Navigating the Windows 10 File Explorer: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Navigating the Windows 10 File Explorer: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Windows 10 File Explorer: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Windows 10 File Explorer: A Comprehensive Guide
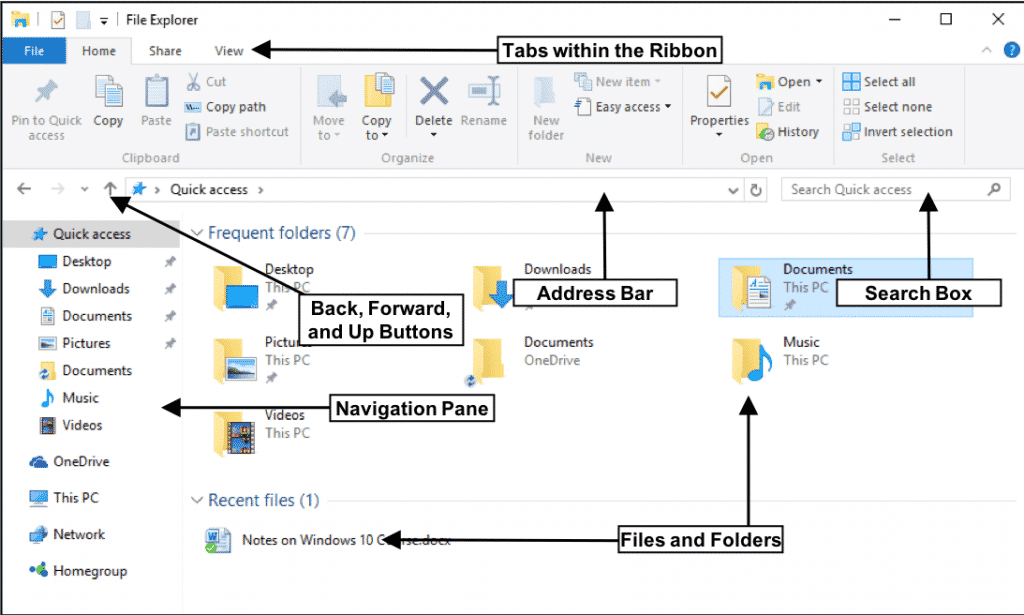
The Windows 10 File Explorer serves as the central hub for managing files and folders on your computer. It provides a user-friendly interface for accessing, organizing, and manipulating data. This guide delves into the intricacies of the File Explorer, offering insights into its features, functionalities, and best practices for efficient file management.
Understanding the File Explorer Interface
The File Explorer window presents a familiar layout:
- Navigation Pane: Located on the left, this pane displays a hierarchical view of your computer’s drives, libraries, and network locations. It allows quick access to frequently used folders and devices.
- Address Bar: Situated above the main window, this bar displays the current location within the file system. You can directly type a path or browse through folders using the drop-down menu.
