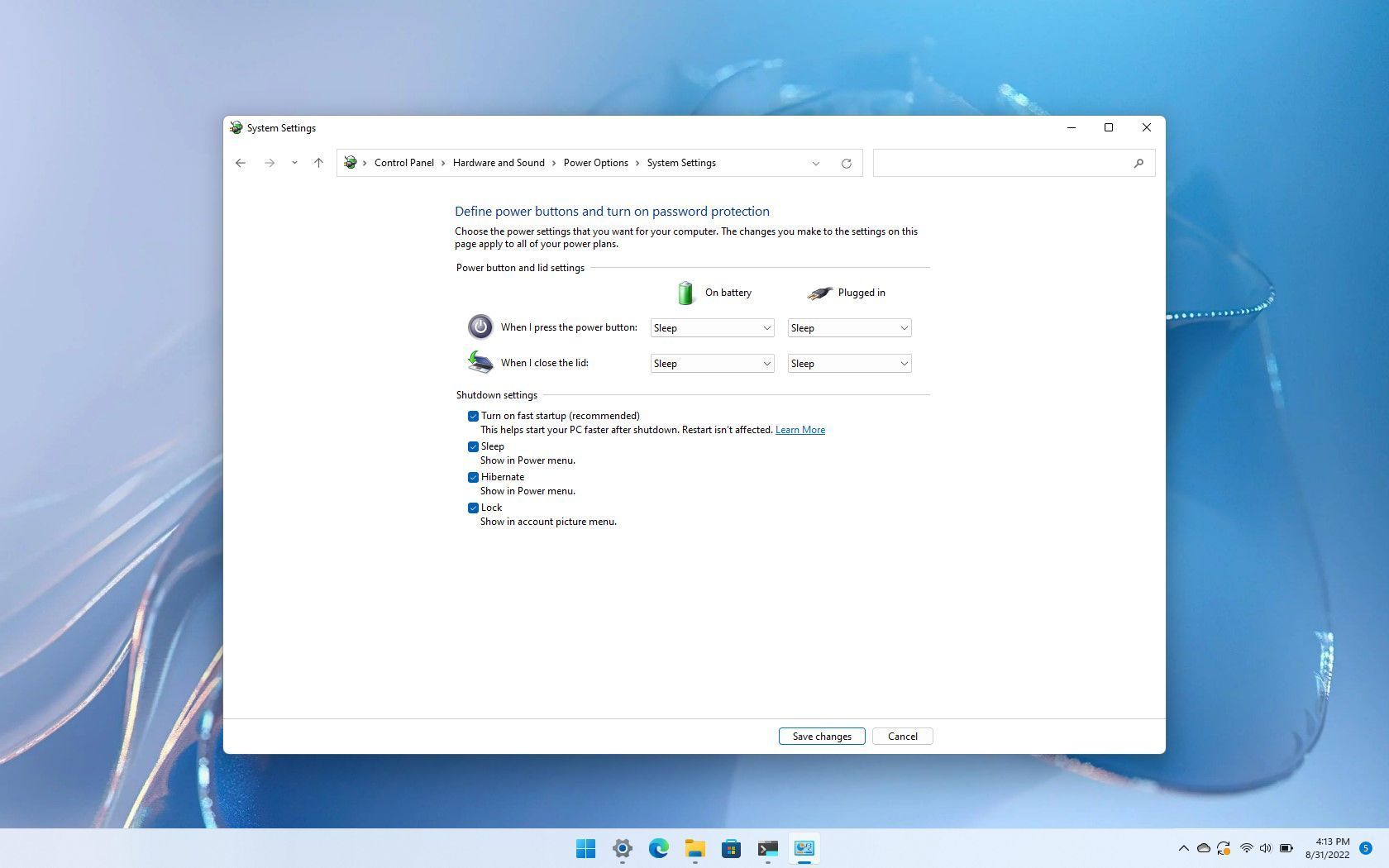
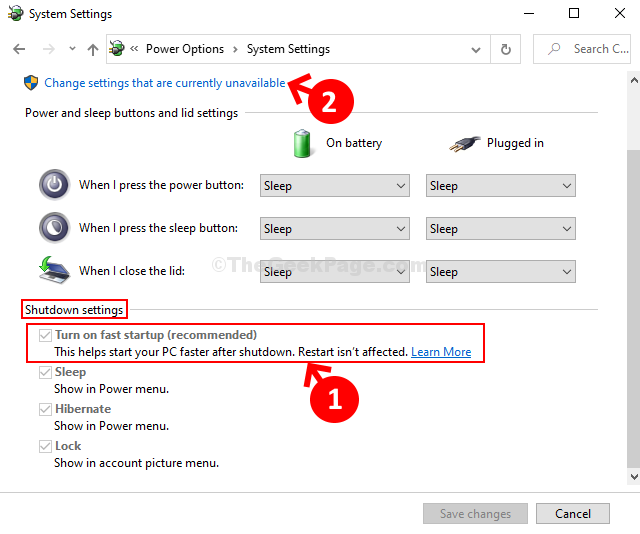
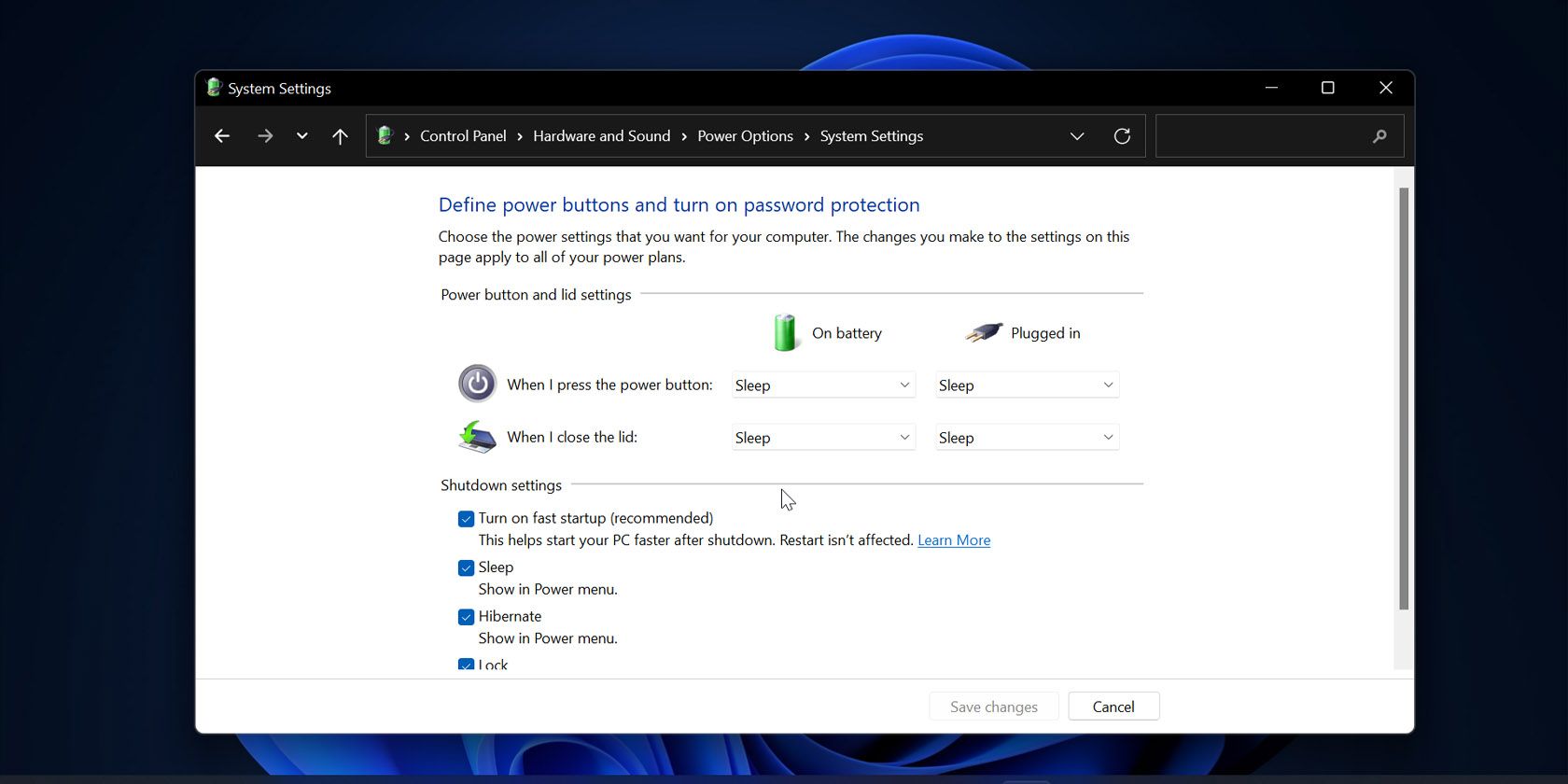
Before exploring the absence of Fast Startup in Windows 11, it’s crucial to understand its core function. Fast Startup, introduced in Windows 8, was a hybrid approach to system startup, combining elements of traditional boot processes with hibernation. When enabled, the system wouldn’t fully shut down upon "powering off." Instead, it would save the current system state to a hibernation file, allowing for a quicker boot-up by resuming from this saved state. This significantly reduced boot times, providing a noticeably faster user experience.
