Navigating the Digital Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Desktop File Explorer
Related Articles: Navigating the Digital Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Desktop File Explorer
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Digital Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Desktop File Explorer. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Digital Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Desktop File Explorer
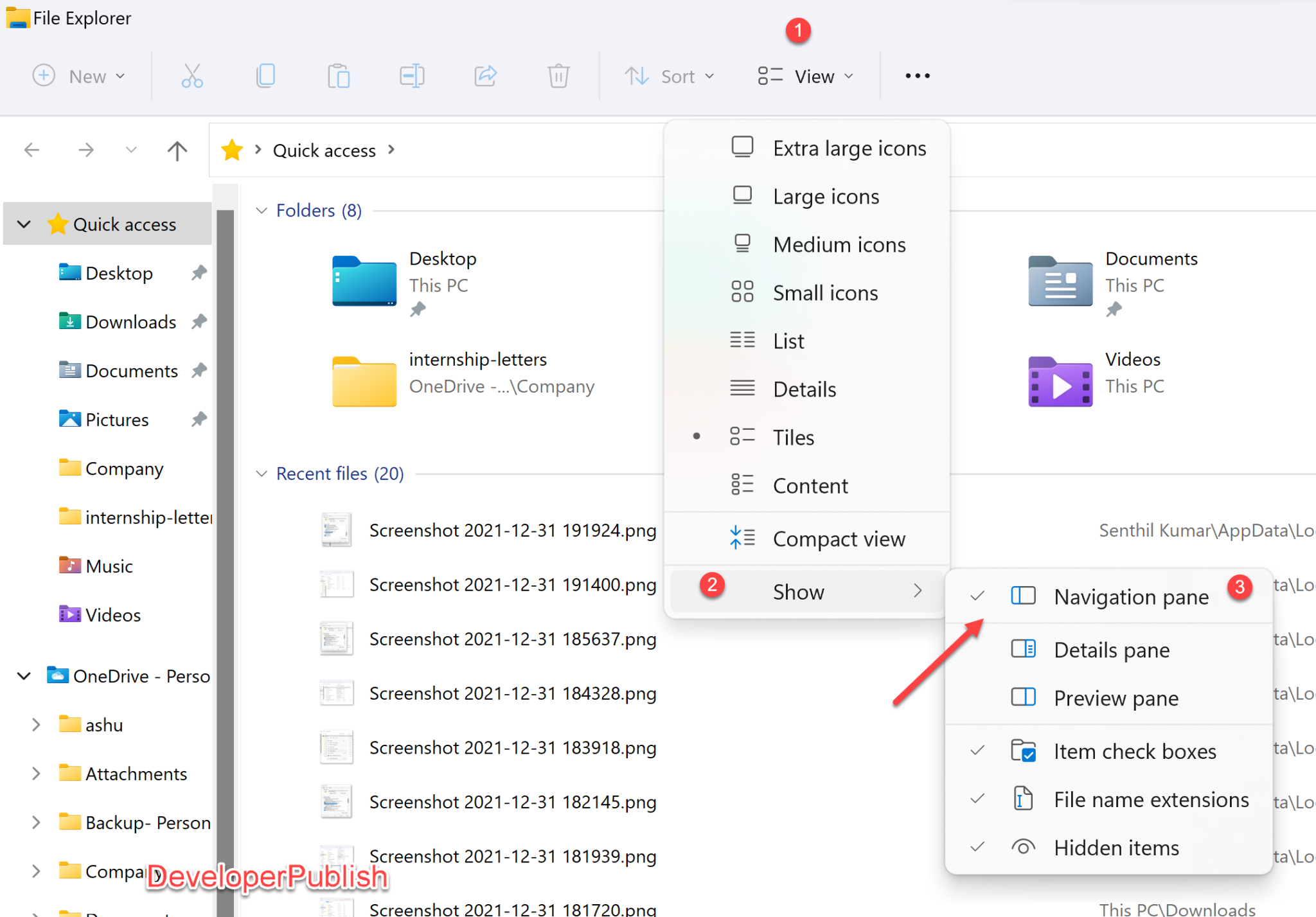
The desktop file explorer, a ubiquitous tool in the modern digital landscape, serves as the central hub for accessing, organizing, and managing files on a computer. Its importance lies in its ability to facilitate seamless interaction with data, making it an indispensable component of any computing experience. This article provides a comprehensive guide to understanding and effectively utilizing desktop file explorer, encompassing its functionalities, troubleshooting tips, and relevant FAQs.
Understanding the Fundamentals of File Explorer
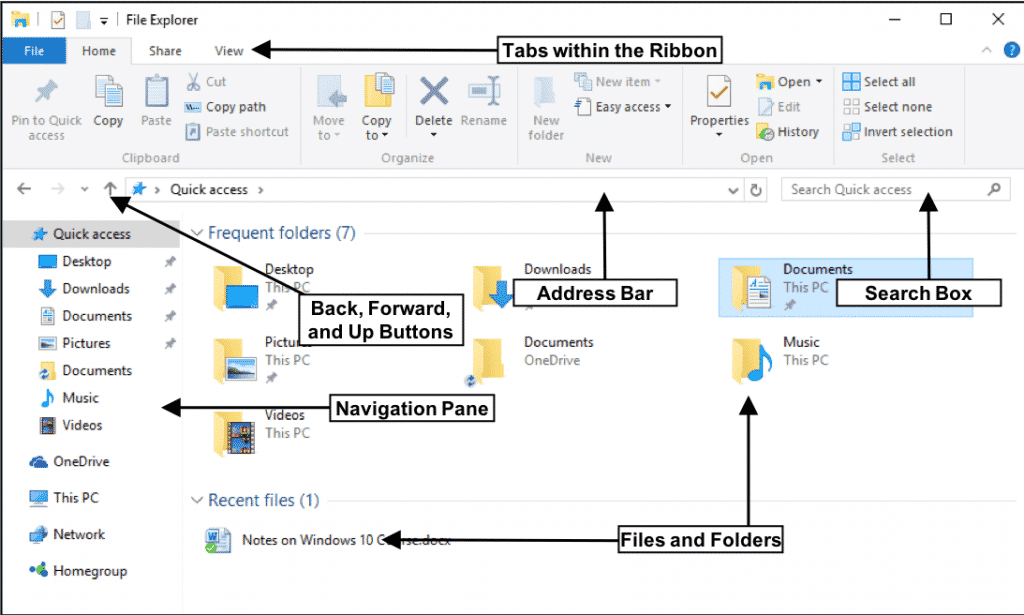
File explorer, often referred to as "My Computer" or "This PC" in various operating systems, provides a visual representation of the hierarchical structure of files and folders on a computer. This hierarchical structure, known as a tree structure, allows for efficient organization and retrieval of data.