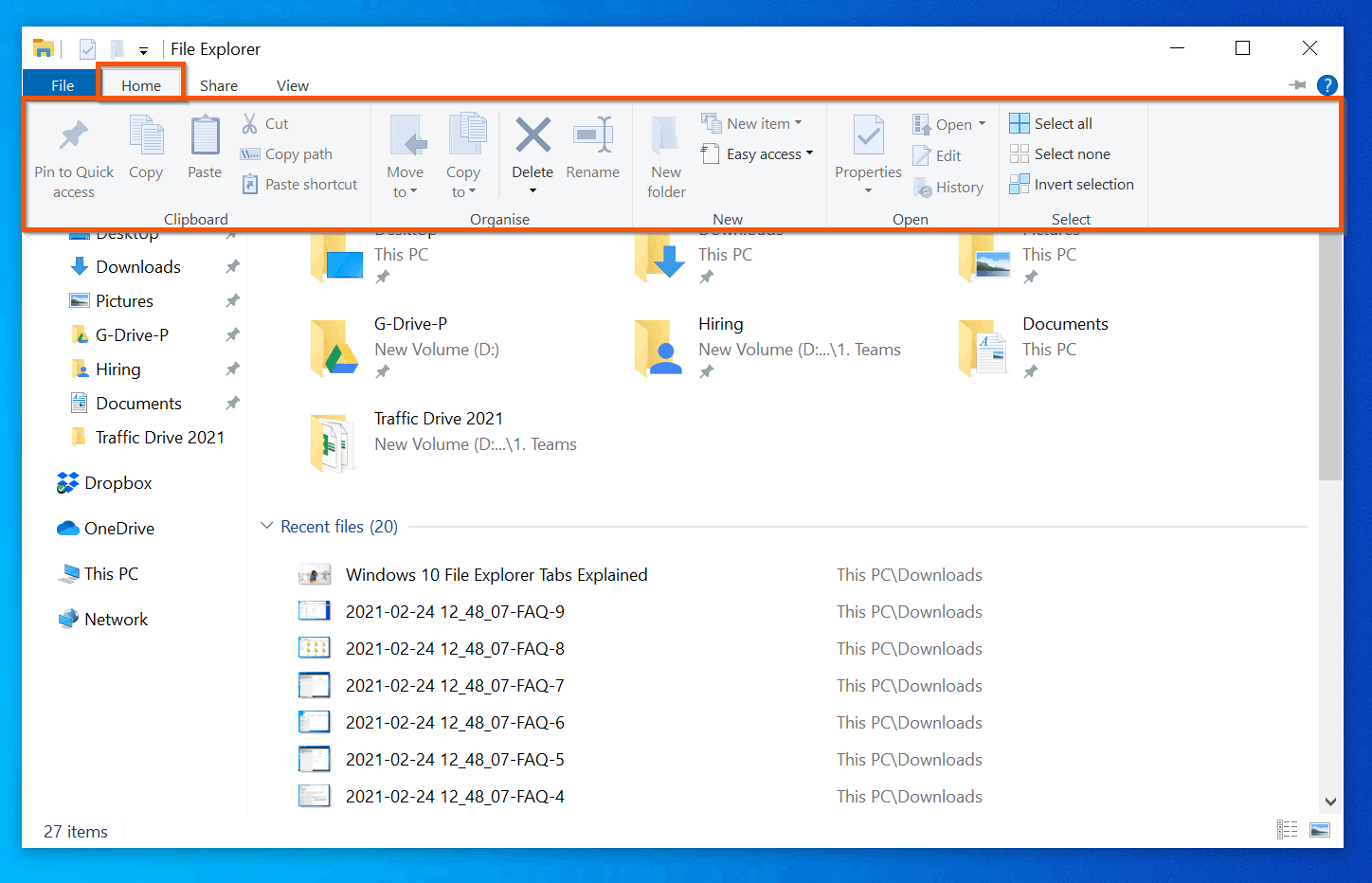
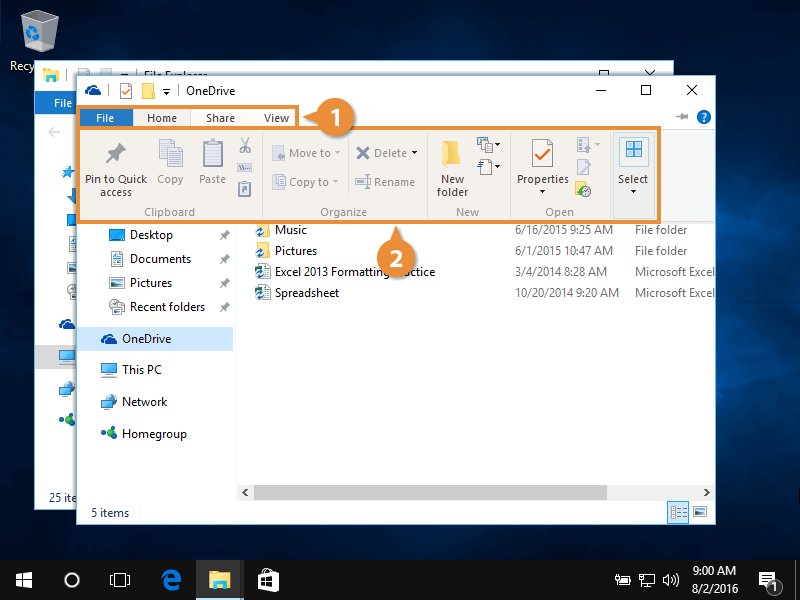
- Ribbon: Positioned at the top, the ribbon houses various commands and tools categorized into tabs like "Home," "Share," and "View." These tabs provide access to functions like copying, moving, deleting, and customizing file properties.