Windows 11’s Shift: Why the Omission?
The absence of Fast Startup in Windows 11 is not an oversight but rather a deliberate decision driven by several factors:
- Security Enhancement: One primary reason for its removal is the enhanced security focus in Windows 11. Fast Startup, while providing speed benefits, stored the system state in a hibernation file that could potentially be vulnerable to malware attacks. Eliminating this feature reduces the attack surface, making the system more secure.
- Focus on Performance: While Fast Startup aimed to improve boot times, it did not always guarantee optimal performance. In certain scenarios, it could lead to slower wake-up times from sleep mode or even system instability. By removing Fast Startup, Microsoft aims to streamline the system’s performance and ensure a smoother user experience across various scenarios.
- Simplified Boot Process: The removal of Fast Startup simplifies the boot process, making it more straightforward and predictable. This aligns with Microsoft’s goal of providing a more intuitive and streamlined user experience.
Implications for Users:
The removal of Fast Startup has a noticeable impact on user experience:
- Longer Boot Times: The most immediate consequence is the increased boot time. While Windows 11 is generally faster than its predecessors, the lack of Fast Startup can make the initial boot-up process noticeably slower.
- Potential for Confusion: Users accustomed to Fast Startup may be confused by its absence and wonder why their system seems slower. This can lead to frustration and unnecessary troubleshooting efforts.
- Shift in Power Management: The change in boot behavior necessitates a shift in power management habits. Users need to adapt to the absence of Fast Startup and understand the implications for battery life and system performance.
Addressing the Absence: Potential Solutions:
While Fast Startup is not directly available in Windows 11, users can explore alternative methods to achieve a similar effect:
- Utilize Sleep Mode: Sleep mode offers a comparable solution to Fast Startup, although it may not be as fast. Sleep mode saves the system’s current state in RAM, allowing for quick resumption.
- Optimize System Settings: Ensure that Windows 11 is configured for optimal performance. This includes disabling unnecessary startup programs, managing background processes, and ensuring that system updates are installed promptly.
- Consider Third-Party Tools: Some third-party tools claim to provide functionalities similar to Fast Startup, but caution should be exercised as these tools may not be fully compatible with Windows 11 or could introduce security risks.
FAQs Regarding the Absence of Fast Startup in Windows 11:
Q: Is Fast Startup completely gone from Windows 11?
A: Yes, the Fast Startup option is not available in Windows 11’s power settings.
Q: Can I re-enable Fast Startup in Windows 11?
A: Unfortunately, no. The feature is permanently removed from Windows 11.
Q: What are the alternatives to Fast Startup in Windows 11?
A: Sleep mode is the most comparable alternative. Optimizing system settings and minimizing unnecessary background processes can also contribute to faster boot times.
Q: Is the absence of Fast Startup a security concern?
A: While Fast Startup provided speed benefits, it introduced a potential security vulnerability. Its removal in Windows 11 is part of a broader security enhancement strategy.
Q: Why did Microsoft remove Fast Startup in Windows 11?
A: The decision was driven by a combination of security enhancements, performance optimization, and a desire to simplify the boot process.
Tips for Optimizing System Performance in Windows 11:
- Disable unnecessary startup programs: Minimize the number of programs that automatically launch at startup.
- Manage background processes: Limit the number of background apps and services running simultaneously.
