Navigating Windows 10’s Safe Mode: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Navigating Windows 10’s Safe Mode: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating Windows 10’s Safe Mode: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating Windows 10’s Safe Mode: A Comprehensive Guide
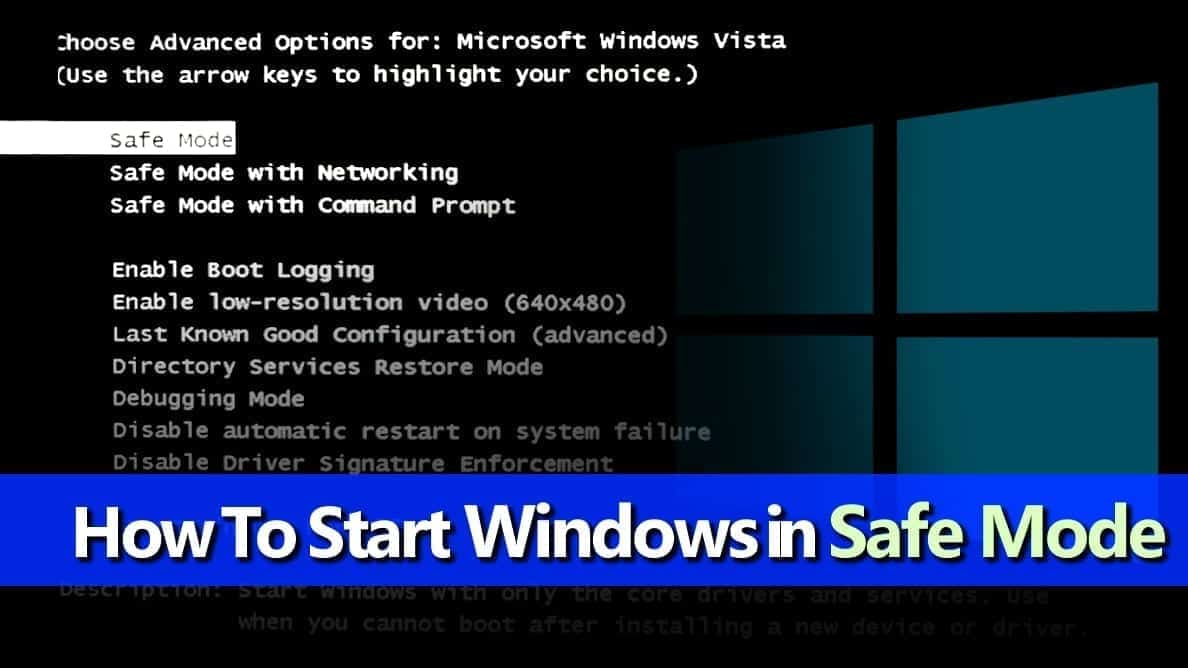
Safe Mode, a diagnostic startup environment, presents a stripped-down version of Windows 10, running only essential drivers and services. This mode is a valuable tool for troubleshooting system issues, resolving conflicts caused by newly installed software or drivers, and addressing malware infections.
Understanding the Importance of Safe Mode
Imagine your computer behaving erratically, displaying error messages, or experiencing slowdowns. These issues could stem from various sources, including faulty drivers, malware, or even corrupted system files. Safe Mode offers a solution by eliminating potential culprits, allowing you to identify and resolve the problem effectively.
