Navigating the Digital Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to File Explorer
Related Articles: Navigating the Digital Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to File Explorer
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Digital Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to File Explorer. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Digital Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to File Explorer

The File Explorer, a ubiquitous tool in Windows operating systems, serves as the primary interface for accessing, managing, and organizing files and folders. Its importance lies in its ability to streamline digital workflows, ensuring efficient data management and retrieval. This article delves into the intricacies of the File Explorer, providing a comprehensive guide to understanding its features, navigating its interface, and utilizing its capabilities to enhance productivity.
Understanding the Basics: A Primer on File Explorer
The File Explorer, previously known as Windows Explorer, is the graphical user interface (GUI) that enables users to interact with the file system of a Windows computer. It provides a visual representation of the hierarchical structure of files and folders, allowing users to browse, open, create, modify, delete, and move them.
Navigating the File Explorer Interface
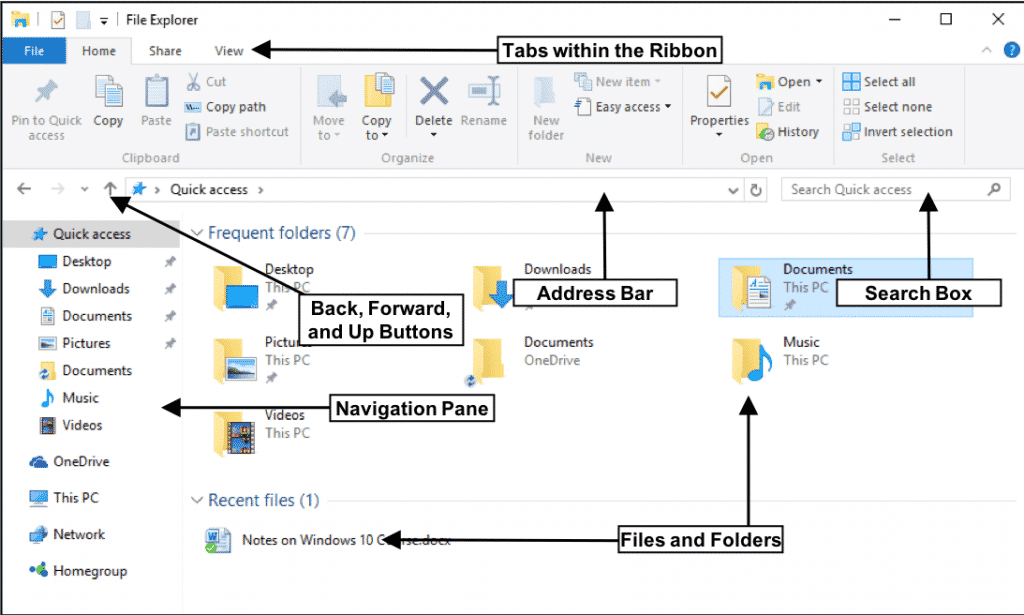
The File Explorer window is divided into distinct sections, each serving a specific purpose:
- Navigation Pane: Located on the left side, this pane displays the hierarchical structure of the file system, allowing users to navigate through drives, libraries, and folders.
- Address Bar: Situated above the navigation pane, this bar displays the current location in the file system, enabling users to quickly access specific folders.
- Ribbon: Positioned at the top of the window, the ribbon houses various commands and tools organized into tabs, such as "Home," "Share," and "View."
- File List: Occupying the main area of the window, the file list displays the contents of the currently selected folder.
- Details Pane: Located on the right side, this pane provides additional information about selected files, such as size, type, date modified, and attributes.
Essential Functions: Utilizing File Explorer for Optimal Data Management
File Explorer offers a wide array of functions designed to facilitate efficient data management:
- File and Folder Creation: Users can easily create new folders and files directly within the File Explorer.
- File and Folder Management: The File Explorer allows users to move, copy, rename, delete, and organize files and folders.
