Navigating the Digital Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Windows File Explorer
Related Articles: Navigating the Digital Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Windows File Explorer
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Digital Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Windows File Explorer. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Digital Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Windows File Explorer
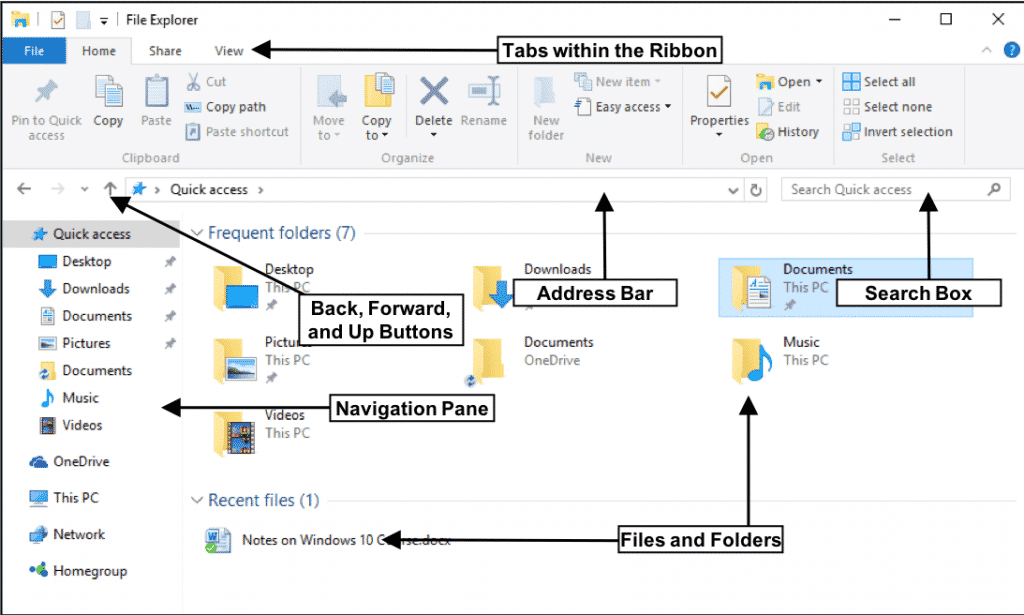
Windows File Explorer, often referred to simply as "Explorer," serves as the primary interface for interacting with files and folders on a Windows computer. Its importance cannot be overstated, as it acts as the central hub for managing data, accessing applications, and navigating the digital landscape. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of Windows File Explorer, exploring its features, functionalities, and troubleshooting tips to empower users to effectively manage their digital assets.
Understanding the Basics
Windows File Explorer is a graphical user interface (GUI) that presents a hierarchical view of the file system. It allows users to:
- Browse and navigate files and folders: Easily locate and access files and folders within the computer’s storage.
- Create, delete, and rename files and folders: Manage the organization and structure of files and folders.
- Copy, move, and delete files: Transfer files between locations and manage storage space.
- Open and run applications: Launch applications stored on the computer.
- Search for files and folders: Quickly locate specific files or folders using keywords or criteria.
- View file properties: Access information about a file, such as size, date modified, and file type.
- Customize the interface: Adjust the display of files and folders, such as sorting options and view modes.