- Main Window: This central area displays the contents of the selected folder, including files, subfolders, and system icons.
Essential File Explorer Features
- Search: The File Explorer’s search function allows users to quickly locate specific files or folders based on keywords, file types, or dates. The search bar is conveniently located in the top right corner of the window.
- Sorting and Filtering: Files can be sorted alphabetically, numerically, or by date. Filters enable users to narrow down results based on file type, size, or other criteria.
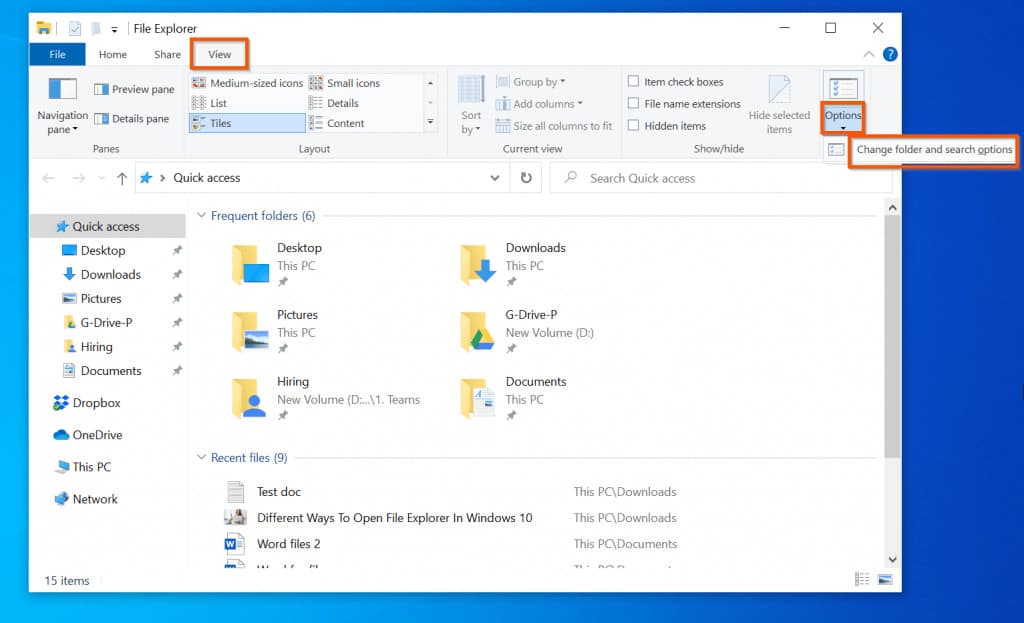
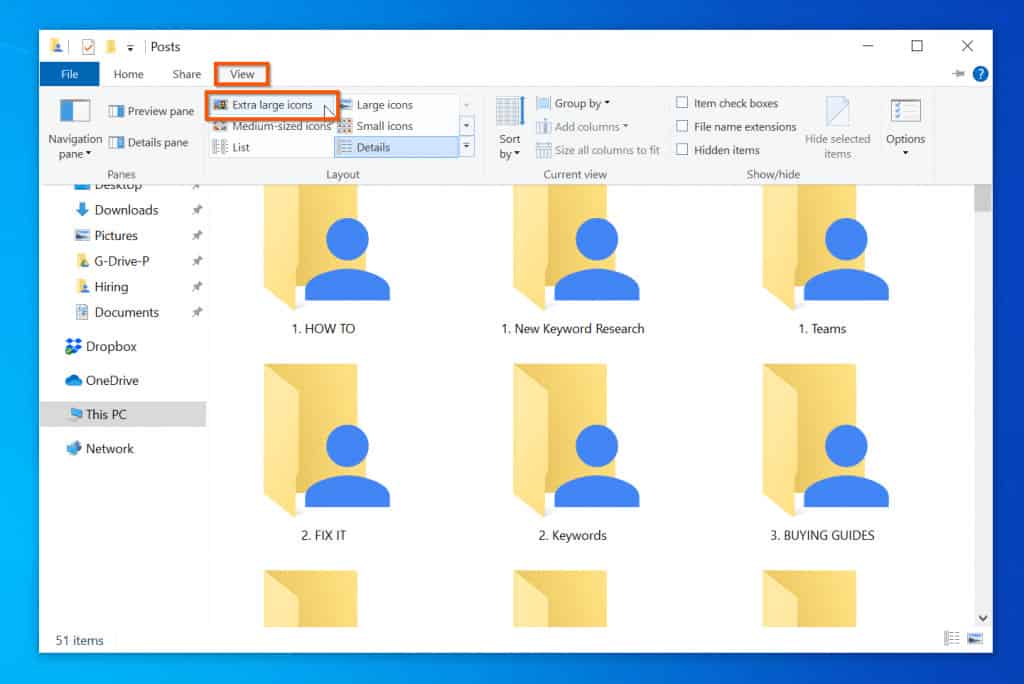
- Viewing Options: The File Explorer offers various viewing modes, including "Details," "Large Icons," "Small Icons," and "List." Each mode provides a different visual representation of files and folders, allowing users to select the view that best suits their needs.
- Sharing and Collaboration: The File Explorer facilitates sharing files with others through email, network drives, or cloud storage services. Users can also collaborate on documents by granting access to specific individuals or groups.
Tips for Efficient File Management
- Create a Consistent Folder Structure: Organizing files into logical folders helps streamline access and retrieval. Consider creating folders based on file types, projects, or dates.
- Utilize Libraries: Libraries provide a centralized location for accessing files from different sources, such as local drives, network drives, and cloud storage.
- Use File Extensions: File extensions provide valuable information about the type of data contained within a file. Understanding these extensions can aid in identifying and opening the correct files.
- Backup Regularly: Regularly backing up important files ensures data safety in case of system crashes or hardware failures.
Troubleshooting Common File Explorer Issues
- File Explorer Not Responding: This issue can be caused by corrupted files, malware, or insufficient system resources. Restarting the computer or running a system scan might resolve the problem.
