Navigating High CPU Utilization in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Navigating High CPU Utilization in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating High CPU Utilization in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating High CPU Utilization in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
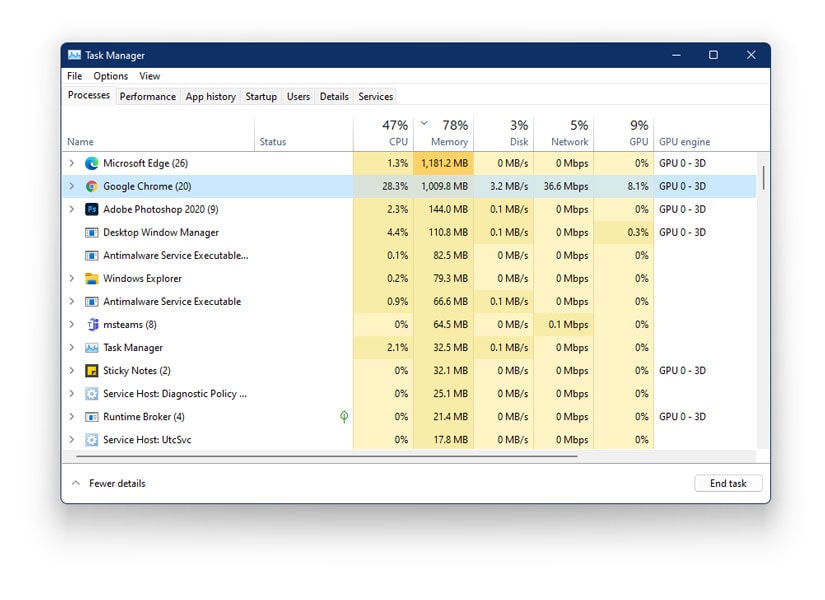
High CPU utilization in Windows 11 can manifest as sluggish performance, system freezes, application crashes, and overall frustration. Understanding the root cause and implementing appropriate solutions is crucial for restoring optimal system responsiveness. This guide provides a comprehensive approach to diagnosing and resolving high CPU usage issues in Windows 11.
Understanding the Problem:
The Central Processing Unit (CPU) acts as the brain of your computer, executing instructions and processing data. When the CPU operates at 100% utilization, it indicates that it is fully occupied and unable to handle additional tasks efficiently. This can arise from various factors, including:
- Resource-Intensive Applications: Programs like video editing software, gaming applications, and complex simulations demand significant processing power, potentially leading to high CPU utilization.
- Malware or Viruses: Malicious software can consume system resources, including CPU cycles, for nefarious purposes, impacting overall system performance.
- Background Processes: Numerous applications and services run in the background, consuming a portion of CPU resources. These can include system updates, antivirus scans, and cloud syncing services.
- Hardware Issues: Faulty hardware components, such as a failing hard drive or overheating CPU, can trigger high CPU utilization.
- Driver Conflicts: Incompatible or outdated device drivers can cause system instability and lead to excessive CPU usage.
- System Errors: Corrupted system files or registry entries can disrupt normal system operations, resulting in high CPU utilization.
Troubleshooting Steps:
Addressing high CPU utilization requires a systematic approach, starting with simple solutions and progressing to more advanced troubleshooting techniques.
