Mastering Windows 10 File Explorer: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Mastering Windows 10 File Explorer: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Mastering Windows 10 File Explorer: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mastering Windows 10 File Explorer: A Comprehensive Guide
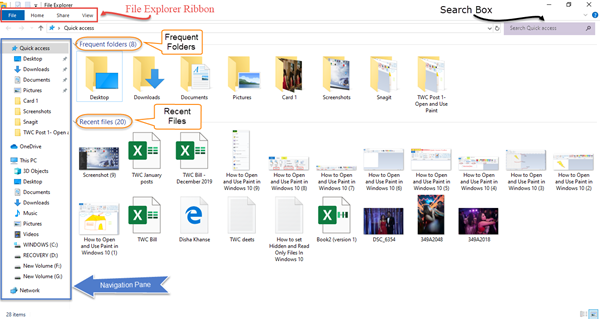
Windows 10’s File Explorer is the central hub for managing files and folders on your computer. It provides a user-friendly interface to access, organize, and manipulate data, making it an essential tool for everyday computing. This guide delves into the intricacies of File Explorer, offering comprehensive insights into its functionality, tips for efficient navigation, and solutions for common challenges.
Understanding the Basics: Navigating File Explorer
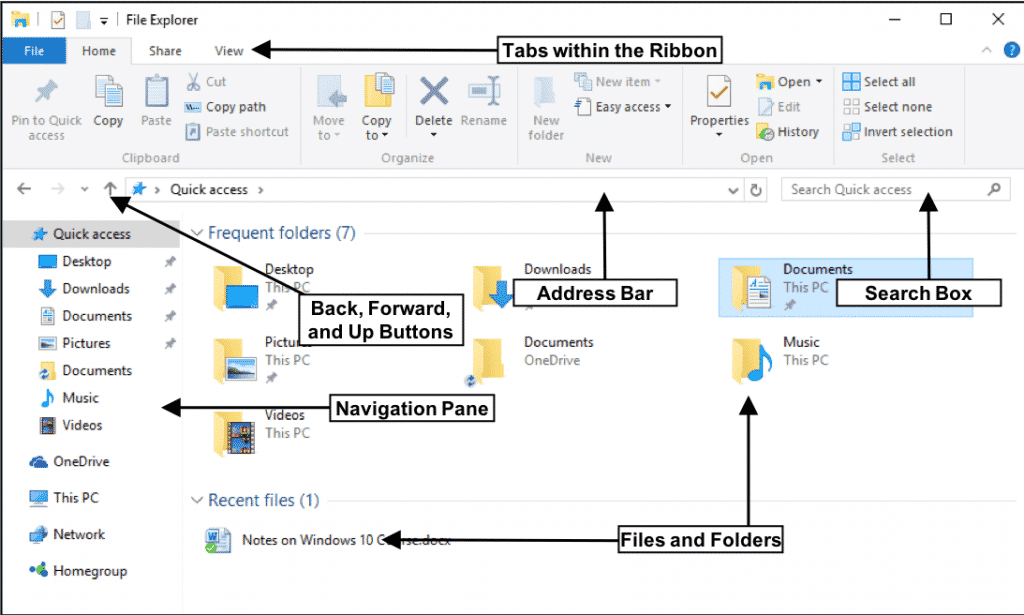
File Explorer’s interface is designed to be intuitive, but a thorough understanding of its components is crucial for effective file management. The main window consists of:
- Navigation Pane: This vertical bar on the left displays a hierarchical tree structure of your computer’s drives, libraries, and network locations. Clicking on an entry reveals its contents in the main pane.
- Address Bar: Located above the navigation pane, this bar shows the current path of the selected folder or file. It allows you to type in a specific location to quickly access desired files.
- Main Pane: This expansive area displays the contents of the currently selected folder or drive. Files and folders are presented in a list or icon view, which can be customized based on your preference.