Exploring Key Features
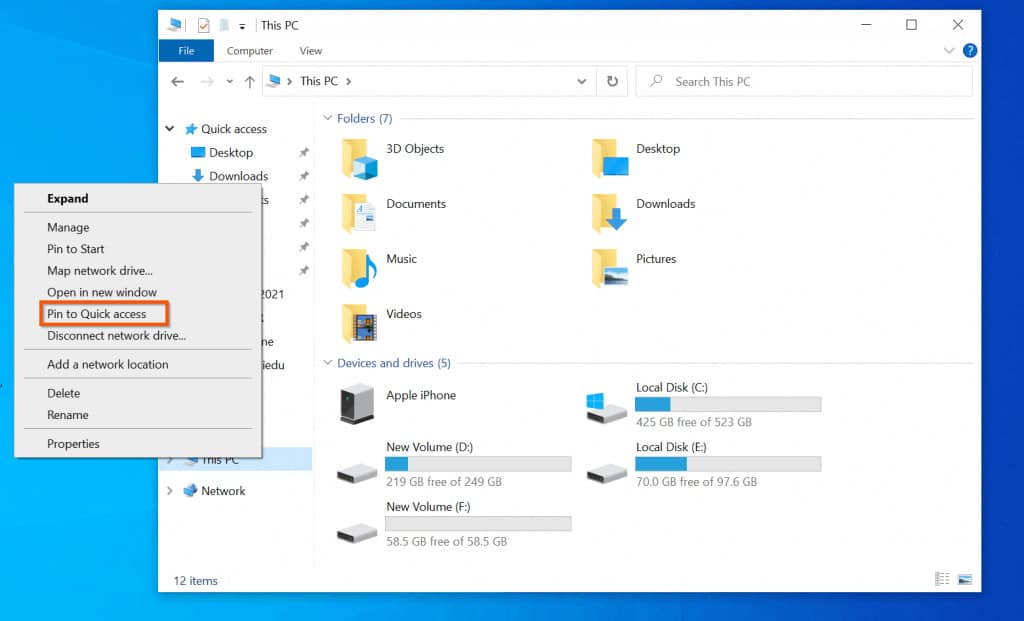
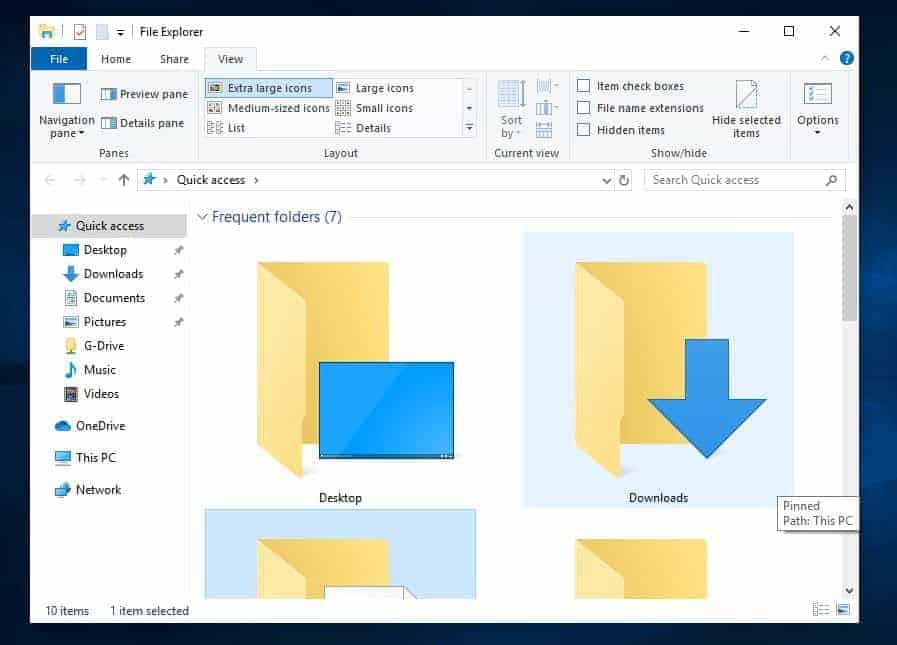
1. Navigation Pane: The left side of File Explorer displays a navigation pane that provides quick access to frequently used locations. These include:
- Quick access: A list of recently accessed files and folders.