- Keep your system updated: Install the latest Windows updates and driver updates to ensure optimal performance.
- Use a solid-state drive (SSD): SSDs offer significantly faster read and write speeds compared to traditional hard disk drives (HDDs), significantly improving boot times and overall system performance.
- Consider a clean install: A clean install of Windows 11 can help eliminate any lingering issues or conflicts that may be slowing down your system.
Conclusion:
The removal of Fast Startup in Windows 11, while initially met with confusion, is a deliberate decision driven by security and performance considerations. While it may result in slightly longer boot times, the focus on security and overall system optimization outweighs the perceived inconvenience. Users can adapt to this change by utilizing alternative methods like Sleep mode, optimizing system settings, and exploring potential third-party solutions. By understanding the rationale behind this change and adopting best practices for performance optimization, users can enjoy a more secure and streamlined experience with Windows 11.

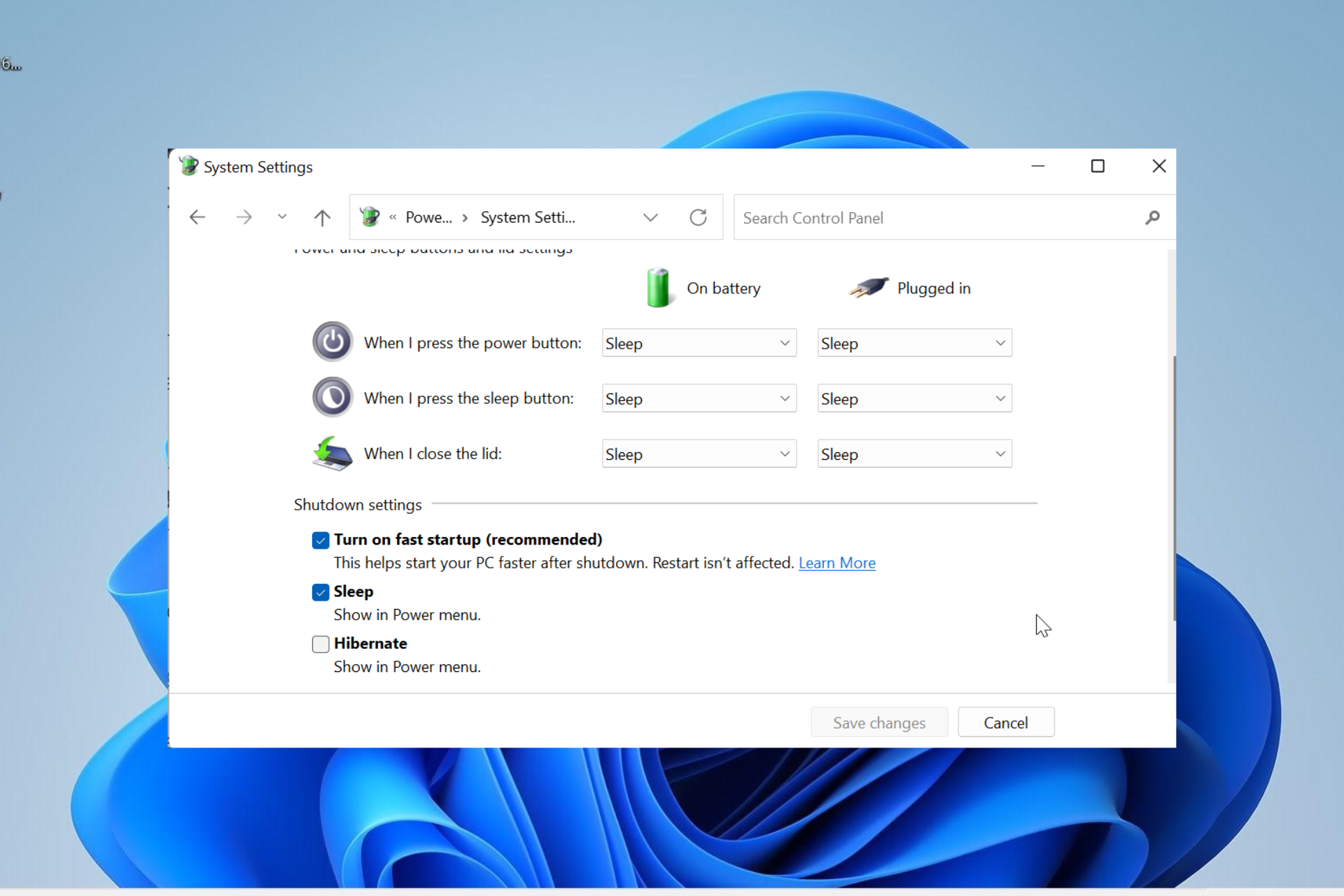
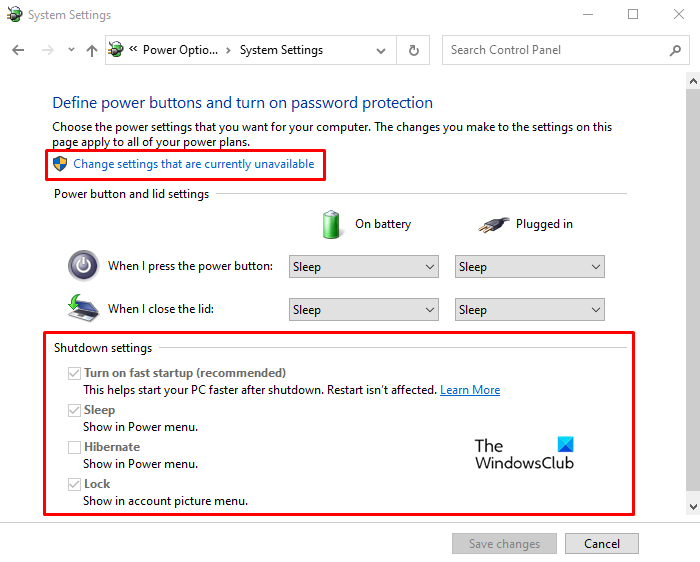

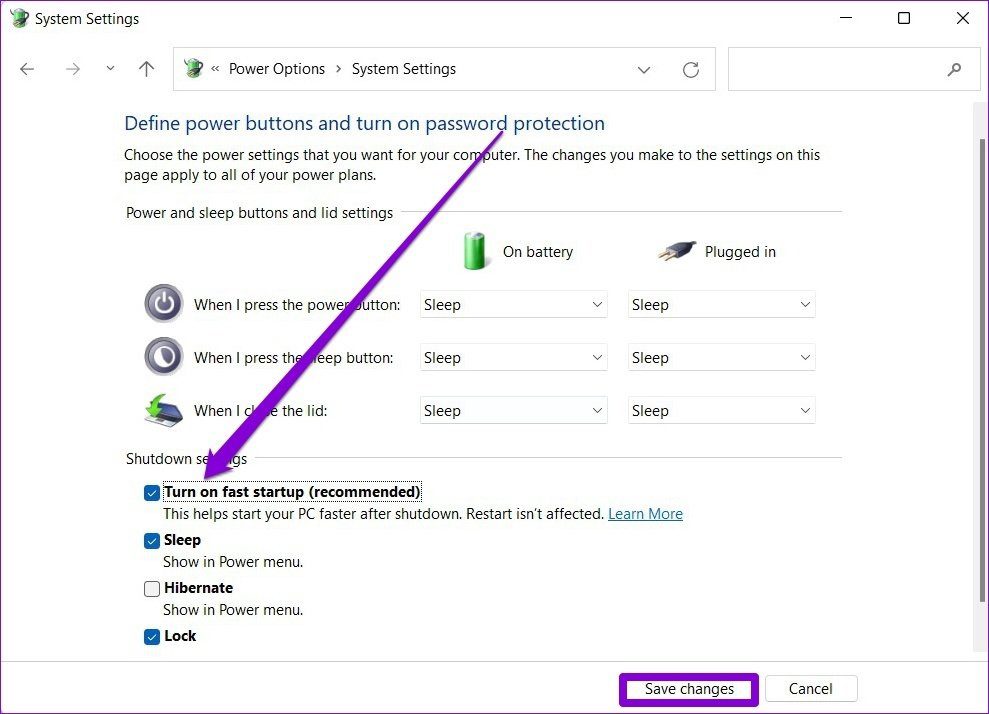
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Missing Speed Boost: Understanding the Absence of Fast Startup in Windows 11. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!