Navigating the UEFI BIOS in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Navigating the UEFI BIOS in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the UEFI BIOS in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the UEFI BIOS in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
![How To Access BIOS Settings/Enter UEFI On Windows 11? Best Guide [2022] - YouTube](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/QmgRGCEquaU/maxresdefault.jpg)
The Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) BIOS is a critical component of your computer’s operating system, offering a gateway to configure hardware settings and system behavior. In Windows 11, accessing the UEFI BIOS is essential for tasks such as:
- Boot Order Management: Prioritizing boot devices, allowing you to select from hard drives, USB drives, or network connections.
- Hardware Configuration: Fine-tuning settings for components like CPU, RAM, storage devices, and network interfaces.
- Security Settings: Configuring security measures like Secure Boot, which helps prevent malicious software from loading at startup.
- Advanced Troubleshooting: Diagnosing and resolving boot issues, hardware conflicts, or system performance problems.
- Overclocking: Enhancing system performance by adjusting CPU and RAM frequencies.
Understanding how to access and navigate the UEFI BIOS in Windows 11 is crucial for maintaining system stability, optimizing performance, and troubleshooting issues. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the process, addressing common scenarios and offering helpful tips.
Accessing the UEFI BIOS in Windows 11
The method for accessing the UEFI BIOS varies slightly depending on the computer manufacturer and model. However, the general steps remain consistent:
- Restart the Computer: Begin by restarting your computer.
-
Press the BIOS Key: As the computer starts, pay close attention to the screen. It will usually display a message indicating the key to press to enter the BIOS setup. Common keys include:
- F2
- F10
- F12
- Delete
- Esc
- Other Function Keys
- Navigate the BIOS Menu: Once inside the BIOS, use the arrow keys, tab key, and Enter key to navigate through the various menus and options. The exact menu structure and options may differ depending on the motherboard manufacturer.
- Make Changes and Save: Carefully review and modify the desired settings. Once you have completed your adjustments, save the changes and exit the BIOS. This is usually achieved by selecting an option like "Save & Exit" or "Exit & Save Changes."
Alternative Methods for Accessing the UEFI BIOS
If the traditional key press method doesn’t work, you can try these alternative approaches:
-
Using the Windows Settings:
- Open the "Settings" app in Windows 11.
- Navigate to "System" > "Recovery."
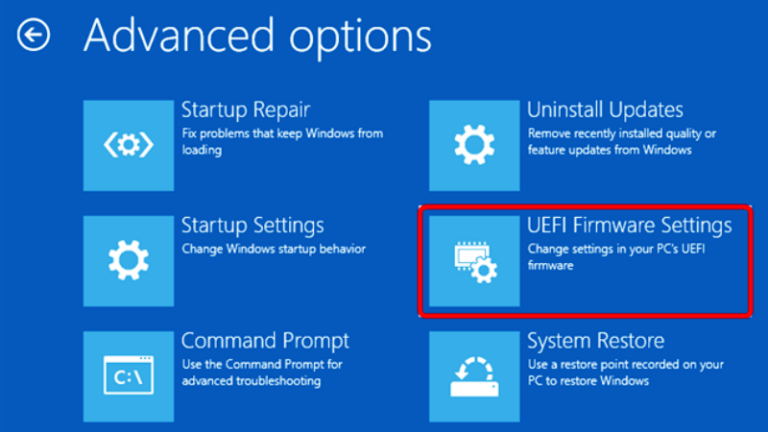
- Under "Advanced startup," click "Restart now."
- In the "Choose an option" screen, select "Troubleshoot" > "Advanced options" > "UEFI Firmware Settings."
-
Using the Boot Menu:
- Restart your computer.
- Press the designated key for accessing the boot menu. Common keys include F8, F11, or Esc.
- Select "UEFI Firmware Settings" or a similar option.
Understanding UEFI BIOS Menus
The UEFI BIOS interface is generally divided into several sections, each dedicated to different aspects of system configuration:
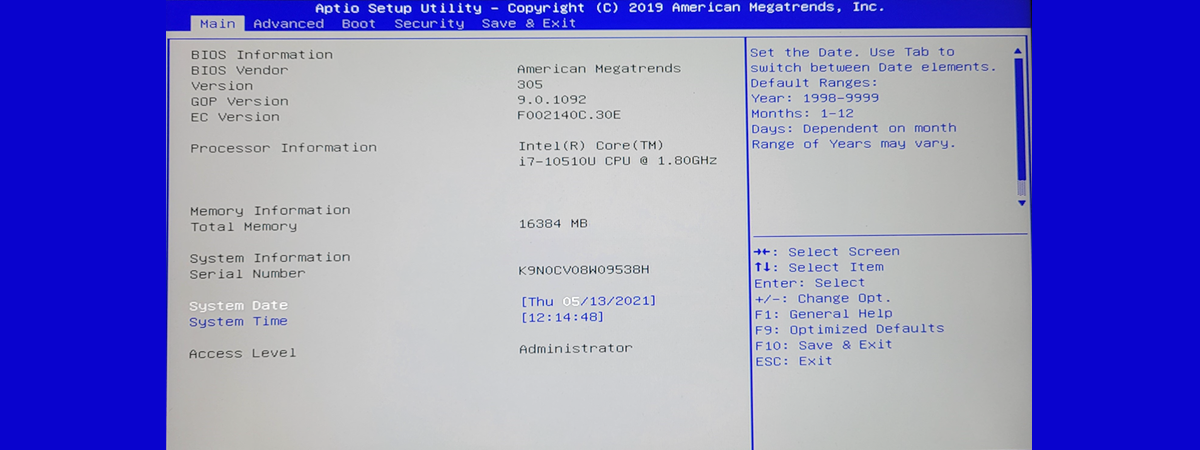
- Main: This section provides an overview of system information, including boot devices, CPU temperature, and memory usage.
