Resuming from Sleep Mode in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Resuming from Sleep Mode in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Resuming from Sleep Mode in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Resuming from Sleep Mode in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
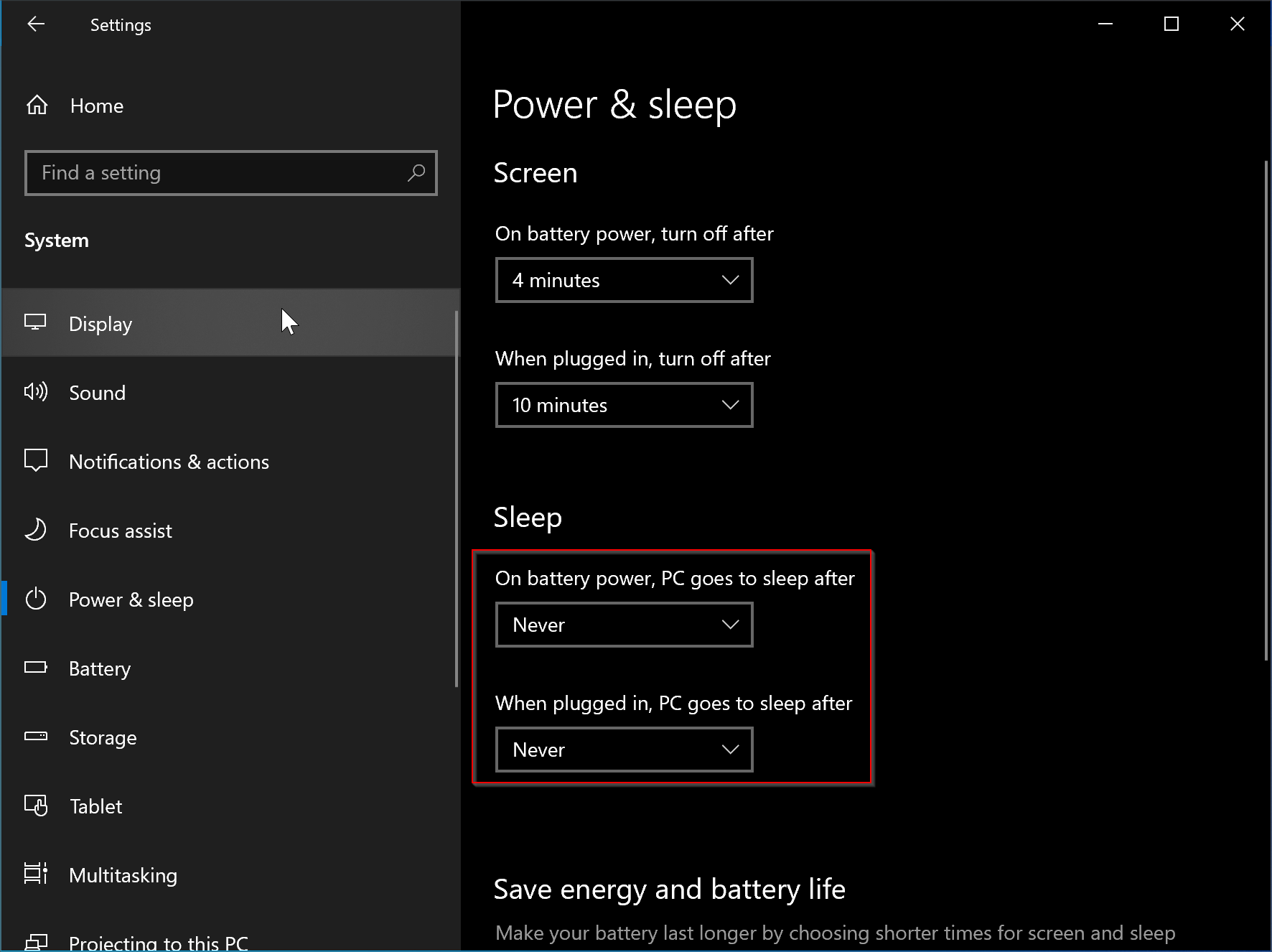
Windows 11, like its predecessors, offers a range of power management options, with sleep mode being a popular choice for conserving energy and preserving battery life. However, understanding how to effectively resume from sleep mode is crucial for a smooth user experience. This article delves into the various methods available to exit sleep mode in Windows 11, providing a comprehensive guide for users of all levels of expertise.