Initiating Safe Mode at Boot: Methods and Considerations
Accessing Safe Mode in Windows 10 can be achieved through different methods, each suited to specific scenarios:
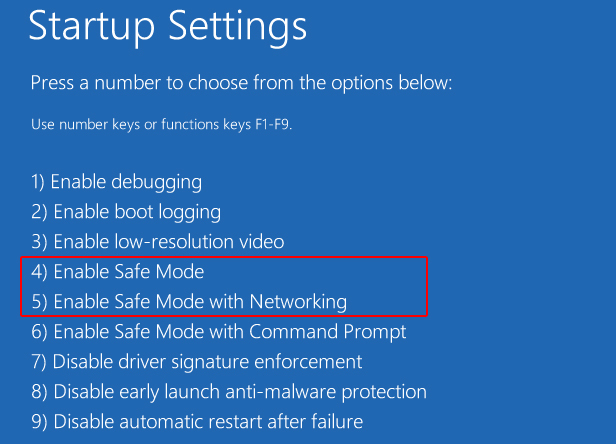
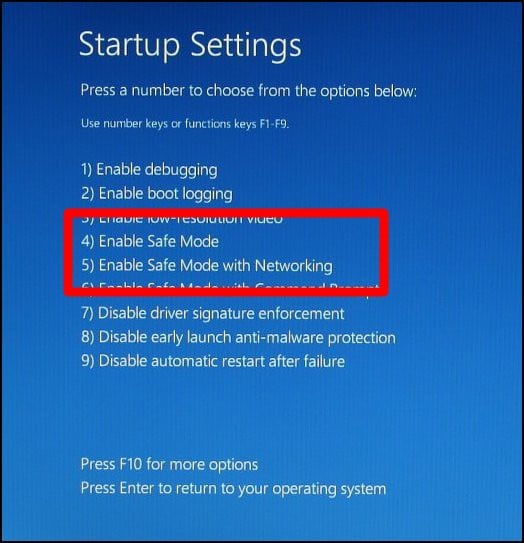
1. Using the Startup Settings Menu:
-
Step 1: Press and hold the Shift key while clicking the Restart option from the Start menu or the Power button in the sign-in screen.
-
Step 2: On the blue screen, select Troubleshoot > Advanced options > Startup Settings.
-
Step 3: Click Restart, and you’ll be presented with a list of options. Choose the desired Safe Mode option:
- Safe Mode: The most basic Safe Mode, loading only essential drivers and services.
- Safe Mode with Networking: Includes network drivers, allowing access to the internet.
- Safe Mode with Command Prompt: Offers a command prompt environment for advanced troubleshooting.
2. Using the System Configuration Utility:
- Step 1: Press Windows key + R to open the Run dialog box.
- Step 2: Type msconfig and press Enter.
- Step 3: Navigate to the Boot tab and check the Safe Boot option.
- Step 4: Choose the desired Safe Mode option from the Boot options dropdown.
- Step 5: Click Apply and OK.
- Step 6: Restart your computer.
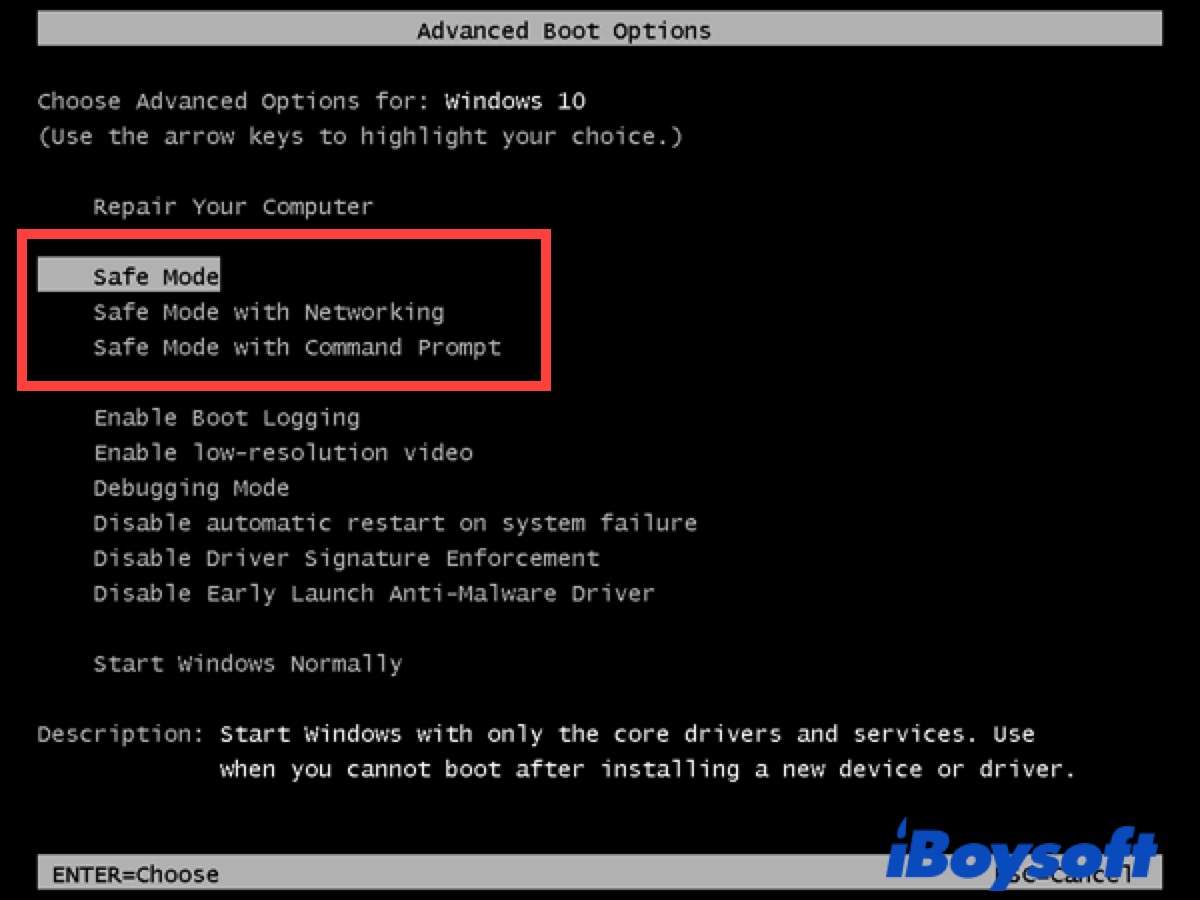
3. Using the Advanced Boot Options Menu:
- Step 1: Restart your computer.
- Step 2: During the boot process, repeatedly press F8 or Shift + F8, depending on your system’s BIOS settings.
- Step 3: Select Safe Mode from the menu.
4. Using the Command Prompt:
- Step 1: Open an elevated command prompt by searching for "cmd" in the Start menu, right-clicking the result, and selecting "Run as administrator."
- Step 2: Type bcdedit /set current safeboot minimal and press Enter. This command enables Safe Mode.
- Step 3: Restart your computer.
Important Considerations:
- BIOS Settings: Some systems might require entering the BIOS settings (usually accessed by pressing Delete, F2, or F10 during boot) to enable Safe Mode options.
- Boot Order: Ensure your computer is booting from the correct drive (usually the hard drive).