Key Features of File Explorer
-
Navigation: File explorer facilitates navigation through the file system, enabling users to traverse different directories, folders, and subfolders. This is achieved through the use of a tree view, where folders are displayed as branches and files as leaves.
-
File Management: Users can perform essential file management tasks within file explorer, including:
- Creating and deleting folders: This allows for organization and categorization of files.
- Copying and moving files: Enables efficient data transfer between different locations.
- Renaming files: Provides the ability to change file names for clarity and organization.
- Searching for files: Facilitates quick and efficient retrieval of specific files based on name, content, or other criteria.
-
File Properties: File explorer displays various file properties, such as file size, type, date modified, and location. This information is useful for understanding and managing files effectively.
-
Viewing Options: Users can customize the way files are displayed in file explorer, including:
- List view: Displays files in a list format, providing detailed information about each file.
- Details view: Offers a more comprehensive view, displaying various file properties.
- Icon view: Presents files as icons, providing a visual representation of their contents.
- Thumbnails view: Displays images and other media files as thumbnails for quick preview.
-
Context Menus: Right-clicking on a file or folder in file explorer reveals a context menu offering a range of actions specific to the selected item. These actions can include opening, editing, deleting, copying, moving, or sharing the selected file or folder.
Troubleshooting Common File Explorer Issues
While file explorer is generally a reliable tool, users may occasionally encounter issues that hinder its functionality. Here are some common problems and their solutions:
-
File Explorer Not Responding: This issue can be caused by a variety of factors, including corrupted files, insufficient memory, or conflicting programs.
- Solution: Restarting the computer often resolves the issue. If the problem persists, try closing other programs, running a system scan, or updating the operating system.
-
File Explorer Opening Slowly: A slow file explorer can be attributed to excessive background processes, a large number of files, or a fragmented hard drive.
- Solution: Identify and close unnecessary background processes, run a disk cleanup utility to remove temporary files, and defragment the hard drive to improve performance.
-
Files Not Displaying Correctly: Incorrect file associations or corrupted system files can cause files to appear as blank or with incorrect icons.
- Solution: Check file associations and ensure that the correct program is associated with each file type. Run a system file checker to repair any corrupted system files.
-
File Explorer Crashes: Frequent crashes may indicate a software conflict or a corrupted file explorer.
- Solution: Try reinstalling the file explorer or the operating system. If the issue persists, contact technical support for assistance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: How can I create a new folder in File Explorer?
A: Navigate to the desired location where you want to create the folder. Right-click within the empty space and select "New" followed by "Folder." Alternatively, you can use the keyboard shortcut "Ctrl+Shift+N" to create a new folder.
Q: How do I find a specific file in File Explorer?
A: In the search bar at the top of the File Explorer window, type the name or part of the name of the file you are looking for. You can also refine your search by using keywords, file types, or dates.
Q: How do I change the default view in File Explorer?
A: In the "View" tab, click on the "Layout" drop-down menu to choose from different view options, such as "List," "Details," "Icon," or "Thumbnails."
Q: How do I restore the File Explorer to its default settings?
A: In the "View" tab, click on the "Reset Folders" button. This will reset the File Explorer to its default settings, including layout, view options, and other preferences.
Q: What is the difference between "Copy" and "Move" in File Explorer?
A: "Copy" creates a duplicate of the selected file or folder, leaving the original intact. "Move" transfers the selected file or folder to a new location, removing it from its original location.
Tips for Maximizing File Explorer Efficiency
-
Use Keyboard Shortcuts: Familiarize yourself with keyboard shortcuts for common file management tasks, such as "Ctrl+C" for copy, "Ctrl+V" for paste, "Ctrl+X" for cut, and "Delete" for deletion.
-
Customize the Ribbon: The ribbon at the top of File Explorer offers various options and commands. You can customize the ribbon by adding or removing tabs and commands to suit your specific needs.
-
Use Search Filters: Utilize search filters to narrow down search results based on file type, size, date modified, or other criteria.
-
Pin Important Folders: Pin frequently accessed folders to the Quick Access section in File Explorer for easy access.
-
Utilize the File Explorer History: File Explorer keeps a history of recently accessed files and folders. You can access this history by clicking on the "Quick Access" section or by using the "Back" and "Forward" buttons.
Conclusion
The desktop file explorer is an essential tool for managing files and navigating the digital landscape. Understanding its features, functionalities, and troubleshooting techniques empowers users to effectively interact with their data, ensuring efficient organization, retrieval, and management. By embracing the tips and best practices outlined in this guide, users can maximize their productivity and leverage the full potential of this versatile tool.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Digital Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Desktop File Explorer. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!