Understanding Sleep Mode
Sleep mode is a power-saving state that significantly reduces energy consumption while maintaining the system’s current state. When a device enters sleep mode, it:
- Reduces power to most components: The CPU, hard drive, and other peripherals are powered down, minimizing energy usage.
- Preserves system memory: The contents of RAM are retained, allowing for a quick resumption of the previous state.
- Reactivates quickly: Upon receiving an input, the device awakens from sleep mode within seconds, restoring the user’s workflow without restarting the entire system.
Methods to Exit Sleep Mode
Several methods can be employed to bring a Windows 11 device out of sleep mode, each offering distinct advantages depending on the situation.
1. Mouse or Keyboard Input:
The most common and straightforward method involves interacting with the device through the mouse or keyboard. A simple mouse click, keyboard key press, or even a touch on the screen will be sufficient to awaken the device from sleep mode. This method is particularly useful for short breaks, as the system resumes quickly without requiring any further action.
2. Power Button:
The power button serves as a reliable alternative to mouse or keyboard input. Pressing the power button once will typically initiate the wake-up process. However, it is important to note that some devices may require a longer press or a specific combination of keystrokes to exit sleep mode. Consult the device’s documentation for specific instructions.
3. Wake-on-LAN (WOL):
Wake-on-LAN (WOL) is a network-based method that allows a device to be woken up from sleep mode remotely. This feature requires enabling WOL in