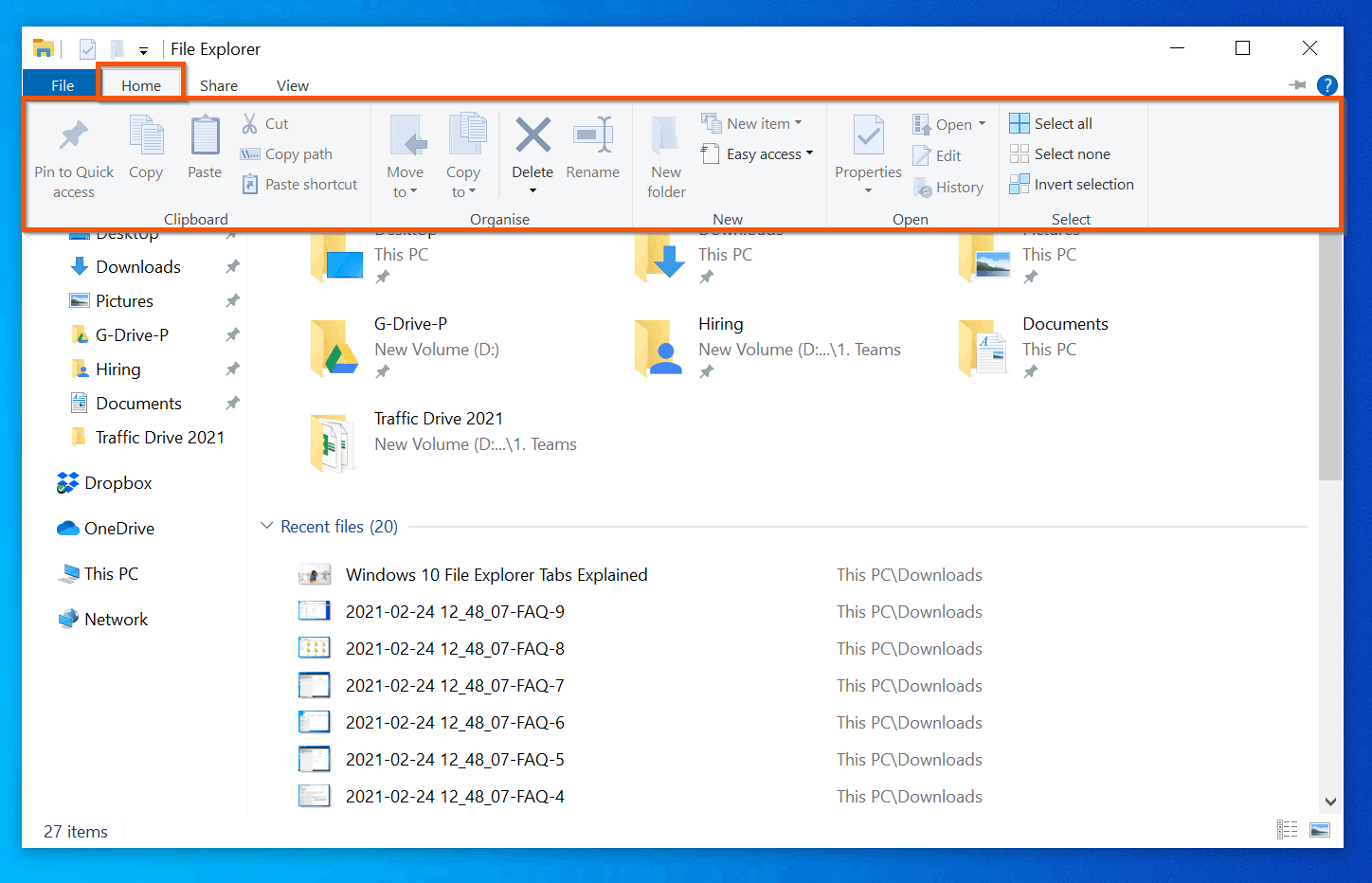
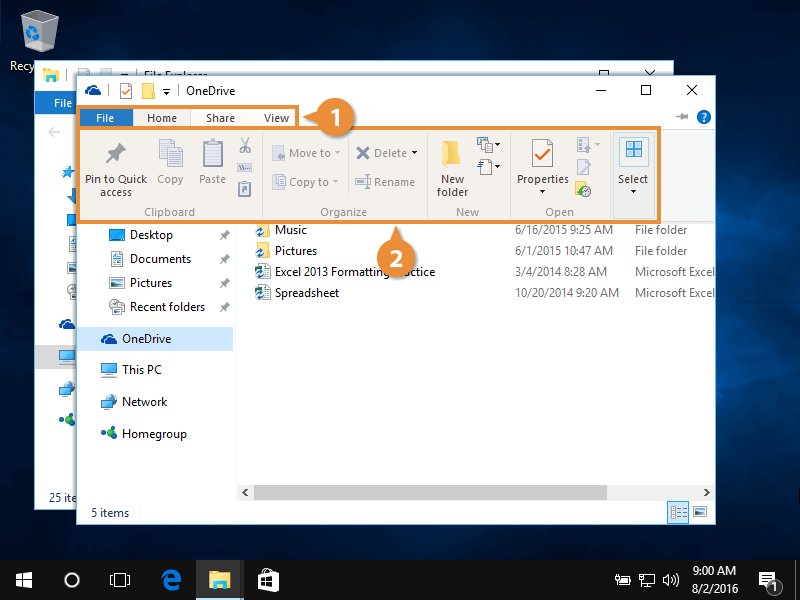
- Ribbon: Situated at the top of the window, the ribbon houses various commands and options for file management tasks like copying, pasting, deleting, renaming, and sharing.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced File Explorer Features
File Explorer offers a range of advanced features to enhance your productivity and streamline file management:
- Search: The search bar in the top-right corner allows you to quickly locate specific