Navigating the Digital Landscape: A Guide to File Explorer in Windows 10
Related Articles: Navigating the Digital Landscape: A Guide to File Explorer in Windows 10
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Digital Landscape: A Guide to File Explorer in Windows 10. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Digital Landscape: A Guide to File Explorer in Windows 10
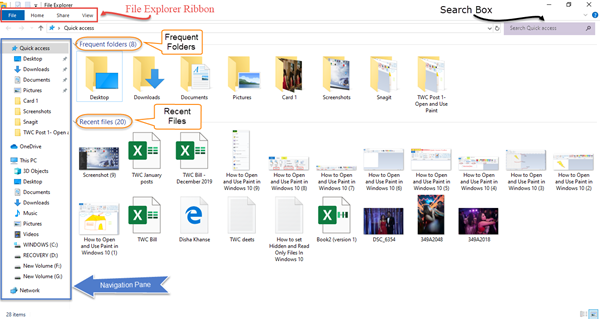
The digital world is a vast and complex ecosystem, filled with data, documents, and applications. To effectively manage this digital landscape, a robust file management system is essential. Windows 10, with its intuitive File Explorer, provides users with a powerful tool for organizing, accessing, and manipulating their digital assets. This article delves into the intricacies of File Explorer, outlining its key features, functionalities, and potential challenges, while providing practical tips and solutions for maximizing its utility.
Understanding the Foundation: The Core Features of File Explorer
File Explorer, formerly known as Windows Explorer, serves as the primary interface for navigating the file system in Windows 10. It allows users to:
- Browse and Access Files and Folders: File Explorer provides a hierarchical view of the file system, enabling users to traverse through drives, folders, and subfolders with ease. This structured approach ensures efficient location and retrieval of specific files.
-
Manage Files and Folders: Beyond simple browsing, File Explorer empowers users to perform essential file management tasks:
- Create, Rename, and Delete Files and Folders: Users can effortlessly create new files and folders, modify their names, and remove them when no longer needed.
- Copy, Move, and Paste: File Explorer facilitates the transfer of files and folders between locations within the system or external storage devices.
- Organize Files with Folders: Folders act as containers for grouping related files, allowing users to structure their data logically and maintain a clear organizational hierarchy.
- Search for Files: The built-in search function within File Explorer enables users to quickly locate specific files based on keywords, file types, or other criteria. This feature significantly reduces time spent searching for files manually.
- View File Properties: File Explorer allows users to access detailed information about individual files, such as file size, creation date, modification date, and file type. This information can be crucial for understanding the nature and purpose of files.
- Share Files: File Explorer integrates with Windows’ sharing functionalities, allowing users to easily share files with other users on the local network or through cloud storage services.
Unveiling the Power: Advanced Features and Customization
While the core functionalities of File Explorer are essential for basic file management, Windows 10 offers a range of advanced features and customization options that enhance its capabilities and tailor it to individual needs.
- Ribbon Interface: The familiar ribbon interface at the top of File Explorer provides quick access to various commands and tools. Users can customize the ribbon by adding or removing tabs and groups to prioritize frequently used functions.
- File History: File History automatically creates backups of files stored in specific locations, safeguarding data against accidental deletion or system crashes. Users can restore previous versions of files or recover lost data through File History.
- File Explorer Options: Users can customize File Explorer’s appearance and behavior through the "Options" settings. This includes options for managing file previews, controlling folder view options, and configuring the behavior of File Explorer’s navigation pane.
- Third-Party File Management Tools: For users seeking more specialized file management capabilities, a wide array of third-party file management tools are available, offering features like advanced file searching, synchronization, and data compression.
Addressing Common Challenges: Troubleshooting and Optimizing File Explorer
While File Explorer is a powerful tool, users may encounter challenges or issues that hinder its functionality. Recognizing and addressing these challenges is crucial for maintaining efficient file management.
- Slow Performance: File Explorer’s performance can be affected by factors like insufficient system resources, fragmented hard drives, or excessive data storage. Optimizing system performance, defragmenting hard drives, or upgrading hardware can improve File Explorer’s responsiveness.
- File Access Errors: Errors related to file access, such as "Access Denied" or "File Not Found," can arise from various causes, including file permissions issues, corrupted files, or software conflicts. Troubleshooting these errors often requires identifying the root cause and implementing appropriate solutions.
- Missing or Corrupted Files: Accidental deletion or corruption of files can lead to data loss. File History, as mentioned earlier, can be a valuable tool for recovering lost files. However, for more complex data recovery scenarios, specialized data recovery software might be required.
- Security Concerns: File Explorer can be a potential target for malware and other threats. It’s essential to practice safe file management habits, such as avoiding opening suspicious attachments, downloading files from untrusted sources, and regularly updating antivirus software.
Exploring the Beyond: Integrating File Explorer with Other Tools and Services
File Explorer’s capabilities extend beyond its core functions. Its integration with other Windows tools and services further enhances its utility:
- Cloud Storage Integration: File Explorer seamlessly integrates with cloud storage services like OneDrive, Google Drive, and Dropbox, allowing users to access, manage, and synchronize files across multiple devices.
- Sharing Files with Other Users: File Explorer allows users to share files with other users on the local network or through email. This feature simplifies collaboration and file exchange.
- Using File Explorer with Command Prompt: Users familiar with the command prompt can leverage its power in conjunction with File Explorer to perform complex file management tasks, including batch operations and scripting.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about File Explorer
Q: How can I customize the appearance of File Explorer?
A: You can customize File Explorer’s appearance through the "Options" settings. This includes changing the folder view options, such as displaying file icons, thumbnails, or detailed information panels. You can also customize the navigation pane, add or remove ribbon tabs, and adjust other visual elements.
Q: How can I recover deleted files?
A: If you have enabled File History, you can access previous versions of files and potentially recover deleted data. Alternatively, you can use specialized data recovery software for more complex data recovery scenarios.
Q: How can I troubleshoot file access errors?
A: File access errors can be caused by various factors. Check file permissions, ensure the file is not corrupted, and investigate potential software conflicts. You can also consult online resources or seek assistance from Microsoft support for specific error messages.
Q: How can I improve File Explorer’s performance?
A: Optimize your system’s performance by defragmenting hard drives, managing system resources, and ensuring sufficient storage space. You can also disable unnecessary background programs and processes that might consume resources.
Q: How can I protect my files from malware?
A: Practice safe file management habits by avoiding suspicious attachments, downloading files from untrusted sources, and regularly updating antivirus software. You can also consider using a firewall and enabling Windows Defender’s real-time protection.
Tips for Maximizing File Explorer’s Utility
- Organize Your Files: Create a logical folder structure to categorize and organize your files efficiently.
- Use Search Effectively: Leverage File Explorer’s search function to quickly locate specific files based on keywords, file types, or other criteria.
- Take Advantage of File History: Enable File History to automatically create backups of your files, safeguarding against data loss.
- Explore Advanced Features: Experiment with File Explorer’s advanced features, such as customization options, cloud storage integration, and sharing functionalities.
- Stay Updated: Keep your Windows operating system and antivirus software up to date to ensure optimal performance and security.
Conclusion: Mastering the Digital Landscape with File Explorer
File Explorer serves as the cornerstone of file management in Windows 10, providing users with a comprehensive tool for organizing, accessing, and manipulating their digital assets. By understanding its core features, exploring advanced functionalities, and addressing potential challenges, users can effectively manage their digital landscape and unlock the full potential of File Explorer. From simple file organization to advanced data management, File Explorer empowers users to navigate the digital world with confidence and efficiency.

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Digital Landscape: A Guide to File Explorer in Windows 10. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!