Navigating the Windows Restart Loop: A Comprehensive Guide to Troubleshooting and Repair
Related Articles: Navigating the Windows Restart Loop: A Comprehensive Guide to Troubleshooting and Repair
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Windows Restart Loop: A Comprehensive Guide to Troubleshooting and Repair. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Windows Restart Loop: A Comprehensive Guide to Troubleshooting and Repair
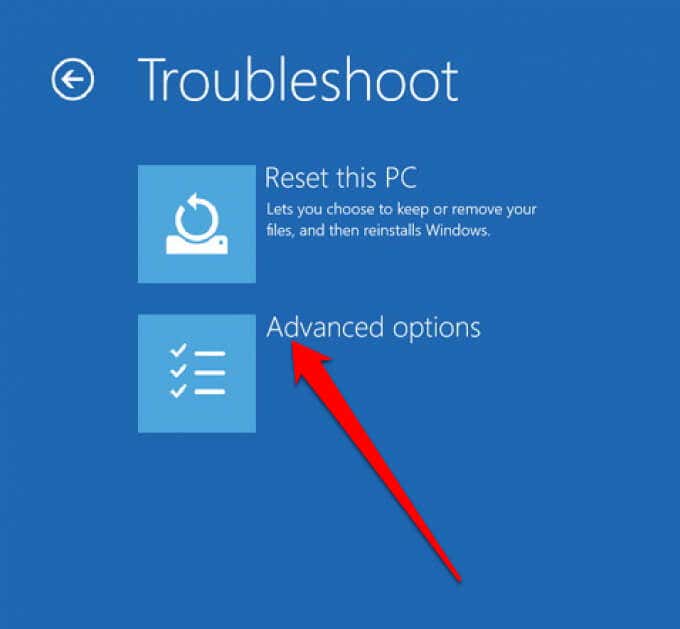
The dreaded Windows restart loop, characterized by a continuous cycle of booting, restarting, and failing to load the operating system, can be a frustrating experience for any computer user. This issue can arise due to various factors, ranging from corrupted system files to hardware malfunctions. Fortunately, there are several troubleshooting methods and repair strategies that can help resolve this problem and restore your computer to a functional state.
Understanding the Root Causes
Before embarking on the troubleshooting process, it is crucial to understand the potential causes of the Windows restart loop. This will help in narrowing down the possible solutions and focusing efforts on the most likely culprits.
1. Corrupted System Files: A common culprit is damage to essential system files, which can occur due to various factors, including:
* **Software Conflicts:** Incompatible or faulty software installations can corrupt system files, leading to instability.
* **Virus or Malware Infections:** Malicious software can infect and damage system files, disrupting the normal boot process.
* **Hardware Failures:** Faulty hard drives or RAM modules can cause data corruption, affecting system files.
* **Improper Shutdowns:** Abrupt power outages or improper shutdowns can lead to incomplete file writes and damage to system files.
* **Incomplete Updates:** Failed or interrupted Windows updates can leave system files in an inconsistent state.2. Hardware Malfunctions: Faulty hardware components, particularly those directly involved in the boot process, can also cause a restart loop. These include:
* **Hard Drive Errors:** A failing hard drive can prevent the system from loading, leading to repeated restarts.
* **RAM Issues:** Faulty RAM modules can cause memory errors, leading to system instability and restarts.
* **Motherboard Problems:** Defective motherboard components, such as the BIOS chip or chipset, can disrupt the boot process.
* **Power Supply Unit (PSU) Issues:** A malfunctioning PSU can provide insufficient or unstable power, leading to system crashes and restarts.3. Boot Configuration Errors: The Windows boot configuration, which determines the order and methods of loading the operating system, can be corrupted or misconfigured. This can result in the system failing to find or load the necessary files, leading to repeated restarts.
Troubleshooting Strategies
Once you have a general understanding of the potential causes, you can begin troubleshooting the restart loop. The following steps outline a systematic approach to identifying and addressing the problem:
1. Check for Hardware Issues:
* **Power Cycle:** Start by restarting your computer. This simple step can sometimes resolve temporary glitches and clear memory errors.
* **Inspect Connections:** Ensure all cables, including power cords, data cables, and peripheral connections, are securely connected.
* **RAM Testing:** If you suspect RAM issues, try removing and reinserting the RAM modules. You can also use a memory testing tool to diagnose individual modules for errors.
* **Hard Drive Check:** Run a hard drive health check using tools like CrystalDiskInfo or chkdsk to identify potential errors or failures.