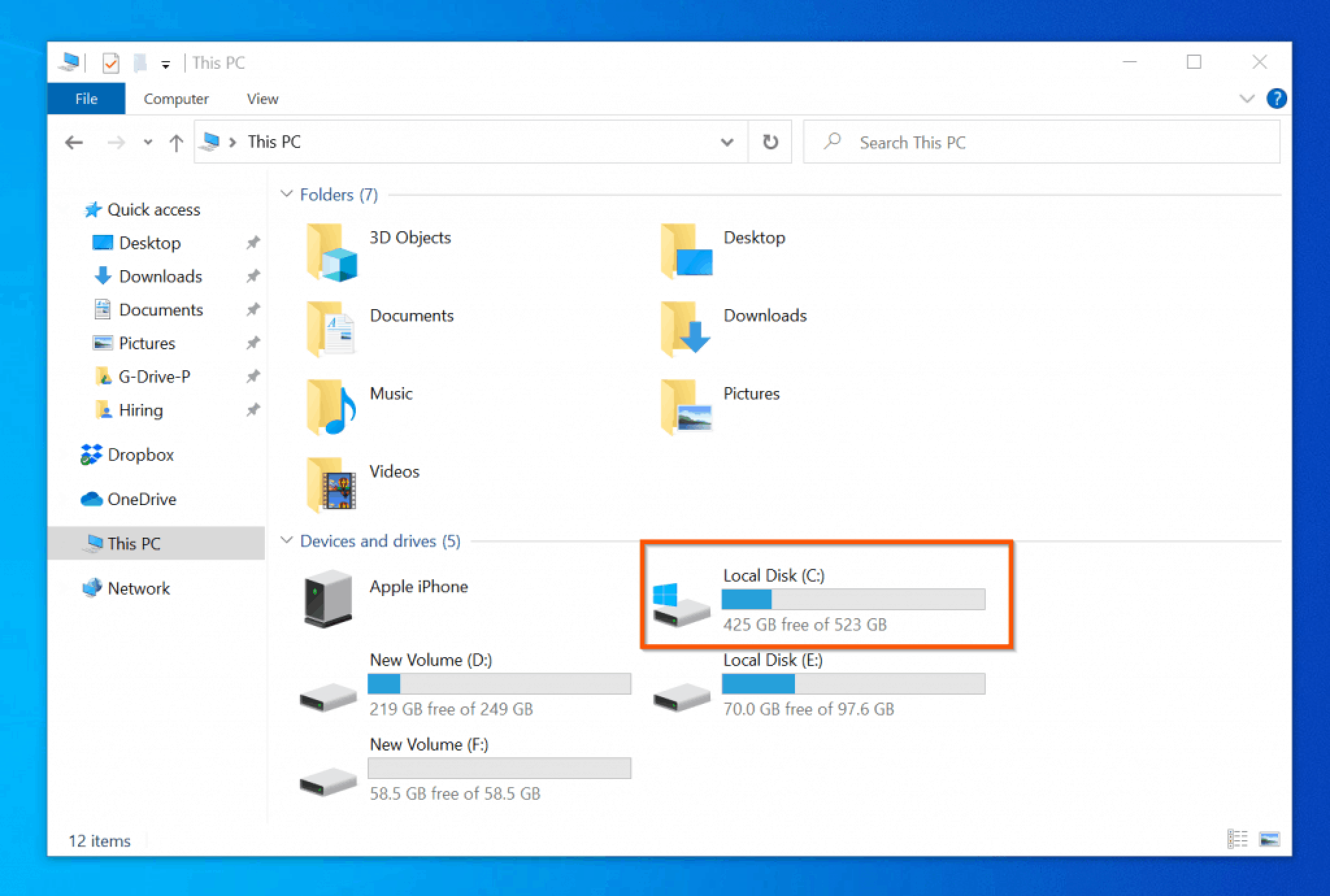
- This PC: A summary of all connected drives, including hard drives, optical drives, and network drives.
- Network: A list of computers and devices connected to the network.
- Favorites: A customizable list of frequently accessed locations.