1. Identify the Culprit:
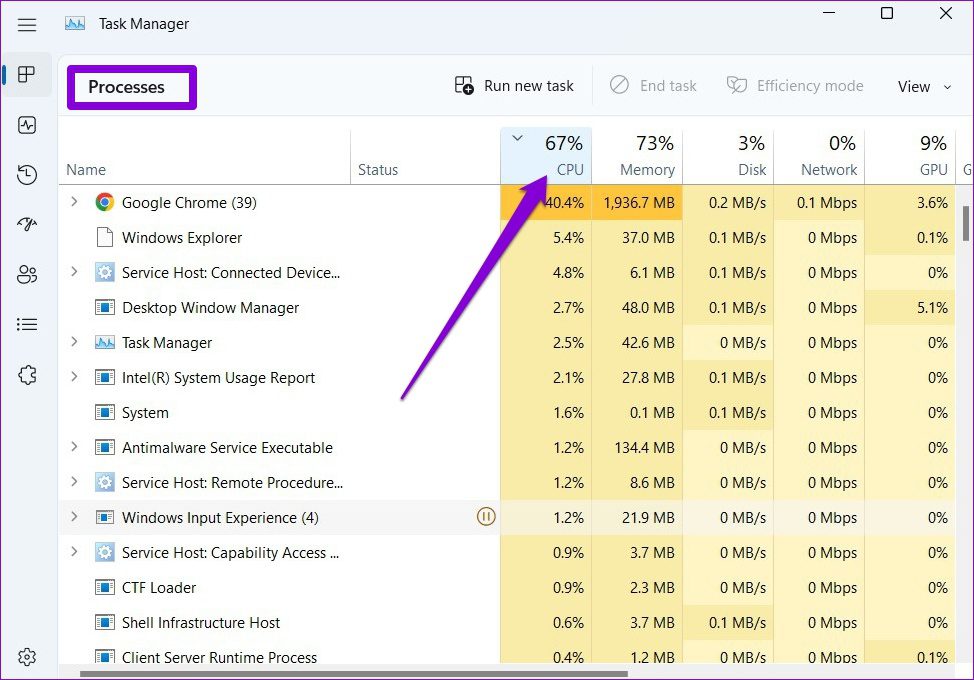
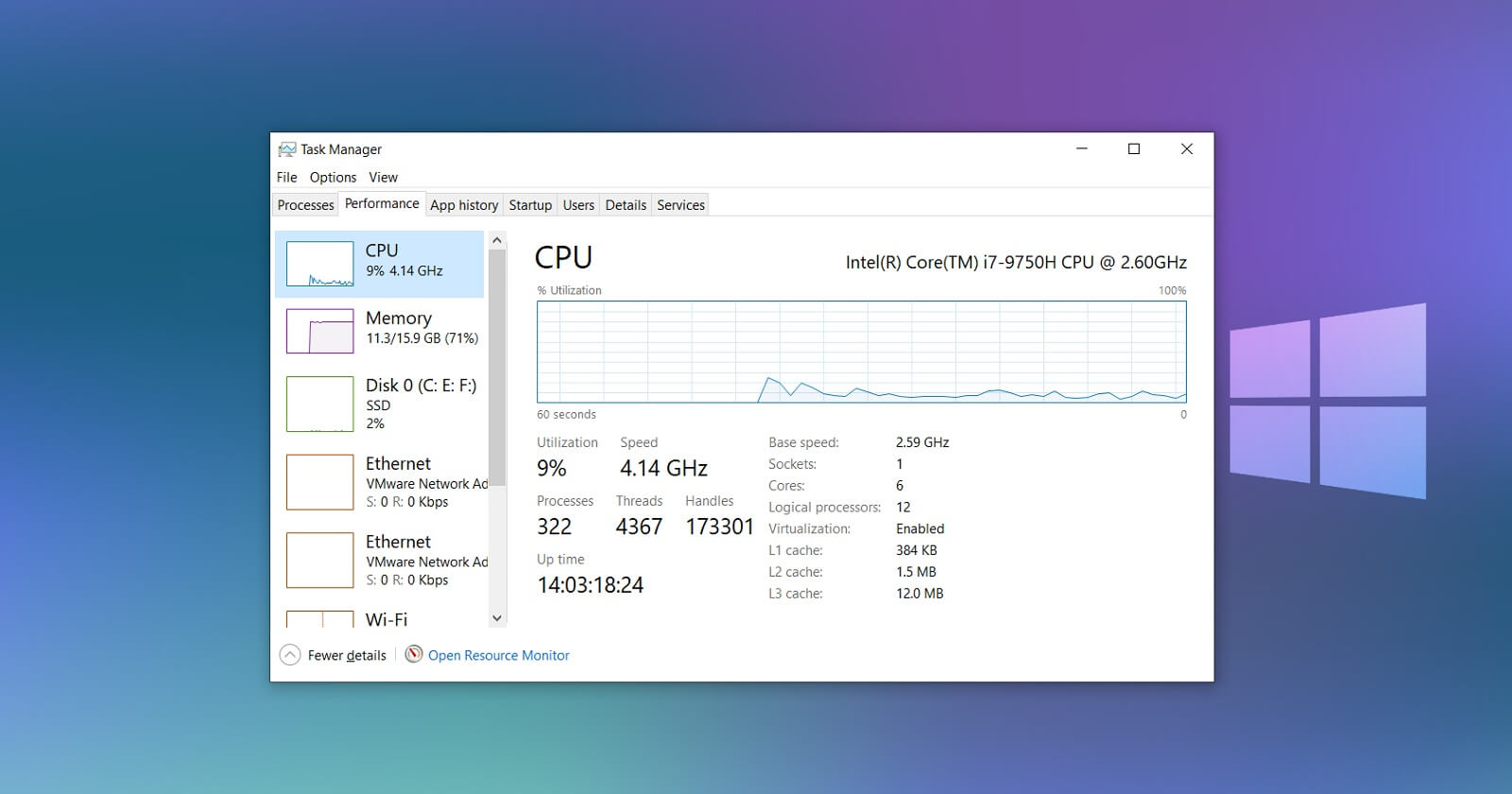
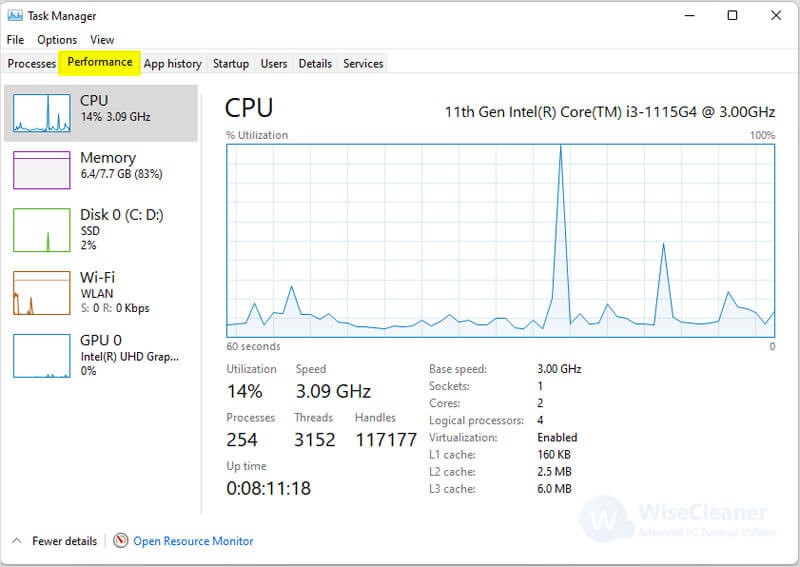
- Task Manager: The Task Manager provides a detailed overview of CPU usage by individual processes. To access it, press Ctrl+Shift+Esc. Navigate to the "Processes" tab and sort the list by CPU usage. This will identify the application or service consuming the most CPU resources.
- Resource Monitor: For a more in-depth analysis, utilize the Resource Monitor (accessible by searching "Resource Monitor" in the Start menu). It offers a comprehensive view of CPU utilization across various categories, including system processes, user processes, and kernel processes.
2. Optimize System Resources:
- Close Unnecessary Programs: Minimizing the number of applications running simultaneously can reduce CPU load. Close any programs that are not actively in use.
- Disable Unnecessary Startup Programs: Many applications launch automatically at startup, consuming system resources. To disable these, access the Task Manager, navigate to the "Startup" tab, and disable unnecessary programs.