* **BIOS Update:** Check for BIOS updates from your motherboard manufacturer and update the BIOS if available. An outdated BIOS can sometimes cause compatibility issues.2. Access the Boot Options:
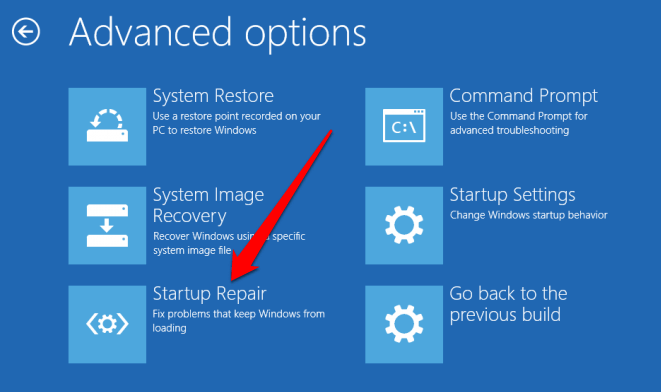
* **Advanced Startup Options:** Attempt to access the Advanced Startup Options menu. This menu can be accessed by pressing F8 during the boot process. This menu provides options for troubleshooting, including safe mode, system restore, and startup repair.
* **System Recovery:** If you can access the Advanced Startup Options, attempt to run a system recovery or restore to a previous point. This can help revert system changes and potentially resolve the restart loop.3. Utilize Safe Mode:
* **Safe Mode with Networking:** Try booting into Safe Mode with Networking. This mode loads a minimal set of drivers and services, which can help identify software conflicts or malware infections.
* **Troubleshooting in Safe Mode:** Once in Safe Mode, try running a virus scan or uninstalling recently installed software that may be causing conflicts.4. Run System File Checker (SFC):
* **Command Prompt Access:** If you can access the Command Prompt, run the System File Checker (SFC) tool. This tool scans and repairs corrupted system files.
* **SFC Command:** Open the Command Prompt and type `sfc /scannow` and press Enter. The tool will scan and repair any corrupted system files it finds.5. Perform a Clean Boot:
* **Disable Startup Items:** Perform a clean boot by disabling all non-essential startup items and services. This can help isolate software conflicts that might be causing the restart loop.
* **Clean Boot Steps:** Follow the instructions provided in the Microsoft support article for performing a clean boot.6. Consider Reinstallation or Reset:
* **Backup Data:** Before attempting a reinstallation or reset, ensure you have backed up all your important data.
* **Reinstallation:** If troubleshooting fails, you can try reinstalling Windows. This process will erase all data on your hard drive, so ensure you have a backup.
* **Reset:** If reinstallation is not an option, you can perform a reset, which will reinstall Windows while preserving your personal files.7. Seek Professional Help:
* **Data Recovery:** If you have lost data due to a hard drive failure, consider contacting a data recovery specialist.
* **Hardware Repair:** If you suspect hardware issues, consult a qualified technician for diagnosis and repair.FAQs on Windows Restart Loop
1. Why is my computer restarting repeatedly?
The restart loop can be caused by various factors, including corrupted system files, hardware malfunctions, boot configuration errors, and software conflicts.
2. How do I fix a Windows restart loop without reinstalling?
You can try several methods, such as accessing the Advanced Startup Options menu, booting into Safe Mode, running the System File Checker, and performing a clean boot.
3. What if my computer won’t boot into Safe Mode?
If you cannot access Safe Mode, you can try using a bootable USB drive with a system repair tool, such as the Windows Recovery Environment or a third-party repair disk.
4. How do I know if my hard drive is failing?
You can use hard drive health check tools, such as CrystalDiskInfo or chkdsk, to identify potential errors or failures. Listen for unusual noises from the hard drive, such as clicking or grinding sounds.
5. What should I do if my RAM is faulty?
If you suspect RAM issues, try removing and reinserting the RAM modules. You can also use a memory testing tool to diagnose individual modules for errors. If a module is faulty, it should be replaced.
6. Can a virus cause a restart loop?
Yes, a virus or malware infection can corrupt system files and cause a restart loop. Run a thorough virus scan using a reputable antivirus software.
7. How can I prevent a restart loop from happening again?
Regularly back up your data, keep your system updated with the latest software patches and security updates, and avoid installing software from untrusted sources.
Tips for Preventing Windows Restart Loop
1. Regular Updates: Keep your Windows operating system and software updated with the latest patches and security updates. Updates often include fixes for known bugs and vulnerabilities that can cause system instability.
2. Virus Protection: Install and maintain a reputable antivirus software to protect your computer from malware infections that can corrupt system files.
3. Software Installation: Be cautious when installing software, particularly from unknown sources. Avoid installing software that may be incompatible with your system or that has a history of causing problems.
4. Hardware Maintenance: Regularly clean your computer’s internal components, including the fan, heatsink, and hard drive, to prevent overheating and dust accumulation.
5. Data Backup: Regularly back up your important data to an external hard drive, cloud storage service, or other reliable backup solution. This will ensure that you can recover your files if your system fails.
Conclusion
A Windows restart loop can be a frustrating problem, but it is often solvable with proper troubleshooting and repair strategies. By understanding the potential causes and following the steps outlined in this guide, you can effectively diagnose and address the issue, restoring your computer to a functional state. Remember to back up your data before attempting any major repairs, and consider seeking professional assistance if you encounter difficulties or suspect hardware malfunctions.
![Windows 11 Keeps Restarting Loop FIX [Tutorial] - YouTube](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/HYsYnpuGEUU/hqdefault.jpg)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Windows Restart Loop: A Comprehensive Guide to Troubleshooting and Repair. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!