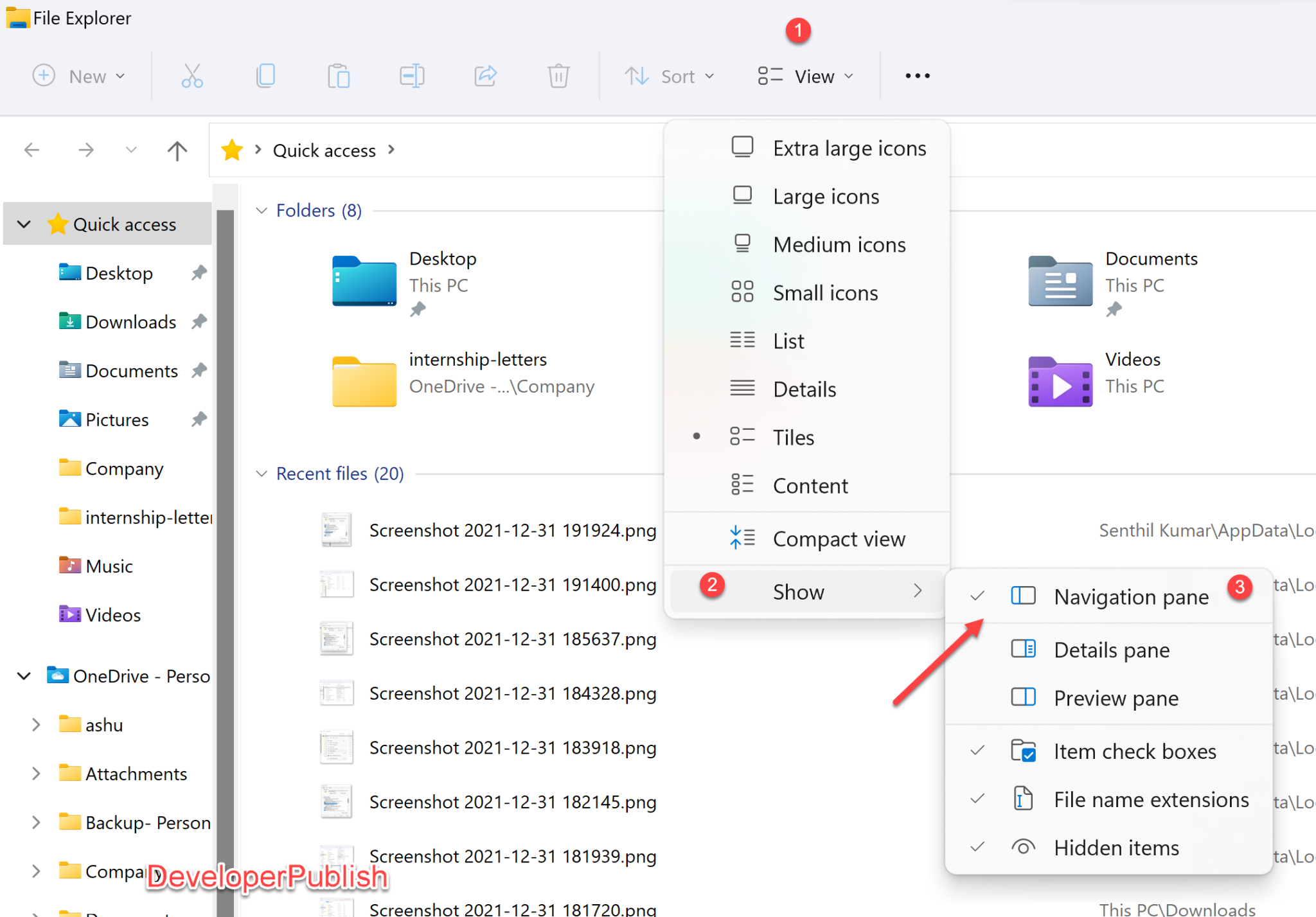
2. File List: The main area of File Explorer displays the contents of the selected location. Users can customize the view by:
- Changing the view: Choose from different view modes, such as icons, list, details, and thumbnails.
- Sorting files: Arrange files by name, size, date modified, or other criteria.
- Filtering files: Narrow down the list by searching for specific files or folders.
