Managing Administrative Privileges in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Managing Administrative Privileges in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Managing Administrative Privileges in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Managing Administrative Privileges in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Managing Administrative Privileges in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3.1 The Significance of Managing Administrator Accounts
- 3.2 Methods for Modifying Administrator Privileges
- 3.3 Step-by-Step Guide: Changing Administrator Privileges in Windows 10
- 3.4 Additional Considerations:
- 3.5 FAQs:
- 3.6 Tips for Secure Administration:
- 3.7 Conclusion:
- 4 Closure
Managing Administrative Privileges in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide
Windows 10, like its predecessors, employs a hierarchical user account system. At the apex of this system lies the administrator account, possessing the highest level of privileges and access to the operating system’s core functionalities. While this inherent power is crucial for managing system settings, installing software, and troubleshooting issues, it also presents a potential security vulnerability if misused or compromised. Consequently, understanding how to manage administrative accounts is paramount for maintaining a secure and efficient computing environment.
This article will delve into the intricacies of managing administrative privileges in Windows 10, providing a comprehensive guide to modifying and assigning these privileges. We will explore various methods, from using the built-in tools to leveraging advanced techniques, all while emphasizing the importance of secure practices and responsible administration.
The Significance of Managing Administrator Accounts
The need for careful management of administrator accounts stems from their inherent power. An administrator account grants access to critical system files, allowing for modifications that can impact the system’s stability and security. Furthermore, unauthorized access to an administrator account can lead to:
- Data Theft: Sensitive information stored on the computer, including personal files, passwords, and financial details, becomes vulnerable to unauthorized access.
- Malware Infection: Malicious software can be installed and executed, potentially compromising the system’s security and functionality.
- System Instability: Unintentional changes to system settings can lead to system crashes, data loss, and performance issues.
- Account Hijacking: Hackers can gain complete control over the computer, making it difficult to recover and potentially leading to financial losses or identity theft.
Therefore, assigning and managing administrator privileges with caution is essential for maintaining a secure and functional computing environment.
Methods for Modifying Administrator Privileges
Windows 10 offers various methods for managing administrator accounts, catering to different levels of technical expertise and specific needs. These methods can be broadly categorized into two main approaches:
1. Using Built-in Tools:
-
Local Users and Groups: This is the primary tool for managing user accounts and their privileges in Windows 10. Accessed through the Control Panel, it allows for:
- Adding New Accounts: Creating new user accounts with specific permissions.
- Modifying Existing Accounts: Changing account names, passwords, and group memberships.
- Deleting Accounts: Removing user accounts from the system.
- Assigning Administrative Privileges: Granting or revoking administrator privileges to individual accounts.
-
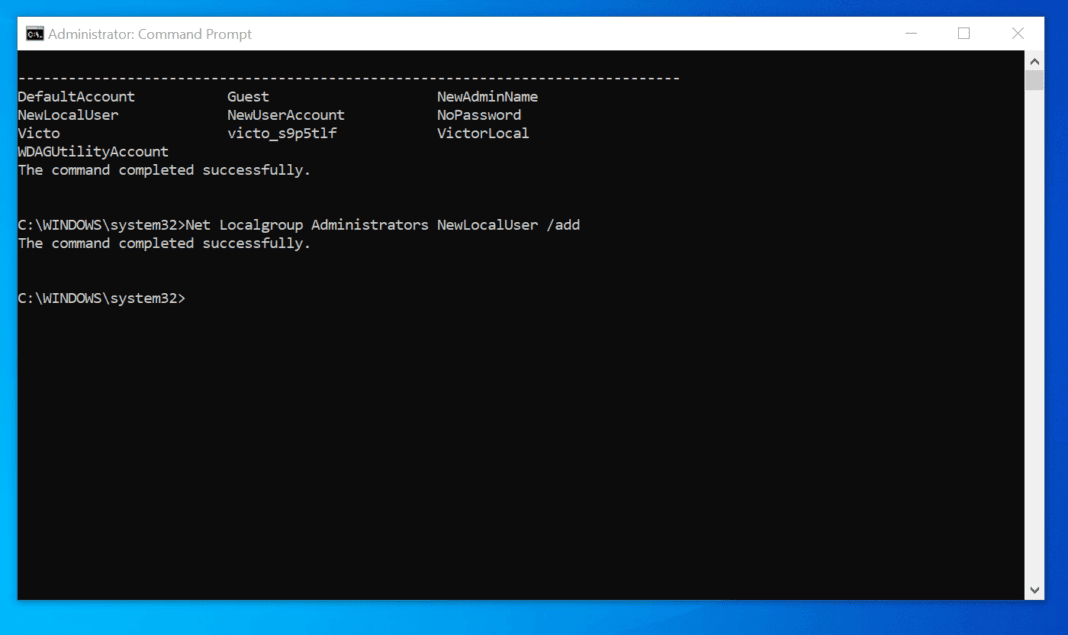
Command Prompt (cmd.exe): This powerful command-line interface offers advanced options for managing user accounts and their privileges. It provides a wider range of commands for more complex tasks, including:
- Net User: Creating, modifying, and deleting user accounts.