- Slow File Explorer Performance: Factors like low disk space, excessive background processes, or outdated drivers can lead to sluggish performance. Consider freeing up disk space, closing unnecessary programs, or updating drivers.
- Unable to Access Specific Files or Folders: Permission issues, corrupted files, or malware infections can prevent access to certain files or folders. Use the "Properties" option to check file permissions or run a virus scan.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How can I restore deleted files in the File Explorer?
A: The Recycle Bin acts as a temporary storage location for deleted files. You can access the Recycle Bin through the File Explorer and restore deleted files from there. However, permanently deleted files cannot be recovered using the Recycle Bin.
Q: What is the purpose of the "Quick Access" section in the File Explorer?
A: "Quick Access" displays frequently accessed files and folders, providing quick access to recently opened items. Users can customize the "Quick Access" list by adding or removing folders.
Q: How can I change the default File Explorer view?
A: The "View" tab in the File Explorer ribbon offers various viewing options. Users can select the desired view mode, such as "Details," "Large Icons," or "List," and set it as the default view.
Conclusion
The Windows 10 File Explorer is an essential tool for managing files and folders on your computer. By understanding its features, functionalities, and best practices, users can leverage the File Explorer to optimize file organization, access, and sharing. This comprehensive guide provides a foundation for navigating and utilizing the File Explorer effectively, empowering users to manage their digital assets with efficiency and ease.
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Windows 10 File Explorer: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!