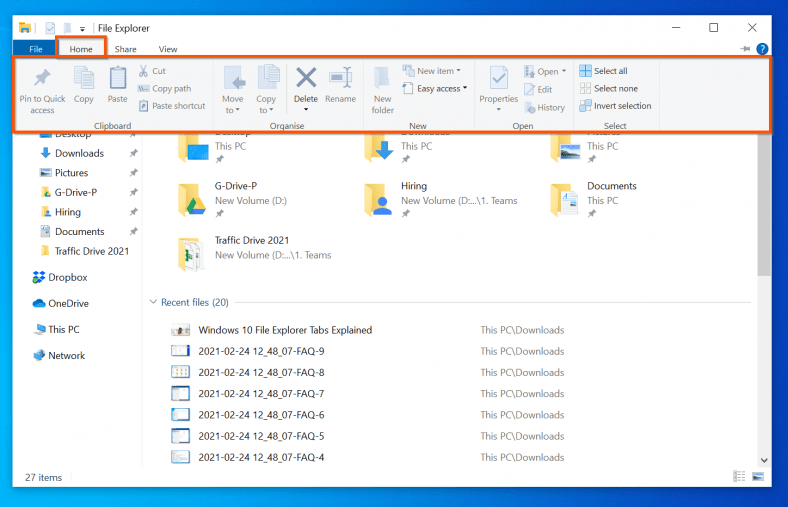
3. Ribbon: The top of File Explorer features a ribbon that provides access to various commands and features. This includes:
- Home tab: Contains common commands for managing files and folders, such as copy, move, delete, rename, and share.
- Share tab: Provides options for sharing files and folders with others.
- View tab: Allows customization of the file list view, including changing the view mode, sorting options, and displaying hidden files.
- File tab: Offers options for creating new files and folders, managing libraries, and accessing system settings.
4. Search Bar: The search bar located in the top-right corner allows users to quickly find specific files or folders by entering keywords or using advanced search filters.
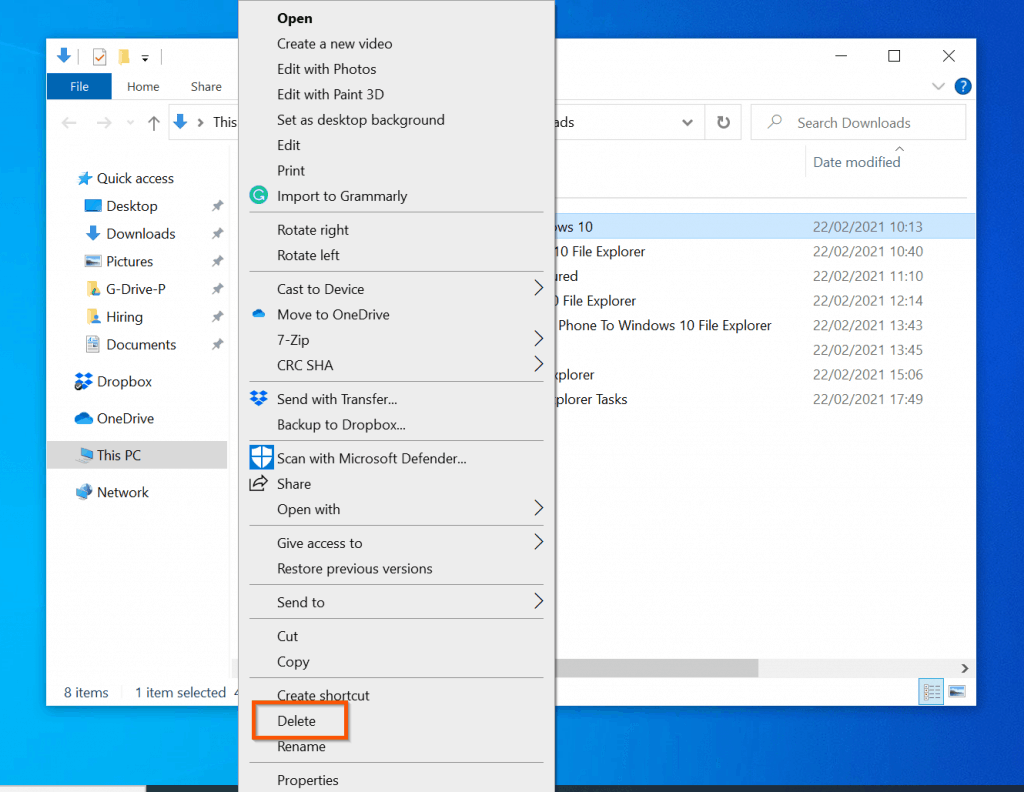
5. File Properties: By right-clicking a file or folder, users can access its properties. This provides information such as:
- General: File name, location, size, date modified, and file type.
