Installing Windows 11 on Unsupported Hardware: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Installing Windows 11 on Unsupported Hardware: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Installing Windows 11 on Unsupported Hardware: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Installing Windows 11 on Unsupported Hardware: A Comprehensive Guide
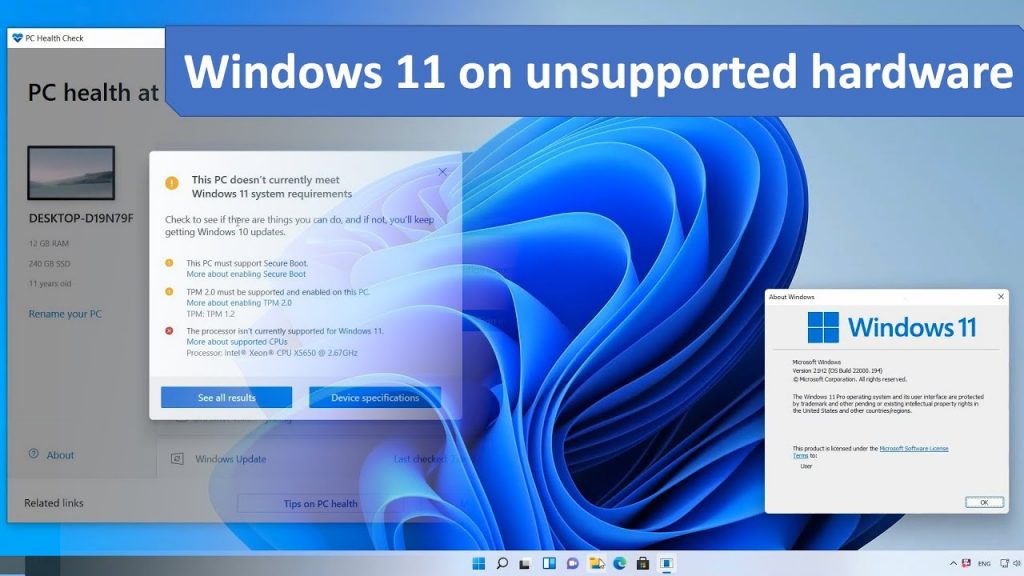
Microsoft’s Windows 11 operating system boasts a refined interface, enhanced security features, and improved performance. However, its strict system requirements have left many users with perfectly functional computers unable to upgrade. This guide provides a comprehensive understanding of how to install Windows 11 on unsupported hardware, exploring the process, potential risks, and alternative solutions.
Understanding Windows 11’s System Requirements
Windows 11 mandates specific hardware configurations to ensure optimal performance and compatibility. These requirements include:
- Processor: 1 gigahertz (GHz) or faster with 2 or more cores on a compatible 64-bit processor or System on a Chip (SoC).
- RAM: 4 gigabytes (GB) of RAM.
- Storage: 64 GB or larger storage device.
- System firmware: UEFI, Secure Boot capable.
- TPM: Trusted Platform Module (TPM) version 2.0.
- Display: High definition (720p) display with a minimum screen size of 9 inches.
The Challenges of Installing Windows 11 on Unsupported Hardware
While Windows 11 offers numerous benefits, installing it on a system that does not meet the minimum requirements can lead to several challenges:
- Performance Issues: The operating system may struggle to run smoothly, leading to slowdowns, crashes, and general instability.
- Security Risks: Windows 11’s security features, including TPM 2.0, are designed for newer hardware. Bypassing these requirements can leave the system vulnerable to security threats.
- Driver Compatibility: Older hardware might lack compatible drivers, resulting in malfunctioning peripherals and devices.
- Limited Support: Microsoft officially supports Windows 11 only on systems meeting the minimum requirements. This means users might encounter difficulties accessing technical support or receiving updates.
Methods for Installing Windows 11 on Unsupported Hardware
Despite the challenges, there are methods to circumvent the system requirements and install Windows 11 on unsupported hardware. However, these methods are not officially sanctioned by Microsoft and should be approached with caution.
1. Using the Registry Editor
This method involves modifying the Windows 11 installation files to bypass the system checks. It requires familiarity with the registry editor and carries the risk of system instability if not executed correctly.
Steps:
- Download the Windows 11 ISO file: Obtain the ISO file from Microsoft’s website.
- Create a bootable USB drive: Use a tool like Rufus or the Windows USB/DVD Download Tool to create a bootable USB drive from the ISO file.
-
Modify the registry:
- Boot from the USB drive and select "Repair your computer."
