Navigating Windows 10 Troubles: A Guide to Safe Mode
Related Articles: Navigating Windows 10 Troubles: A Guide to Safe Mode
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating Windows 10 Troubles: A Guide to Safe Mode. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating Windows 10 Troubles: A Guide to Safe Mode

Windows 10, despite its robust nature, can occasionally encounter issues that hinder its smooth operation. These problems can range from minor glitches to severe system malfunctions, rendering the operating system unstable or inaccessible. In such scenarios, a powerful troubleshooting tool comes to the rescue: Safe Mode.
Safe Mode is a diagnostic startup environment that loads Windows with only essential drivers and services. This stripped-down state eliminates the interference of potentially problematic software, allowing users to identify and address the root cause of system issues.
While the traditional method of accessing Safe Mode using the F8 key during startup is no longer available in Windows 10, there are alternative methods to initiate this crucial troubleshooting mode. This article delves into the various ways to boot into Safe Mode on Windows 10, outlining the benefits of using this feature and providing detailed instructions for each method.
Understanding the Significance of Safe Mode
Safe Mode serves as a vital tool for resolving various Windows 10 issues. Its utility stems from its ability to isolate and diagnose problems by minimizing the number of programs and services running during startup. This allows users to:
- Identify and Troubleshoot Software Conflicts: When multiple programs clash with each other, causing system instability, Safe Mode provides a clean environment to pinpoint the conflicting software. By selectively enabling programs within Safe Mode, users can isolate the culprit and take appropriate action, such as uninstalling the problematic software.
- Resolve Driver Issues: Drivers, the software that enables communication between hardware and the operating system, can sometimes become corrupted or incompatible. Safe Mode allows users to update or reinstall problematic drivers, restoring proper functionality.
- Remove Malicious Software: Viruses and malware can disrupt system performance and security. Safe Mode, with its limited access to resources, prevents malicious software from interfering with removal processes, enabling effective malware removal.
- Perform System Repairs: When Windows 10 encounters critical errors, Safe Mode provides a platform to run system repair tools like System Restore or Startup Repair. These tools can revert system changes or fix corrupted system files, restoring stability.
- Test Hardware: Safe Mode allows users to test hardware components without the interference of other software. This helps identify faulty hardware that might be causing system issues.
Methods to Access Safe Mode in Windows 10
1. Using the Startup Settings Menu
This method utilizes the advanced startup options within Windows 10 to access Safe Mode.
- Step 1: Open the Settings app (Windows key + I).
- Step 2: Navigate to Update & Security > Recovery.
- Step 3: Under "Advanced startup," click Restart now.
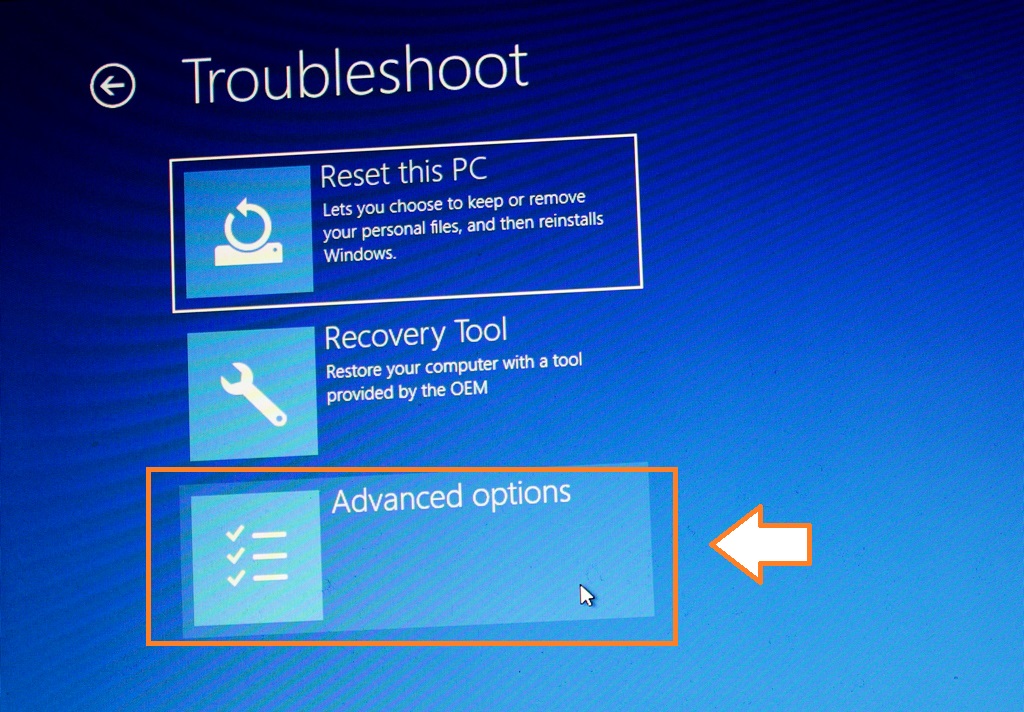
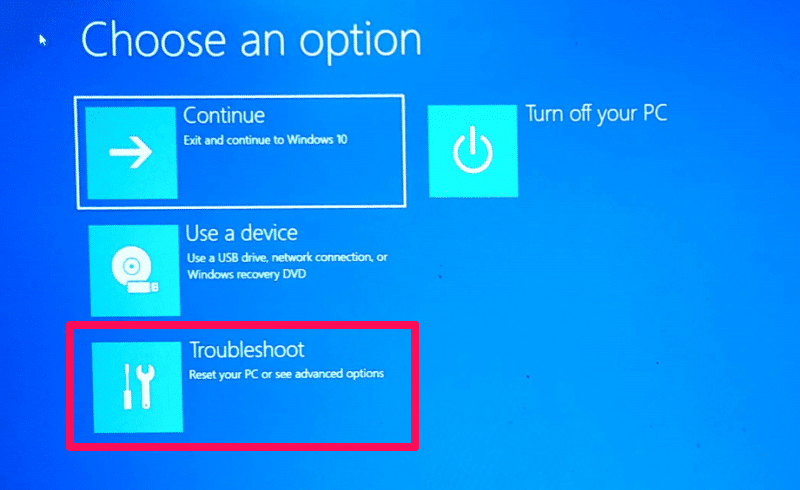
- Step 4: Upon restarting, the computer will enter the Choose an option screen. Select Troubleshoot > Advanced options > Startup Settings > Restart.