- Details: Additional information about the file, depending on its type.
- Security: Permissions and access controls for the file or folder.
- Previous Versions: Access to previous versions of the file, if available.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
While Windows File Explorer is a robust and reliable tool, users may encounter occasional issues. Here are some common problems and their solutions:
1. File Explorer Not Responding:
- Restart Windows Explorer: Press Ctrl+Shift+Esc to open Task Manager, locate "Windows Explorer" in the "Processes" tab, right-click and select "Restart."
- Check for Malware: Run a full system scan with a reputable antivirus program.
- Disable Add-ins: In File Explorer, click "File" > "Options" > "Add-ins" and disable any suspicious add-ins.
- Repair Windows: Use the "System File Checker" tool by typing "sfc /scannow" in the Command Prompt.
2. Slow File Explorer Performance:
- Disable Background Programs: Close unnecessary programs and disable background applications that may be consuming resources.
- Optimize Disk: Run a disk cleanup and defragmentation to free up space and improve performance.
- Disable Indexing: If indexing is causing slowdowns, disable it by searching for "Indexing Options" in the Start menu.
- Upgrade Hardware: Consider upgrading to a faster processor, more RAM, or a faster hard drive for improved performance.
3. Files Missing or Not Visible:
- Check Hidden Files: In File Explorer, click "View" > "Hidden items" to display hidden files and folders.
- Restore Previous Versions: If files were deleted accidentally, check for previous versions by right-clicking the folder and selecting "Properties" > "Previous Versions."
- Use Data Recovery Software: If files are lost due to data corruption or accidental deletion, use a data recovery software to recover the lost data.
4. File Explorer Crashing:
- Update Windows: Ensure that your operating system is up to date with the latest updates.
- Update Drivers: Update graphics drivers and other hardware drivers to ensure compatibility.
- Run a System Scan: Use the "System File Checker" tool to scan for and repair corrupted system files.
- Reinstall Windows: If all else fails, consider reinstalling Windows to restore the system to a clean state.
FAQs about Windows File Explorer
Q: How do I create a new folder in File Explorer?
A: Navigate to the desired location in File Explorer, click the "New folder" button in the ribbon, or right-click in the file list and select "New" > "Folder."
Q: How do I copy and paste files in File Explorer?
A: Select the files or folders you want to copy, right-click and select "Copy," navigate to the destination location, right-click, and select "Paste."
Q: How do I share files and folders in File Explorer?
A: Select the files or folders you want to share, click the "Share" tab in the ribbon, and select the desired sharing options.
Q: How do I view hidden files and folders in File Explorer?
A: Click the "View" tab in the ribbon and select "Hidden items."
Q: How do I change the view mode in File Explorer?
A: Click the "View" tab in the ribbon and select the desired view mode from the "View modes" group.
Tips for Effective File Management
- Organize files into folders: Create a hierarchical folder structure to keep files organized and easily accessible.
- Use descriptive file names: Name files clearly and concisely to easily identify their content.
- Use search filters: Utilize the search bar and advanced search filters to quickly locate specific files.
- Backup important files: Regularly back up important files to prevent data loss in case of hardware failure or accidental deletion.
- Clean up storage space: Delete unnecessary files and folders to free up disk space and improve performance.
- Utilize cloud storage: Consider using cloud storage services to store files online and access them from multiple devices.
Conclusion
Windows File Explorer is an essential tool for managing files and folders on a Windows computer. By understanding its features, functionalities, and troubleshooting tips, users can effectively navigate their digital landscape, organize their data, and optimize their file management experience. From basic browsing and navigation to advanced file management and sharing, Windows File Explorer empowers users to take control of their digital assets and efficiently manage their computing environment.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Digital Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Windows File Explorer. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!