- Limit Background Processes: Reduce the number of background processes running by disabling or adjusting settings for services like cloud syncing, automatic updates, and antivirus scans.
- Optimize Visual Effects: Windows 11 offers various visual effects that can impact performance. Navigate to "System Settings" > "System" > "Display" and adjust the visual effects settings to prioritize performance over aesthetics.
3. Address Malware and Viruses:
- Run a Full System Scan: Employ a reputable antivirus software to perform a full system scan. This will identify and remove any malicious software that might be consuming CPU resources.
- Consider Malware Removal Tools: If a standard antivirus scan fails to resolve the issue, consider using specialized malware removal tools, such as Malwarebytes.
4. Update Drivers and Software:
- Check for Driver Updates: Outdated or incompatible device drivers can cause system instability and high CPU usage. Visit the manufacturer’s website or use Windows Update to install the latest drivers for your hardware.
- Update Windows: Ensure that your Windows 11 installation is up-to-date. Windows updates often include performance improvements and bug fixes that can address high CPU usage issues.
- Update Applications: Regularly update your software applications, as updates often include performance enhancements and bug fixes.
5. Repair System Files:
-
System File Checker (SFC): This tool scans for and repairs corrupted system files. Open Command Prompt as administrator and run the command:
sfc /scannow. -
Deployment Image Servicing and Management (DISM): This tool repairs the Windows image. Open Command Prompt as administrator and run the command:
DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth.
6. Check Hardware:
- Monitor CPU Temperature: Overheating can cause system instability and high CPU utilization. Utilize monitoring tools like HWMonitor to track CPU temperature. If it exceeds the recommended threshold, ensure proper cooling solutions.
- Check for Hardware Failures: Run diagnostic tests on your hard drive and other hardware components to rule out any potential failures.
7. Consider Reinstallation:
- Clean Install: In extreme cases, a clean installation of Windows 11 can resolve persistent high CPU usage issues. This involves formatting the hard drive and reinstalling the operating system from scratch.
FAQs:
Q: What is the normal CPU usage in Windows 11?
A: The normal CPU usage in Windows 11 varies depending on the system load. Idle systems typically have a CPU utilization of around 5-15%. During heavy tasks, it can reach 80-90% or even 100% for short periods. Sustained 100% CPU usage for extended periods indicates a potential problem.
Q: How can I monitor CPU usage in real-time?
A: You can monitor CPU usage in real-time using the Task Manager or Resource Monitor. The Task Manager provides a basic overview, while the Resource Monitor offers a more detailed analysis.
Q: What is the best way to identify the cause of high CPU usage?
A: The best approach is to use a combination of tools, including Task Manager, Resource Monitor, and antivirus software. Analyzing the processes consuming the most CPU resources and checking for malware infections can help pinpoint the cause.
Q: How can I prevent high CPU usage in the future?
A: Regularly maintain your system by updating drivers, software, and Windows. Limit the number of background processes and avoid running resource-intensive applications simultaneously. Ensure proper cooling and monitor CPU temperature to prevent overheating.
Tips:
- Use a Performance Monitoring Tool: Utilize performance monitoring tools like HWMonitor or Perfmon to track CPU usage, temperature, and other system parameters. This can help identify potential issues early on.
- Prioritize Performance Over Aesthetics: Adjust visual effects and disable unnecessary background processes to prioritize system performance over aesthetics.
- Consider Hardware Upgrades: If your computer is older or has limited processing power, consider upgrading your CPU or RAM to improve performance.
Conclusion:
High CPU utilization in Windows 11 can significantly impact system performance and user experience. By understanding the potential causes and implementing the troubleshooting steps outlined in this guide, users can effectively diagnose and resolve high CPU usage issues, restoring optimal system responsiveness and productivity. Remember to approach the problem systematically, starting with simple solutions and progressing to more advanced techniques if necessary. Regular system maintenance and preventative measures can help minimize the occurrence of such issues in the future.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating High CPU Utilization in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!