Navigating Windows 10’s Safe Mode: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Navigating Windows 10’s Safe Mode: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating Windows 10’s Safe Mode: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating Windows 10’s Safe Mode: A Comprehensive Guide
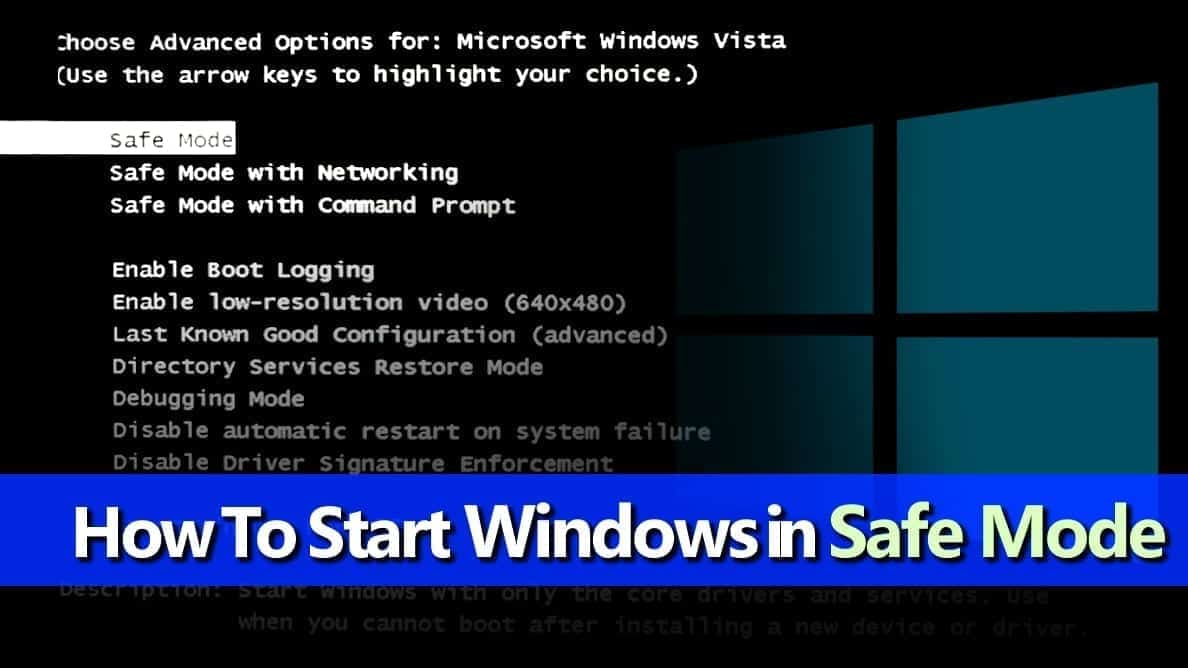
Windows 10’s Safe Mode presents a stripped-down version of the operating system, offering a troubleshooting environment for addressing various system issues. This mode starts with a limited set of drivers and programs, minimizing potential conflicts and enabling users to diagnose and resolve problems that might otherwise be masked by the full operating system.
Understanding the Benefits of Safe Mode
Safe Mode serves as a powerful tool for resolving various Windows 10 issues, including:
- Driver Conflicts: A malfunctioning driver can cause system instability or prevent certain hardware from functioning correctly. Safe Mode, by loading only essential drivers, can help identify the problematic driver.
- Malware Removal: Some malware can deeply embed itself within the operating system, hindering standard removal attempts. Safe Mode provides a secure environment to run anti-malware programs and eliminate persistent threats.
- Troubleshooting System Errors: When Windows 10 encounters errors or crashes, Safe Mode helps determine if the issue stems from a specific program or a system-wide problem.
- Software Installation and Updates: If a recent software installation or update causes issues, Safe Mode allows for uninstalling or reverting the changes without encountering further complications.
Accessing Safe Mode: A Step-by-Step Guide
There are three primary methods for accessing Safe Mode in Windows 10:
Method 1: Using the Startup Settings Menu
- Restart the computer: Press the Start button, then click Power > Restart.