- Net LocalGroup: Managing user groups and their memberships.
- Local Users and Groups (lusrmgr.msc): Accessed through the Command Prompt, this tool provides a graphical interface for managing user accounts and group memberships.
2. Advanced Techniques:
-
Group Policy: This powerful tool allows for centralized management of user accounts and their privileges across multiple computers within a network. Group Policy can be used to:
- Define Security Policies: Setting specific rules for user accounts, including password complexity, account lockout policies, and access rights.
- Create User Templates: Defining standardized user account configurations for different user groups, ensuring consistent security practices across the network.
-
Active Directory: This directory service, typically used in enterprise environments, provides a centralized platform for managing user accounts, groups, and their permissions. Active Directory offers:
- Centralized Account Management: Creating, modifying, and deleting user accounts and groups from a single location.
- Fine-grained Access Control: Assigning specific permissions to individual users and groups for different resources, ensuring granular control over access.
Step-by-Step Guide: Changing Administrator Privileges in Windows 10
This section outlines the process of changing administrator privileges using the built-in "Local Users and Groups" tool.
1. Accessing the "Local Users and Groups" Tool:
- Method 1: Open the "Control Panel" by searching for it in the Windows search bar.
- Method 2: Press the "Windows Key + R" to open the "Run" dialog box. Type "control" and click "OK."
- Method 3: Type "lusrmgr.msc" in the Windows search bar and press "Enter."
2. Navigating to the User Accounts:
- Within the "Control Panel," navigate to "Administrative Tools."
- Locate and double-click "Local Users and Groups."
- The "Local Users and Groups" window will appear, displaying a list of user accounts and groups on the left panel.
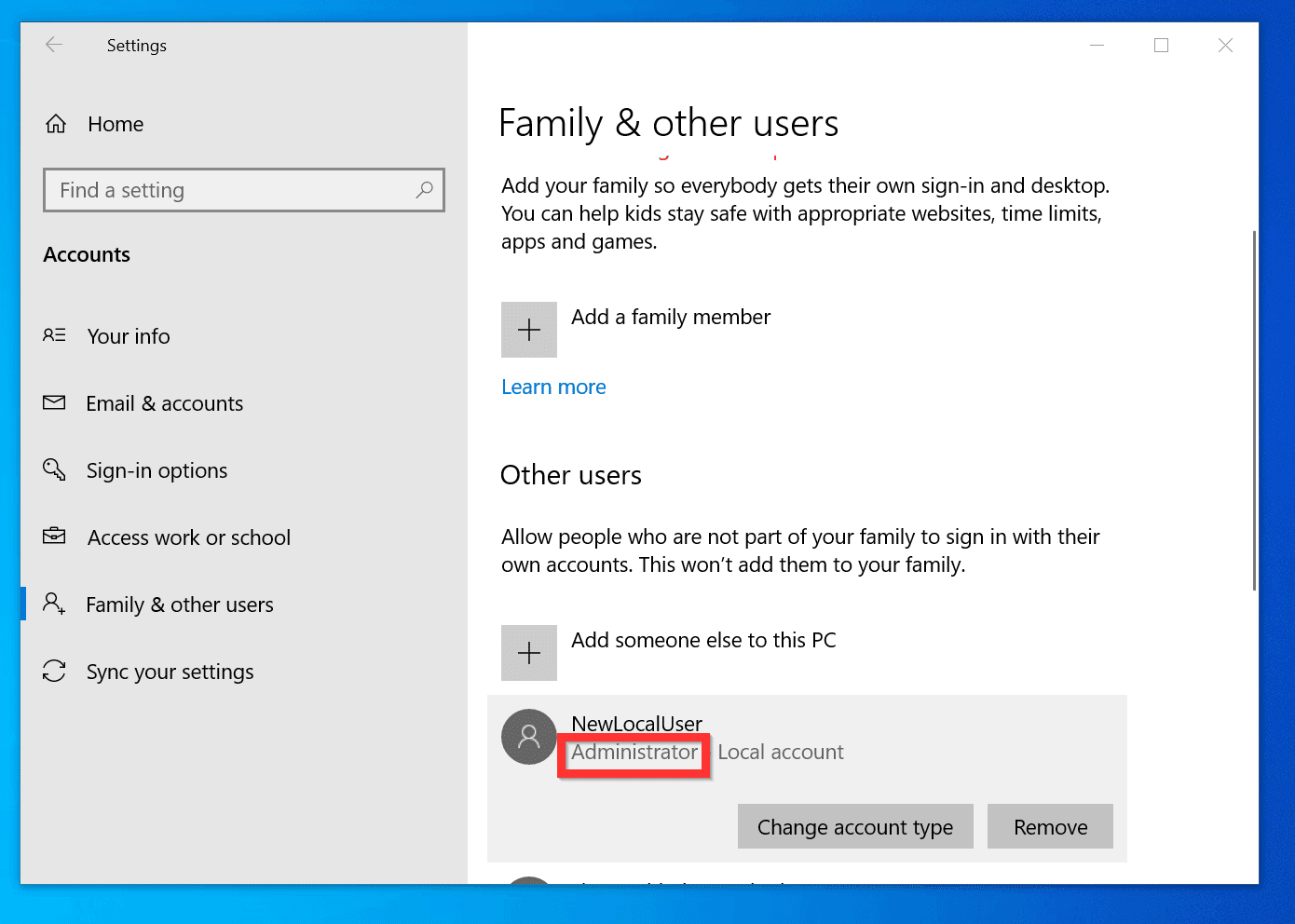
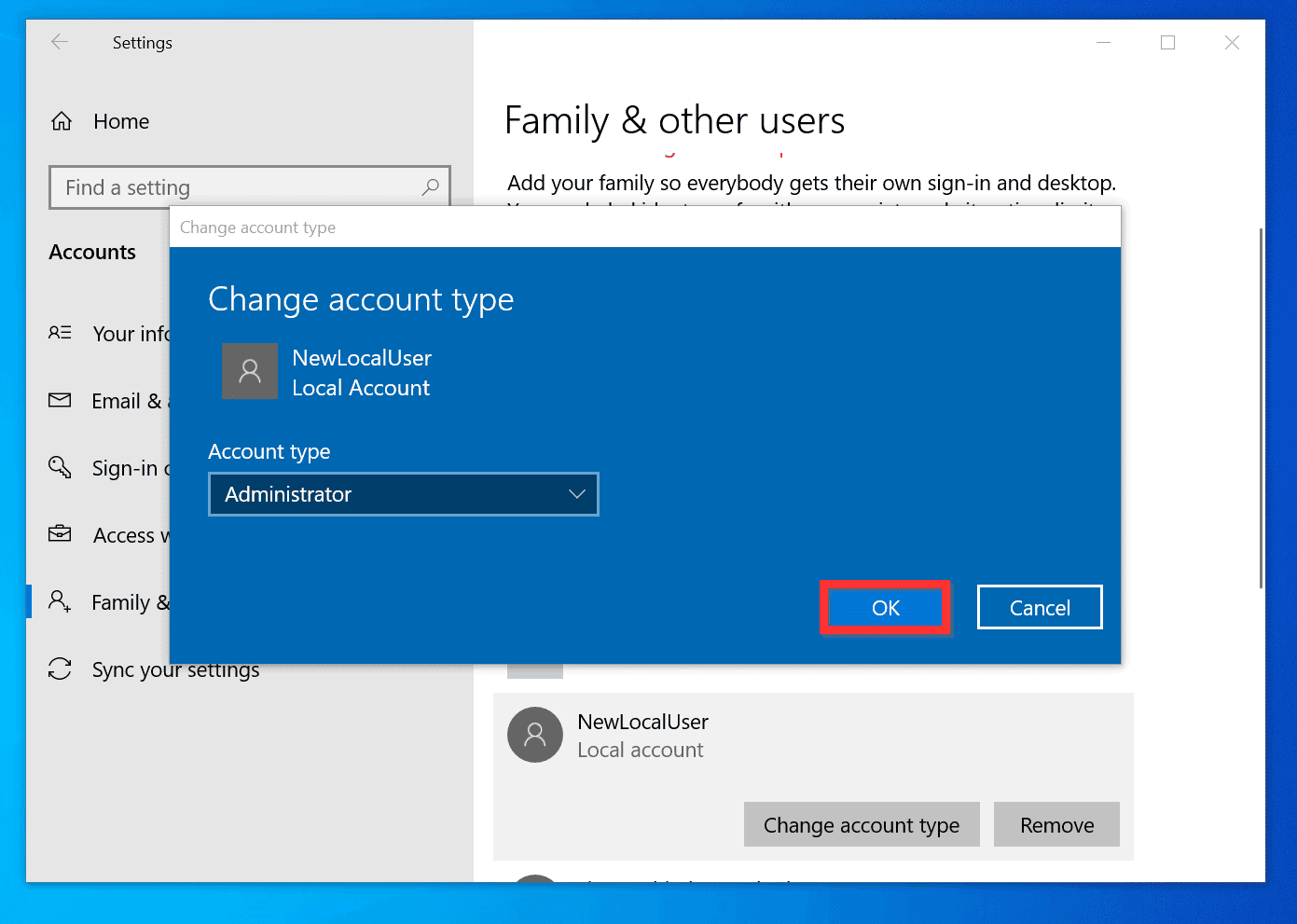
3. Changing Administrator Privileges:
-
For existing accounts:
- Right-click the user account you want to modify.