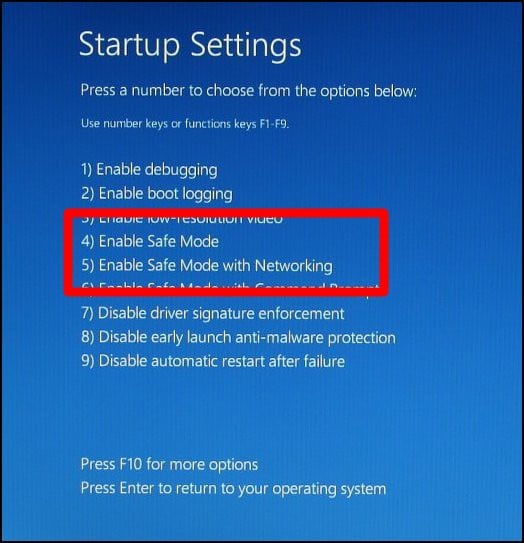
- Step 5: The computer will restart again, presenting a list of options. Press 4 or F4 on the keyboard to select Enable Safe Mode.
2. Using the Command Prompt
This method involves using the command prompt to initiate a restart into Safe Mode.
- Step 1: Open the Start Menu and search for "cmd".
- Step 2: Right-click on Command Prompt and select "Run as administrator".
- Step 3: In the command prompt window, type "shutdown /r /o /f" and press Enter.
- Step 4: The computer will restart and enter the Choose an option screen. Follow steps 3-5 from the previous method to access Safe Mode.
3. Using the System Configuration Utility
This method utilizes the System Configuration utility (msconfig) to modify startup settings and enable Safe Mode.
- Step 1: Open the Start Menu and search for "msconfig".
- Step 2: Select System Configuration.
- Step 3: Go to the Boot tab.
- Step 4: Check the box next to "Safe boot" and select the desired Safe Mode option (Minimal, Network, or Command Prompt).
- Step 5: Click Apply and OK.
- Step 6: Restart the computer.
4. Using the "Shift" Key During Startup
This method involves pressing and holding the Shift key while restarting the computer to access advanced startup options.
- Step 1: Click the Start Menu and select Power > Restart.
- Step 2: While holding down the Shift key, click the Restart option.
- Step 3: The computer will enter the Choose an option screen. Follow steps 3-5 from the first method to access Safe Mode.
5. Using the Windows Recovery Environment (WinRE)
This method uses a recovery environment to access Safe Mode.
- Step 1: Create a bootable USB drive with a Windows installation media.
- Step 2: Boot the computer from the USB drive.
- Step 3: Follow the on-screen instructions to access the Windows Recovery Environment.
- Step 4: Select Troubleshoot > Advanced options > Startup Settings > Restart.
- Step 5: Press 4 or F4 to select Enable Safe Mode.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is the difference between the various Safe Mode options?
A: Safe Mode has three main options:
- Minimal Safe Mode: This option loads only the essential drivers and services required for the operating system to function.
- Safe Mode with Networking: This option includes network drivers, allowing users to connect to the internet.
- Safe Mode with Command Prompt: This option loads the command prompt instead of the graphical user interface, allowing for advanced troubleshooting using command-line tools.
Q: Can I use Safe Mode to access my files?
A: Yes, you can access your files in Safe Mode. However, you may not be able to access all programs or features.
Q: How do I exit Safe Mode?
A: To exit Safe Mode, simply restart your computer normally.
Q: Can I permanently enable Safe Mode?
A: No, Safe Mode is a temporary troubleshooting environment. It cannot be permanently enabled.
Tips for Using Safe Mode Effectively
- Identify the Cause of the Issue: Before entering Safe Mode, try to identify the potential source of the problem. This will help you focus your troubleshooting efforts.
- Run System Scans: Once in Safe Mode, run system scans using tools like Windows Defender or a third-party antivirus to detect and remove malware.
- Update Drivers: Check for and install the latest drivers for your hardware components.
- Uninstall Problematic Software: If you suspect a particular program is causing issues, uninstall it in Safe Mode.
- Use System Restore: If you encounter significant problems, consider using System Restore to revert your system to a previous working state.
Conclusion
Safe Mode is a powerful troubleshooting tool that can help resolve various Windows 10 issues. By understanding its functionalities and mastering the different methods to access it, users can effectively diagnose and fix system problems, restoring stability and functionality to their operating system. Remember to use Safe Mode responsibly, carefully following the instructions provided and taking necessary precautions to protect your data.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating Windows 10 Troubles: A Guide to Safe Mode. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!