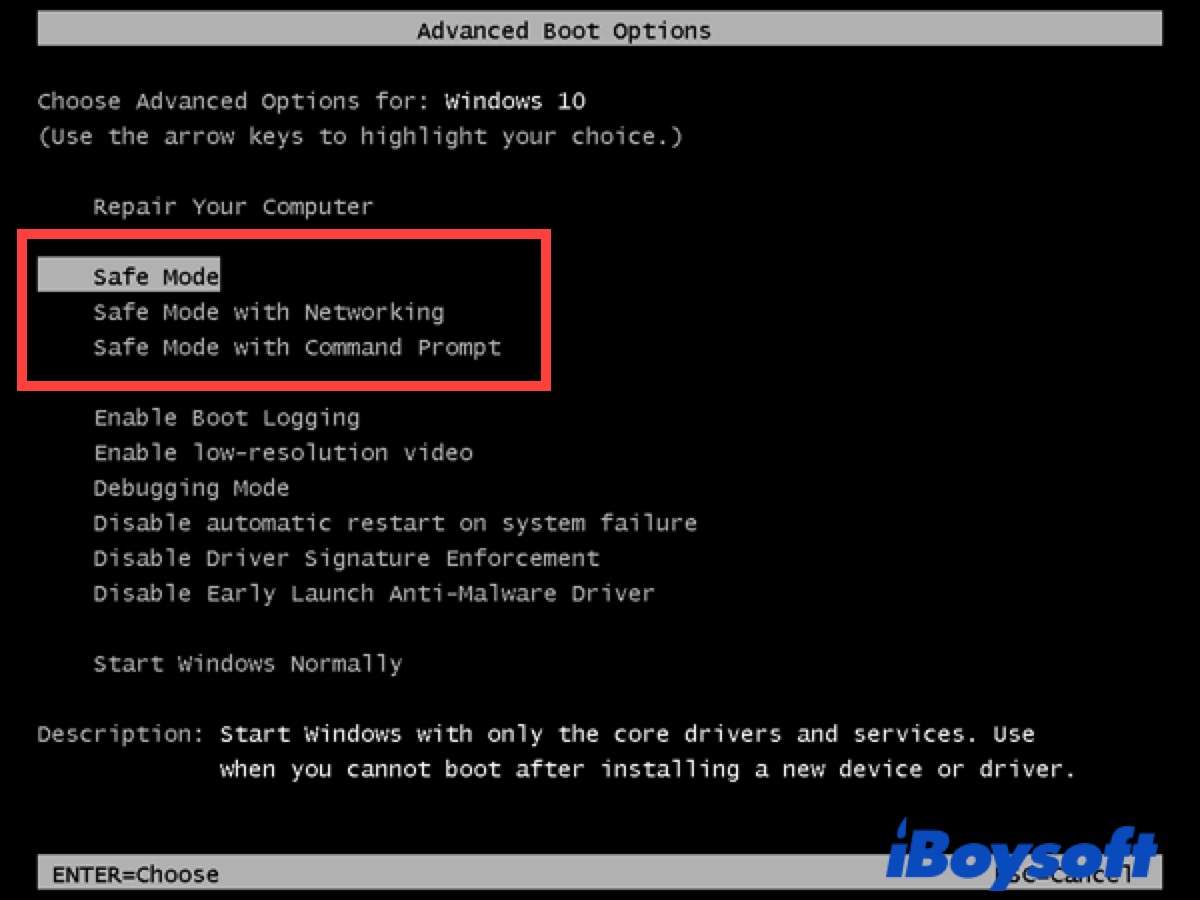
- Access the Advanced Startup Options: As the computer restarts, press and hold the Shift key until the Choose an option screen appears.
- Navigate to Troubleshoot: Select Troubleshoot from the menu.
- Select Advanced options: Click on Advanced options.
- Choose Startup Settings: Select Startup Settings.
- Restart the computer: Click Restart.
-
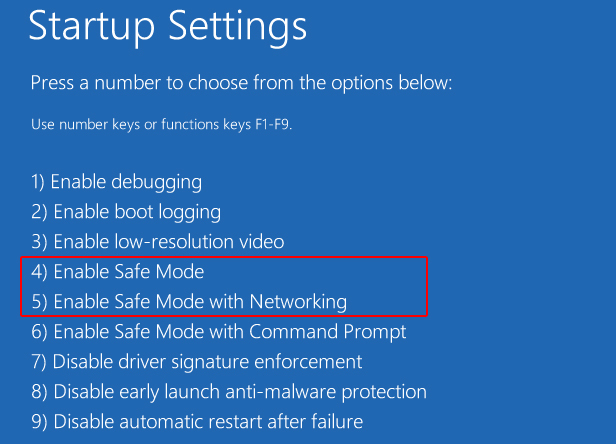
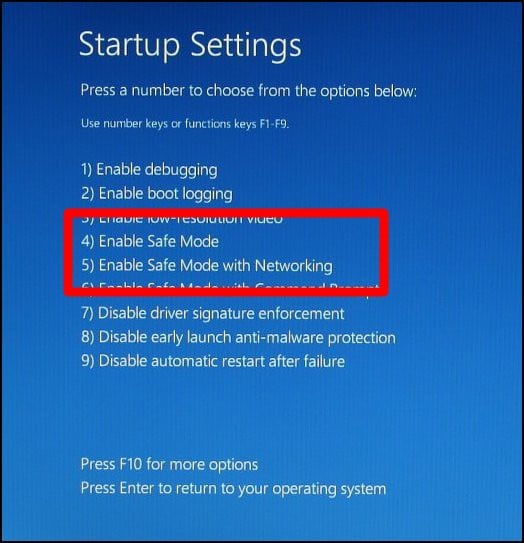
Select Safe Mode: After the computer restarts, you will see a list of options. Press the corresponding number to select the desired Safe Mode variant:
- 4. Enable Safe Mode: Starts Windows 10 with minimal drivers and services.