the device’s BIOS settings and configuring the network adapter to support it. Once enabled, a special network packet can be sent to the device’s MAC address, triggering it to wake up. This method is particularly useful for remote management and troubleshooting.
4. Scheduled Wake-up:
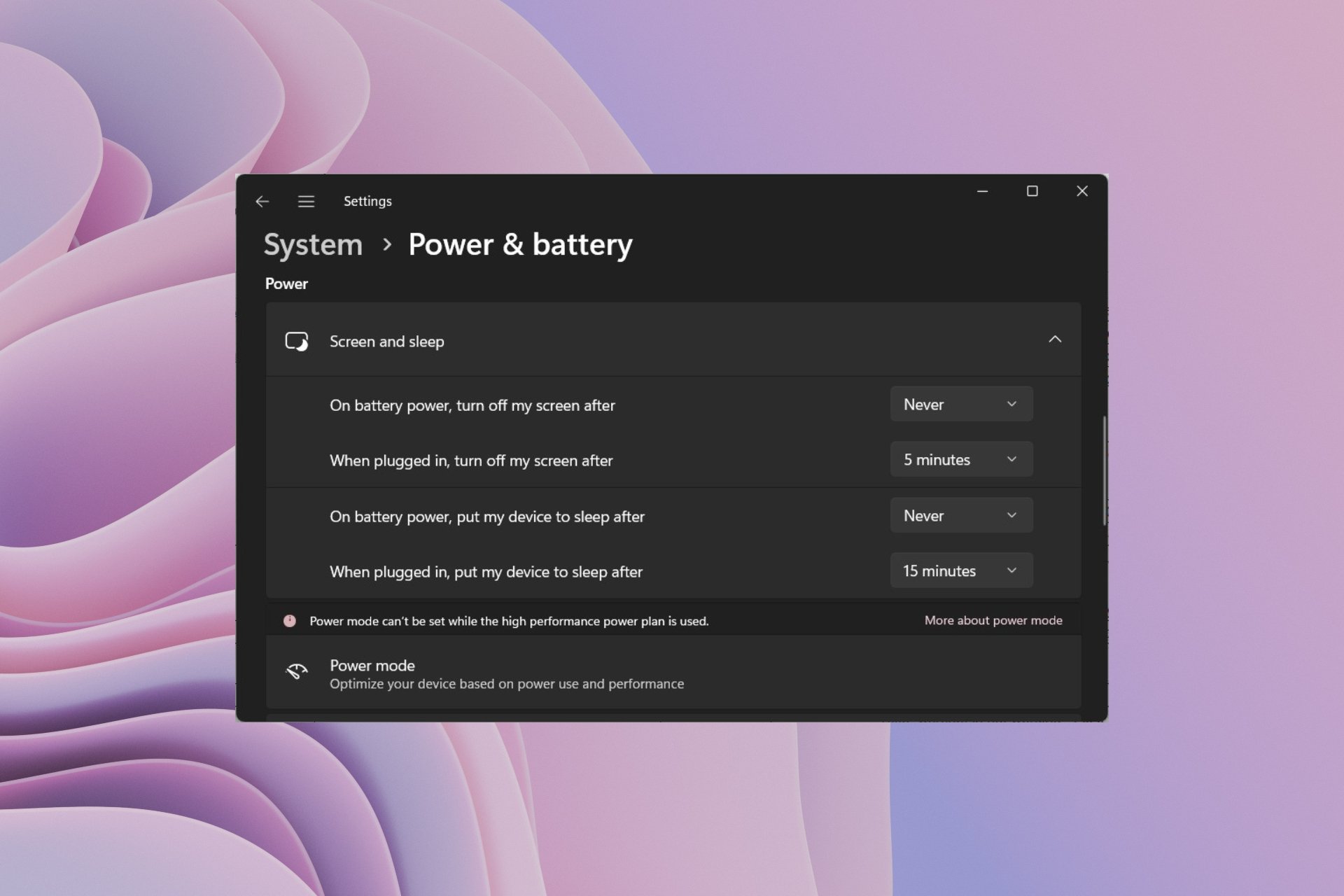
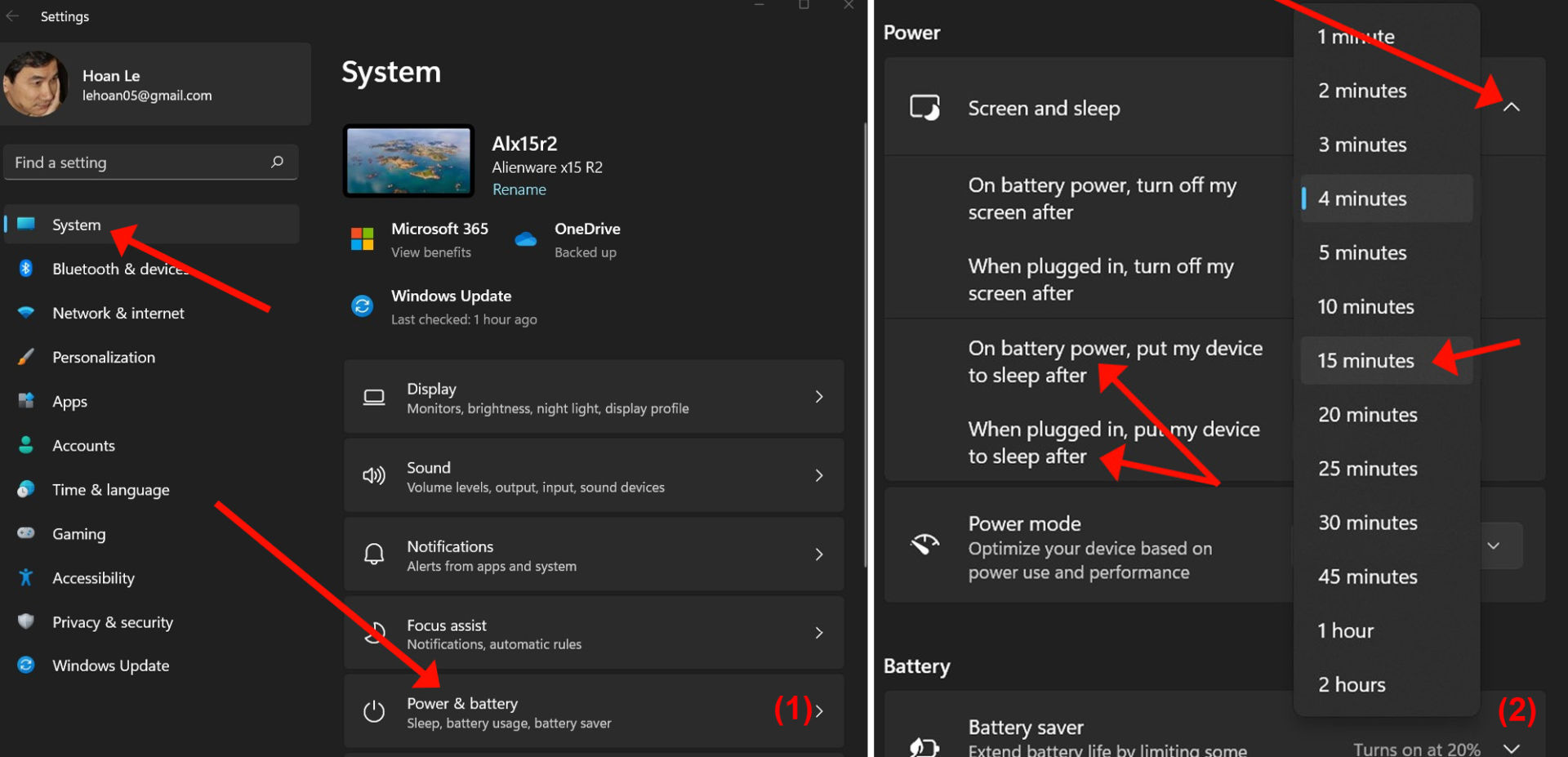
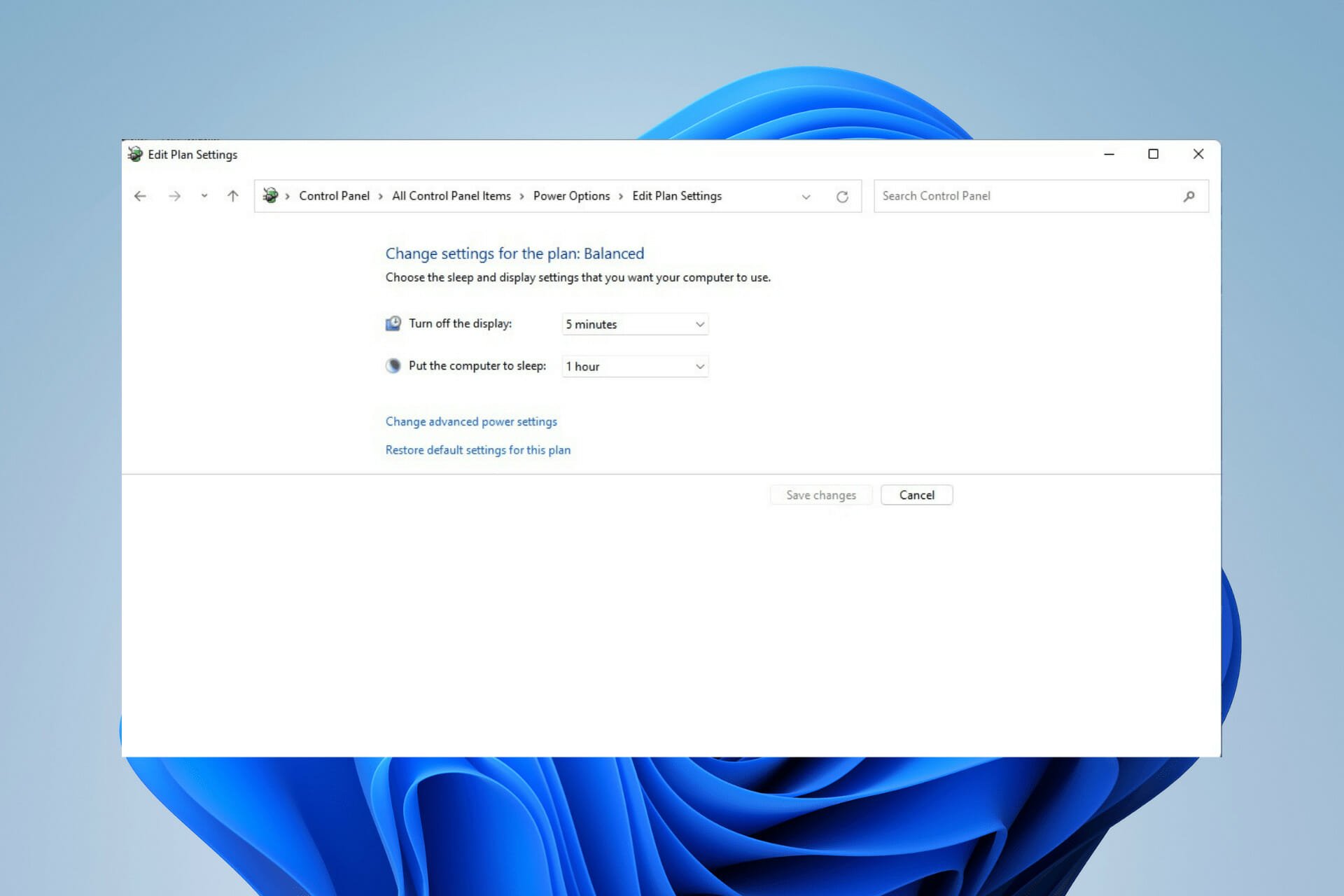
Windows 11 allows users to schedule wake-up times for their devices. This feature is particularly useful for tasks that require the device to be active at specific times, such as downloading files, running backups, or receiving updates. To schedule a wake-up time, navigate to the Power Options settings and select the Change when the computer sleeps option. Here, you can define specific times for the device to wake up automatically.