- Select "Properties."
- Go to the "Member Of" tab.
- To grant administrator privileges, add the account to the "Administrators" group.
- To revoke administrator privileges, remove the account from the "Administrators" group.
-
For new accounts:
- Right-click the "Users" folder.
- Select "New" > "User."
- Enter the desired username and password.
- To grant administrator privileges, check the "Administrator" checkbox.
- Click "Create."
4. Applying Changes and Verifying:
- Close the "Local Users and Groups" window.
- Log out and log back into the system to ensure the changes are applied.
- Verify the account’s administrative privileges by attempting to access system settings or install software.
Additional Considerations:
- Password Management: When changing administrator privileges, it is crucial to set strong passwords for all accounts, including the administrator account. A strong password is at least 12 characters long, includes a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols.
- Two-Factor Authentication: For enhanced security, consider enabling two-factor authentication for the administrator account. This requires an additional verification step, such as a code sent to a mobile device, before granting access.
- Regular Password Changes: Implement a policy for regular password changes for all accounts, particularly the administrator account. This minimizes the risk of unauthorized access in case of a password compromise.
- Account Lockout Policies: Configure account lockout policies to prevent brute-force attacks, where hackers attempt to guess passwords by repeatedly trying different combinations.
- Account Auditing: Regularly monitor account activity to detect any suspicious behavior, such as unauthorized login attempts or changes to system settings.
FAQs:
1. Can I disable the administrator account?
Yes, you can disable the administrator account. However, it is generally not recommended as it can limit access to critical system settings and troubleshooting tools. If you choose to disable it, ensure you have another account with administrator privileges for managing the system.
2. What if I forget the administrator password?
If you forget the administrator password, you may need to reset it using a password reset disk or by using advanced recovery methods. These methods may require technical expertise or professional assistance.
3. What are the benefits of having multiple administrator accounts?
Having multiple administrator accounts allows for different levels of access and responsibility. For example, you can have one account for system administration and another for managing specific applications or user accounts.
4. Can I create a new administrator account without knowing the current administrator password?
No, you need the administrator password to create a new administrator account. However, you can use the "Local Users and Groups" tool to modify the existing administrator account’s password.
5. How can I prevent unauthorized access to my administrator account?
Implement strong passwords, enable two-factor authentication, and regularly change passwords. Additionally, use account lockout policies and monitor account activity for suspicious behavior.
Tips for Secure Administration:
- Principle of Least Privilege: Grant only the necessary permissions to each user account. This minimizes the potential impact of a security breach.
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct regular security audits to identify and address potential vulnerabilities.
- Software Updates: Keep your operating system and software up to date with the latest security patches.
- Antivirus Software: Use reputable antivirus software to protect your computer from malware.
- Firewall: Enable the built-in Windows firewall to block unauthorized access to your computer.
Conclusion:
Managing administrator privileges is crucial for maintaining a secure and functional computing environment. By understanding the different methods for assigning and modifying these privileges, users can effectively control access to critical system resources and mitigate the risks associated with unauthorized access. Implementing strong security practices, such as using strong passwords, enabling two-factor authentication, and regularly monitoring account activity, further enhances the security of the system. By adopting these measures, users can ensure the safety and integrity of their Windows 10 environment.
![[Guide] Windows 10 Administrator Privileges Usage Guide](https://cdn.techloris.com/app/uploads/2023/04/A-Guide-on-Windows-10-Administrator-Privileges.png)

![[Guide] How To Get Administrator Privileges On Windows 10](https://cdn.techloris.com/app/uploads/2023/05/get-admin-rights-on-windows-10.png)
![[Guide] Windows 10 Administrator Privileges Usage Guide](https://cdn.techloris.com/app/uploads/2022/10/select-change-account-type.png)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Managing Administrative Privileges in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!