files or folders by name, content, or date. You can refine your search by using keywords, file types, and location filters.
- Filters: The "Filter" option in the ribbon provides a quick way to narrow down the results displayed in the main pane. You can filter by file type, size, date modified, and other criteria.
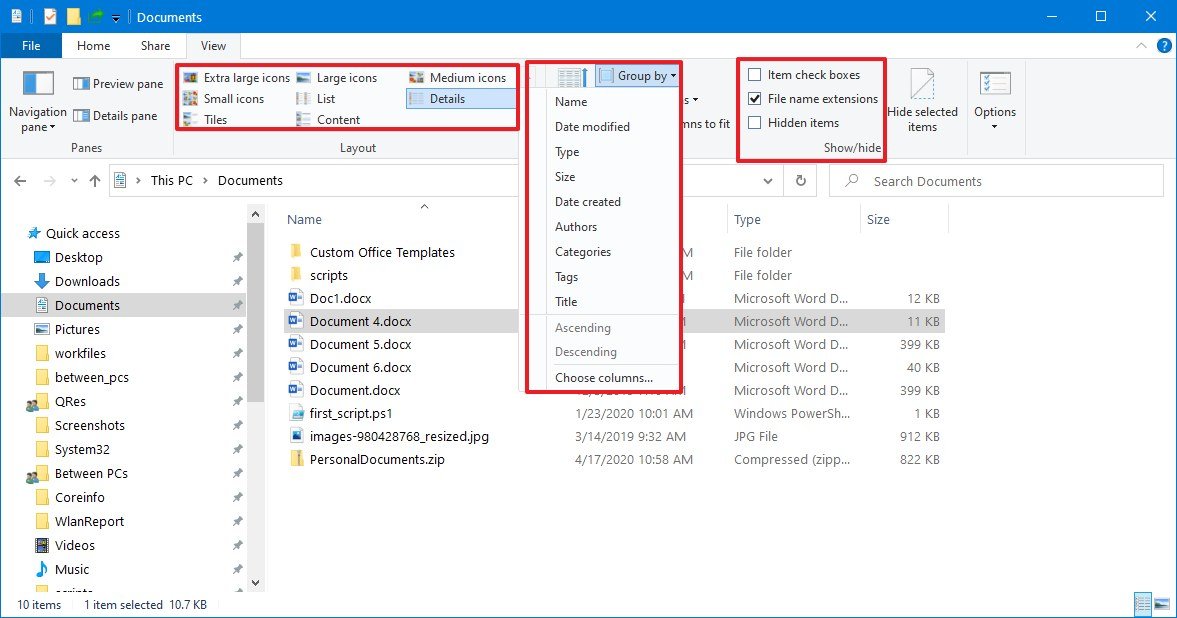
- Sorting: Files and folders can be sorted alphabetically, by date, size, or type. This feature helps you organize your files efficiently and quickly find what you need.