5. External Devices:
Certain external devices, such as USB drives or printers, can be configured to wake up the computer from sleep mode. This feature is typically enabled in the device’s settings. For instance, a USB printer may be configured to wake the computer when a print job is sent, allowing for automatic printing even when the computer is in sleep mode.
6. Wake-up Timers:
Windows 11 provides a built-in wake-up timer that allows the device to wake up after a specified duration. This feature is particularly useful for situations where the device needs to be awake for a limited time, such as a scheduled download or a specific task. To set a wake-up timer, navigate to the Power Options settings and select the Change advanced power settings option. Within the advanced settings, locate the Sleep section and configure the wake-up timer as needed.
Troubleshooting Sleep Mode Issues
While sleep mode is generally a reliable feature, certain issues may arise. Here are some common troubleshooting tips:
- Ensure sufficient power: If the device fails to wake up from sleep mode, ensure it is connected to a power source and that the battery has sufficient charge.
- Check device settings: Verify that sleep mode is enabled in the device’s power settings and that the wake-up settings are configured correctly.
- Update drivers: Outdated drivers can sometimes cause sleep mode issues. Update device drivers to the latest version to ensure compatibility.
- Disable unnecessary peripherals: Some peripherals can interfere with sleep mode. Disable or disconnect unnecessary peripherals to see if it resolves the issue.
- Run system diagnostics: If the issue persists, run system diagnostics to check for hardware problems.
Benefits of Using Sleep Mode
While sleep mode may seem like a simple power management feature, it offers numerous benefits for users:
- Energy Conservation: Sleep mode significantly reduces power consumption, saving energy and reducing electricity bills.
- Prolonged Battery Life: For laptops and tablets, sleep mode helps extend battery life, allowing for longer usage between charges.
- Quick Resumption: Sleep mode allows for a rapid resumption of the system, minimizing downtime and improving productivity.
- Data Preservation: The system’s memory is preserved in sleep mode, ensuring that no data is lost upon waking up.
FAQs
Q: What is the difference between sleep mode and hibernation?
A: Sleep mode is a low-power state that preserves the system’s memory, allowing for a quick resumption. Hibernation, on the other hand, saves the entire system state to the hard drive, allowing for a complete shutdown with no power consumption. Hibernation takes longer to resume but is useful when the device needs to be completely powered off.
Q: Can I use sleep mode with all devices?
A: Sleep mode is a standard feature on most modern devices, including laptops, tablets, and desktops. However, some older devices may not support sleep mode or may have limited functionality.
Q: Can I configure the sleep mode settings?
A: Yes, Windows 11 allows for customization of sleep mode settings. Users can adjust the time it takes for the device to enter sleep mode, configure wake-up settings, and choose whether to enable hibernation.
Q: What happens to my open files and applications when I enter sleep mode?
A: When a device enters sleep mode, the system’s memory is preserved, meaning that all open files and applications remain in their current state. Upon waking up, the device will resume exactly where it left off.