- 5. Enable Safe Mode with Networking: Similar to Safe Mode, but includes network drivers for internet access.
- 6. Enable Safe Mode with Command Prompt: Starts Windows 10 with a command prompt instead of the graphical user interface.
Method 2: Using the Run Command
- Press Windows key + R: This opens the Run dialog box.
-
Type
msconfig: This command launches the System Configuration window. - Navigate to the Boot tab: Click on the Boot tab at the top of the window.
- Check the Safe boot option: Select the Safe boot checkbox.
-
Choose the desired Safe Mode variant: Select the desired variant from the "Boot options" dropdown menu:
- Minimal: Starts Windows 10 with minimal drivers and services.
- Alternative shell: Starts Windows 10 with the command prompt.
- Active Directory repair: Starts Windows 10 with specific settings for Active Directory troubleshooting.
- Network: Starts Windows 10 with network drivers enabled.
- Apply the changes: Click Apply and then OK.
- Restart the computer: The system will prompt you to restart. Once restarted, Windows 10 will boot into Safe Mode.
Method 3: Using the Command Prompt (Advanced)
- Access the Command Prompt: This method requires access to a bootable USB drive or installation disc.
- Boot from the media: Start the computer from the USB drive or installation disc.
- Select the language and keyboard layout: Follow the on-screen prompts to choose your language and keyboard layout.
- Access the Command Prompt: Select Repair your computer and navigate to Troubleshoot > Advanced options > Command Prompt.
-
Run the command: Type the following command and press Enter:
bcdedit /set default safeboot minimal- This command sets the default boot option to Safe Mode with minimal drivers and services.
-
Restart the computer: Type
exitto close the Command Prompt and restart the computer. Windows 10 will now boot into Safe Mode.
Exiting Safe Mode: Returning to Normal Operation
Once the issue is addressed, you need to exit Safe Mode and return to normal operation. This is typically done by restarting the computer. In most cases, Windows 10 will automatically boot into its usual mode.
If you entered Safe Mode through the System Configuration window:
-
Open System Configuration: Press Windows key + R, type
msconfig, and press Enter. - Uncheck the Safe boot option: Go to the Boot tab and uncheck the Safe boot checkbox.
- Apply the changes: Click Apply and then OK.
- Restart the computer: The system will prompt you to restart.
Frequently Asked Questions about Safe Mode
Q: Can I use the internet in Safe Mode?
A: Not in all Safe Mode variants. While Safe Mode with Networking enables internet access, the standard Safe Mode does not.
Q: Will I lose any data while in Safe Mode?
A: No. Safe Mode is a troubleshooting environment, and it does not affect your data or settings.
Q: Can I install programs in Safe Mode?
A: While you can install programs in Safe Mode, it’s generally not recommended. The limited environment may lead to unexpected behavior or incomplete installations.
Q: What if Safe Mode doesn’t work?
A: If you’re unable to access Safe Mode, consider trying a system restore point or a clean installation of Windows 10.
Tips for Using Safe Mode Effectively
- Identify the Issue: Before entering Safe Mode, try to narrow down the problem. This will help you focus your troubleshooting efforts.
- Use the Event Viewer: The Event Viewer in Safe Mode can provide valuable insights into system errors and warnings.
- Run System File Checker (SFC): The SFC command can scan and repair corrupted system files.
- Run a Disk Cleanup: Free up disk space by removing unnecessary files.
- Update Drivers: Update drivers in Safe Mode to ensure compatibility and stability.
- Be Patient: Troubleshooting can take time, so be patient and persistent in your efforts.
Conclusion
Safe Mode provides a vital tool for resolving Windows 10 issues without risking data loss. By understanding its functionality and applying the appropriate methods, users can effectively diagnose and fix various problems, restoring their system to optimal performance. While utilizing Safe Mode, it’s crucial to approach troubleshooting with a systematic and patient mindset, utilizing available resources and tools to effectively address the underlying issue.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating Windows 10’s Safe Mode: A Comprehensive Guide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!