- Preview Pane: This optional pane, enabled by clicking "Preview pane" in the ribbon, displays a preview of the selected file, allowing you to quickly assess its contents without opening it.
- File Properties: Right-clicking on a file or folder and selecting "Properties" reveals detailed information, including size, location, date modified, and attributes. This information is crucial for understanding file characteristics and managing storage space.
- File History: This feature automatically creates backups of your files, allowing you to restore them in case of accidental deletion or data corruption. You can access File History by clicking "This PC" in the navigation pane and selecting "File History."
- Sharing: File Explorer enables easy sharing of files and folders with other users on your network or through cloud storage services. You can share files by right-clicking and selecting "Share," or by using the "Share" button in the ribbon.
Troubleshooting Common File Explorer Issues
While File Explorer is generally reliable, users might encounter occasional issues. Here’s how to address some common problems:
- File Explorer Not Responding: This issue can be caused by various factors, including corrupted files, insufficient system resources, or incompatible software. Restarting your computer is often a quick fix. If the problem persists, try running a system scan using the "System File Checker" tool by typing "sfc /scannow" in the Command Prompt.
- File Explorer Crashing: A crashing File Explorer can be caused by corrupted files, incompatible extensions, or outdated drivers. Try restarting your computer and updating your drivers. If the issue persists, consider reinstalling File Explorer using the "System File Checker" tool.
- File Explorer Slow Performance: Slow performance can be attributed to various factors, including insufficient RAM, fragmented hard drive, or outdated software. Try closing unnecessary programs, defragging your hard drive, and updating your software.
- Unable to Access Files: This issue can be caused by permission restrictions, corrupted files, or malware. Check file permissions by right-clicking the file and selecting "Properties." If the problem persists, run a malware scan using your preferred antivirus software.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How do I change the default view in File Explorer?
A: You can customize the default view by clicking the "View" tab in the ribbon and selecting your desired options. You can choose between list view, icon view, details view, and other options. You can also customize the size of icons and the information displayed in each view.
Q: How do I create a new folder in File Explorer?
A: To create a new folder, navigate to the desired location in the navigation pane, right-click in the main pane, and select "New" followed by "Folder." You can then rename the folder to your liking.
Q: How do I move or copy files between folders?
A: To move a file, select the file, right-click, and select "Cut." Then, navigate to the destination folder, right-click, and select "Paste." To copy a file, select the file, right-click, and select "Copy." Then, navigate to the destination folder, right-click, and select "Paste."
Q: How do I delete a file or folder?
A: To delete a file or folder, select it, right-click, and select "Delete." Alternatively, you can press the "Delete" key on your keyboard. Deleted files are moved to the Recycle Bin, where you can restore them if needed.
Q: How do I compress a file or folder?
A: To compress a file or folder, select it, right-click, and select "Send to" followed by "Compressed (zipped) folder." This creates a compressed archive of the selected files or folders, reducing their size.
Q: How do I create a shortcut to a file or folder?
A: To create a shortcut, select the file or folder, right-click, and select "Create shortcut." The shortcut will be created in the same location as the original file or folder. You can then move the shortcut to a more convenient location, such as the desktop.
Tips for Efficient File Management
- Organize files into folders: Use a logical folder structure to keep your files organized and easily accessible.
- Use descriptive file names: Clearly name your files to easily identify their content.
- Take advantage of file properties: Use file properties to add keywords, tags, and other metadata to help you find files quickly.
- Use search filters: Utilize search filters to quickly narrow down your search results and find specific files.
- Create shortcuts to frequently used files: Create shortcuts to files you frequently access to save time.
- Use cloud storage: Consider using cloud storage services like OneDrive or Google Drive to store your files online and access them from any device.
- Back up your data regularly: Regularly back up your important files to avoid data loss.
Conclusion
Windows 10 File Explorer is a powerful tool for managing files and folders, offering a wide range of features to enhance productivity and streamline data organization. By understanding its functionalities and implementing best practices for file management, users can effectively navigate their computer’s file system, access and organize data efficiently, and ensure data security.

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mastering Windows 10 File Explorer: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!