Tips for Efficient Sleep Mode Usage
- Enable sleep mode: If you’re not using your device, consider enabling sleep mode to conserve energy and extend battery life.
- Set realistic sleep timers: Configure sleep timers to automatically put the device into sleep mode after a specific period of inactivity.
- Disable unnecessary peripherals: Disconnect or disable peripherals that are not actively in use to minimize power consumption during sleep mode.
- Update drivers regularly: Ensure that device drivers are up to date to prevent compatibility issues that may affect sleep mode functionality.
Conclusion
Understanding how to effectively exit sleep mode in Windows 11 is essential for a smooth user experience. From simple mouse clicks to remote network commands, users have a range of options at their disposal. By leveraging these methods and troubleshooting potential issues, users can optimize their device’s power management capabilities, maximizing energy efficiency and preserving battery life. Sleep mode remains a valuable feature in Windows 11, offering a balance between energy conservation and quick resumption, enhancing overall productivity and user convenience.

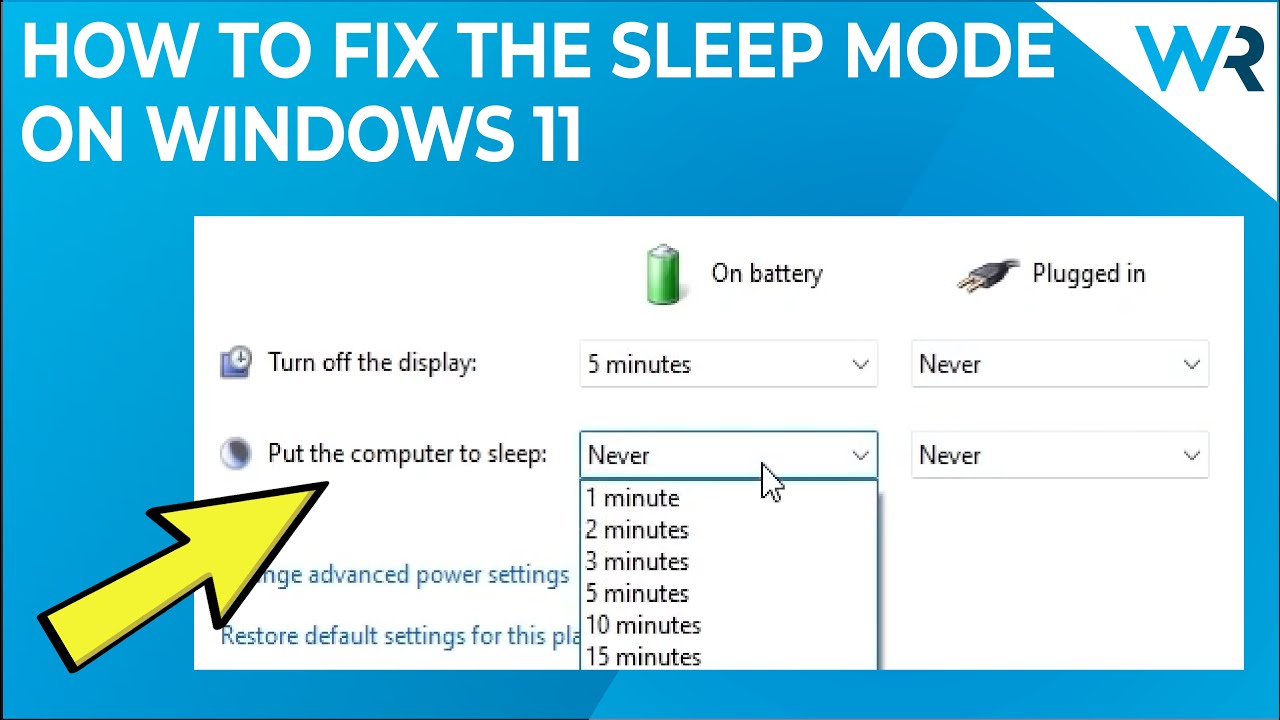
![How to Put a Windows 11 PC to Sleep Mode [Detailed Steps]](https://www.ubackup.com/screenshot/en/others/how-to-put-a-windows-11-pc-to-sleep/change-time-to-never.png)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Resuming from Sleep Mode in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!