- Third-Party Antivirus Software: Some antivirus programs may interfere with Safe Mode access. Temporarily disabling them may be necessary.
Navigating Safe Mode: Essential Tips
- Limited Functionality: Safe Mode operates with a limited set of drivers and services, resulting in a simplified desktop environment.
- Network Access: If you require network access, ensure you select the "Safe Mode with Networking" option.
- Troubleshooting Steps: Once in Safe Mode, perform the necessary troubleshooting steps, such as uninstalling problematic software, scanning for malware, or updating drivers.
- Exiting Safe Mode: After completing the troubleshooting, restart your computer normally to exit Safe Mode.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What are the differences between the various Safe Mode options?
A:
- Safe Mode: The most basic option, loading only essential drivers and services.
- Safe Mode with Networking: Includes network drivers, allowing internet access.
- Safe Mode with Command Prompt: Offers a command prompt environment for advanced troubleshooting.
Q: Can I access the internet in Safe Mode?
A: Only in "Safe Mode with Networking."
Q: How do I exit Safe Mode?
A: Simply restart your computer normally.
Q: Is it safe to use Safe Mode regularly?
A: Safe Mode is intended for troubleshooting and should not be used as a regular operating environment.
Q: Can I install software in Safe Mode?
A: Software installation is generally not recommended in Safe Mode as it lacks necessary drivers and services.
Conclusion
Safe Mode in Windows 10 is a powerful tool for resolving system issues and maintaining a stable operating environment. By understanding its various access methods, navigating its limitations, and employing effective troubleshooting techniques, users can leverage Safe Mode to restore their system to optimal performance. Remember, Safe Mode is a temporary solution, and addressing the underlying issue is crucial for long-term stability.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating Windows 10’s Safe Mode: A Comprehensive Guide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!