- Search Functionality: The integrated search bar enables users to quickly locate specific files or folders based on keywords or criteria.
- Sorting and Filtering: Files and folders can be sorted alphabetically, by size, date modified, or other criteria. Filtering allows users to display only specific file types or those meeting certain conditions.
- Sharing and Collaboration: The File Explorer enables users to share files and folders with others, either locally or remotely.
- File Properties: Accessing the properties of a file or folder provides detailed information about its attributes, including size, type, location, and permissions.
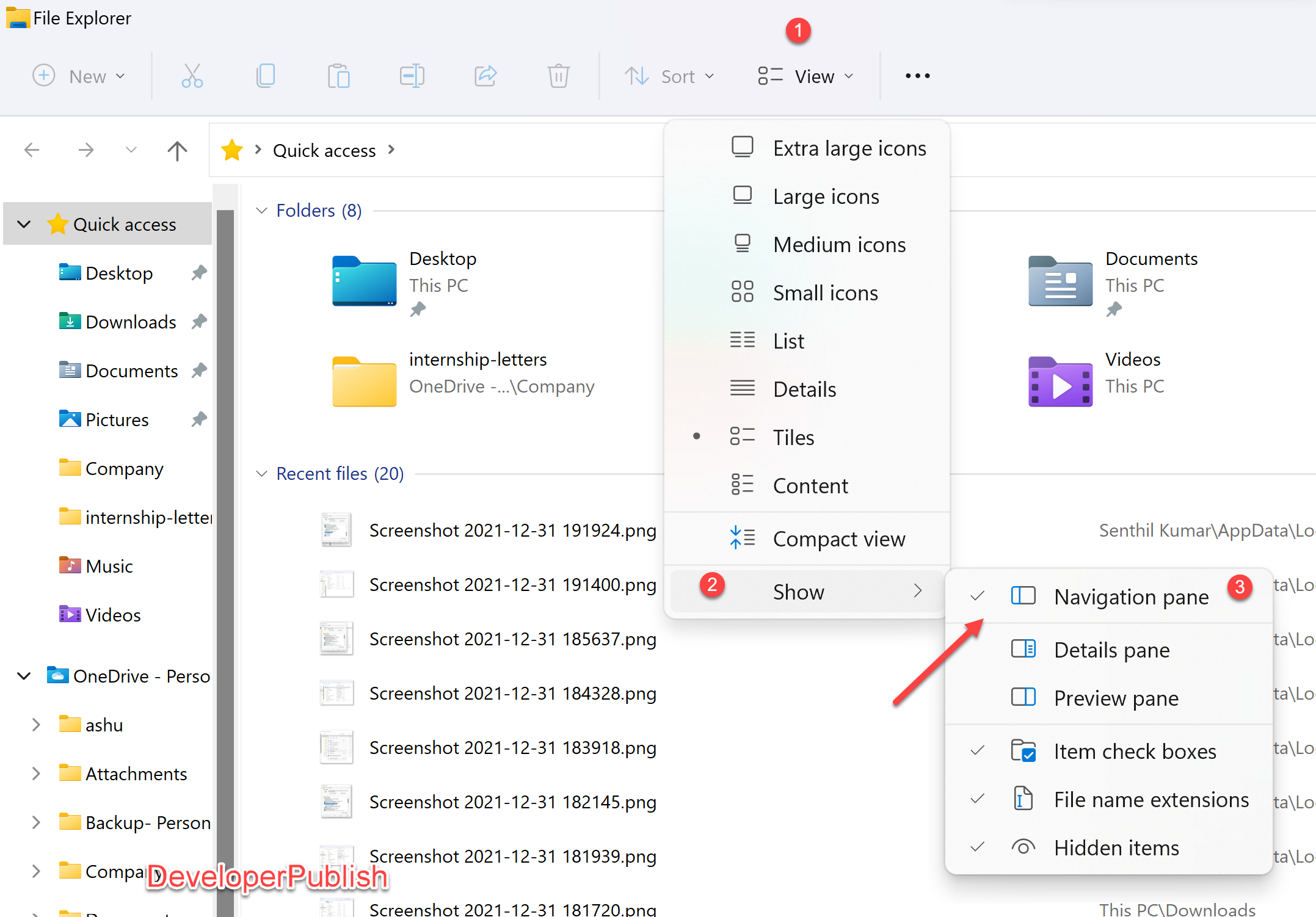
- Customization: Users can customize the File Explorer’s appearance and behavior to suit their preferences, including changing the layout, background, and display options.