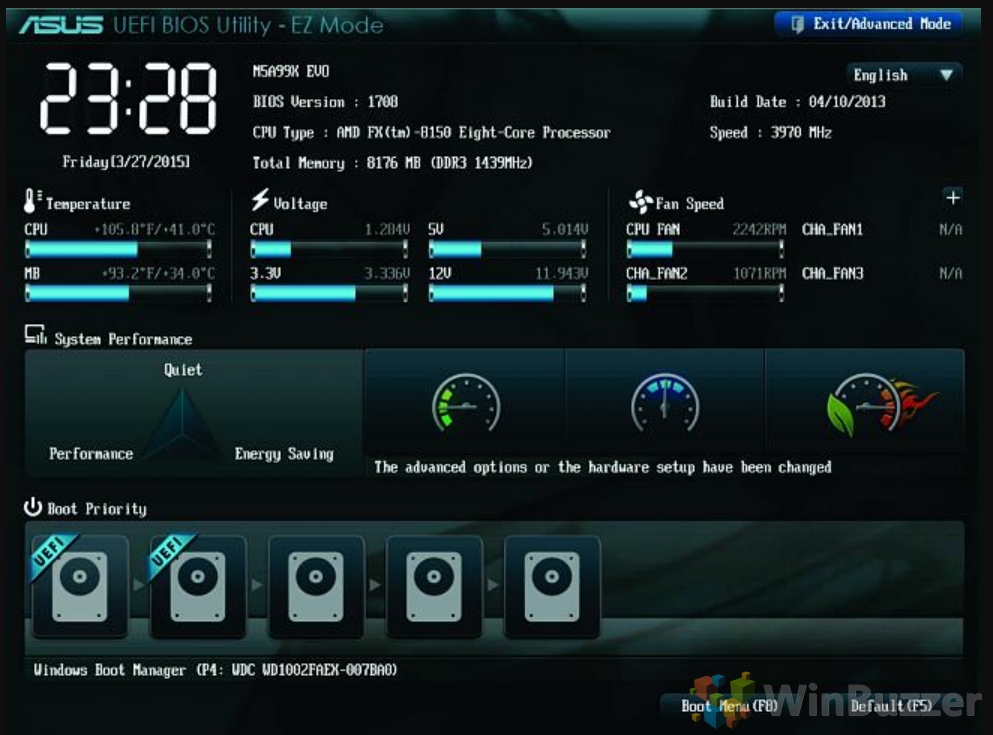
- Boot: This menu allows you to prioritize boot devices, enabling you to boot from a USB drive, CD/DVD, or network connection.
- Advanced: This section contains advanced settings for various components like the CPU, memory, storage devices, and network interfaces.
- Security: This menu allows you to configure security features like Secure Boot, which helps prevent unauthorized software from loading.
- Exit: This section provides options for saving changes and exiting the BIOS.
Tips for Navigating the UEFI BIOS
- Consult Your Motherboard Manual: Refer to the user manual for your specific motherboard for detailed information about the BIOS interface and available settings.
- Use the Help Function: Most UEFI BIOS interfaces offer a help function that provides explanations for specific settings.
- Be Cautious with Changes: Exercise caution when modifying BIOS settings, as incorrect configurations can lead to system instability or boot errors. If you are unsure about a setting, it’s best to leave it at its default value.
- Reset to Defaults: If you encounter issues after making changes, you can usually reset the BIOS settings to their defaults by selecting an option like "Load Defaults" or "Factory Reset."
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is the difference between UEFI BIOS and Legacy BIOS?
A: UEFI BIOS is a modern replacement for the traditional Legacy BIOS. It offers several advantages, including faster boot times, support for larger hard drives, and improved security features.
Q: Can I access the UEFI BIOS if I am running Linux?
A: Yes, you can access the UEFI BIOS in Linux by restarting your computer and pressing the designated BIOS key.
Q: What should I do if I can’t access the UEFI BIOS?
A: If you can’t access the UEFI BIOS using the traditional key press method, try using the alternative methods outlined in this guide. If those methods also fail, consult your computer manufacturer or a qualified technician.
Conclusion
The UEFI BIOS is a powerful tool for managing system settings and troubleshooting issues. By understanding how to access and navigate the BIOS interface, you can optimize your Windows 11 experience, enhance system performance, and ensure a smooth and secure computing environment. Remember to exercise caution when making changes and consult your motherboard manual for detailed information about available settings.



![How to Enter BIOS or UEFI in Windows 11 [5 Easy Steps 2024]](https://10scopes.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/06/how-to-enter-bios-or-uefi-in-windows-11.jpg)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the UEFI BIOS in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!