Addressing Common Challenges: Troubleshooting and Optimizing File Explorer
Despite its intuitive design, users may encounter challenges while using File Explorer. Understanding common issues and their solutions can significantly enhance the user experience:
- Slow File Explorer Performance: Factors such as excessive file fragmentation, insufficient RAM, or background processes can slow down File Explorer. Disk cleanup, defragmentation, and optimizing system resources can improve performance.
- File Explorer Crashes: Corrupted system files, incompatible software, or outdated drivers can lead to File Explorer crashes. Running system file checks, updating drivers, and ensuring software compatibility can resolve these issues.
- Missing or Hidden Files: File Explorer may not display certain files or folders, either by design or due to system settings. Configuring file explorer settings and enabling hidden files can address this issue.
- Unable to Access Files: File access permissions, corrupted files, or system errors can prevent users from accessing files. Checking permissions, running system checks, and utilizing recovery tools can resolve these issues.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced File Explorer Features and Techniques
The File Explorer offers several advanced features and techniques for experienced users:
- Command Prompt Integration: The File Explorer can be used to access the command prompt, enabling users to execute commands and scripts for advanced file management tasks.
- Scripting and Automation: File Explorer can be integrated with scripting languages such as PowerShell, allowing users to automate repetitive tasks and create custom workflows.
- Third-Party File Explorer Enhancements: Various third-party file explorer applications offer enhanced features and functionalities, such as tabbed browsing, file syncing, and cloud storage integration.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: How do I open a specific folder in File Explorer?
A: You can open a specific folder in File Explorer by typing its path in the address bar or by navigating through the file system using the navigation pane.
Q: How do I create a shortcut to a folder or file?
A: Right-click on the desired folder or file, select "Create shortcut," and choose a location to save the shortcut.
Q: How do I change the default view of File Explorer?
A: You can change the default view of File Explorer by clicking the "View" tab in the ribbon and selecting the desired layout, such as "List," "Details," or "Tiles."
Q: How do I search for a specific file within File Explorer?
A: You can search for a specific file by typing the file name or relevant keywords in the search bar at the top of the File Explorer window.
Q: How do I recover deleted files using File Explorer?
A: While File Explorer itself does not have a built-in file recovery feature, you can use third-party recovery software to attempt to recover deleted files.
Tips for Effective File Explorer Usage
- Utilize keyboard shortcuts: Shortcuts like Ctrl+C (copy), Ctrl+V (paste), Ctrl+X (cut), and Ctrl+Z (undo) can significantly speed up file management tasks.
- Create custom folders: Organize files into logical folders based on their type, purpose, or project.
- Use the search bar effectively: Utilize advanced search operators, such as quotation marks for exact matches and asterisks for wildcards, to refine search results.
- Customize the File Explorer layout: Adjust the view settings, such as showing hidden files or changing the file list layout, to optimize your workflow.
- Explore third-party file explorer enhancements: Consider using third-party file explorer applications to enhance functionality and customize the user experience.
Conclusion
The File Explorer is an indispensable tool for navigating the digital landscape, providing a user-friendly interface for managing files and folders. By understanding its features, utilizing its functionalities, and addressing common challenges, users can enhance their productivity and streamline their digital workflows. As technology continues to evolve, the File Explorer will undoubtedly adapt and expand its capabilities, further simplifying data management and empowering users to navigate the ever-growing digital world.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Digital Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to File Explorer. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