- Navigate to "Troubleshoot" -> "Advanced options" -> "Command Prompt."
- Execute the following command: reg add "HKLMSYSTEMSetupMoSetup" /v AllowUpgradesWithUnsupportedTPM /t REG_DWORD /d 1 /f
- Close the command prompt and restart the installation process.
2. Using the "Bypass TPM and Secure Boot" Method
This method involves modifying the boot settings to bypass the TPM and Secure Boot checks. It requires modifying the BIOS settings and can be complex for novice users.
Steps:
- Access the BIOS settings: Restart the computer and press the designated key (usually F2, F10, or Del) to enter the BIOS setup.
- Disable Secure Boot: Locate the "Secure Boot" option and disable it.
- Disable TPM: Locate the "TPM" or "Trusted Platform Module" option and disable it.
- Save changes and exit: Save the changes and exit the BIOS setup.
- Install Windows 11: Proceed with the installation using the bootable USB drive created earlier.
3. Using Third-Party Tools
Several third-party tools claim to bypass Windows 11’s system requirements. However, these tools often come with security risks and might not be reliable. It is crucial to research and choose reputable tools with a good track record.
Potential Risks of Installing Windows 11 on Unsupported Hardware
Installing Windows 11 on unsupported hardware involves several risks:
- Performance Degradation: The operating system might experience slowdowns, crashes, and instability due to incompatibility with the hardware.
- Security Vulnerabilities: Bypassing security features like TPM 2.0 can leave the system vulnerable to malware and other security threats.
- Driver Issues: Older hardware might lack compatible drivers, leading to malfunctioning peripherals and devices.
- Lack of Support: Microsoft officially supports Windows 11 only on systems meeting the minimum requirements. This means users might encounter difficulties accessing technical support or receiving updates.
Alternatives to Installing Windows 11 on Unsupported Hardware
Instead of attempting to install Windows 11 on unsupported hardware, consider these alternatives:
- Upgrade Hardware: The most reliable solution is to upgrade the hardware to meet Windows 11’s minimum requirements. This ensures optimal performance, security, and compatibility.
- Use a Virtual Machine: Install Windows 11 in a virtual machine on your existing computer. This allows you to experience Windows 11 without compromising the functionality of your current operating system.
- Stick with Windows 10: Windows 10 continues to receive security updates and is a stable option for older hardware.
FAQs
1. What happens if I install Windows 11 on an unsupported PC?
Installing Windows 11 on unsupported hardware can lead to performance issues, security vulnerabilities, driver incompatibility, and limited support from Microsoft.
2. Is it legal to install Windows 11 on an unsupported PC?
While Microsoft’s terms of service state that Windows 11 should be installed only on compatible hardware, there are no explicit legal penalties for installing it on unsupported systems. However, it is essential to be aware of the potential risks involved.
3. Can I update my unsupported PC to Windows 11 later?
Microsoft does not guarantee compatibility updates for unsupported hardware. Even if you successfully install Windows 11 on an unsupported system, you might not be able to receive future updates or upgrades.
4. What are the best alternatives to Windows 11?
Windows 10 continues to be a stable and secure operating system, and it is a viable alternative for unsupported hardware. Other operating systems like Linux distributions also offer a wide range of features and are compatible with a broader range of hardware.
5. Is it worth the risk to install Windows 11 on unsupported hardware?
The decision to install Windows 11 on unsupported hardware is a personal one. Weigh the potential benefits against the risks involved before making a decision. Consider factors like the age and condition of your hardware, your technical expertise, and your tolerance for potential problems.
Tips for Installing Windows 11 on Unsupported Hardware
If you decide to proceed with installing Windows 11 on unsupported hardware, consider these tips:
- Back up your data: Before attempting the installation, back up all important data to prevent loss.
- Create a recovery drive: Create a recovery drive to restore your system to its previous state if the installation fails or causes problems.
- Research and choose reputable tools: If using third-party tools, research and choose reputable options with good reviews.
- Be prepared for potential issues: Be aware that installing Windows 11 on unsupported hardware can lead to unforeseen problems.
Conclusion
While Windows 11 offers a modern and refined user experience, installing it on unsupported hardware carries significant risks. It is crucial to weigh the potential benefits against the risks involved before making a decision. If you are unsure about the compatibility of your system, upgrading your hardware or using a virtual machine are more reliable and secure alternatives. Remember, installing Windows 11 on unsupported hardware is not officially supported by Microsoft, and users are responsible for any consequences that may arise.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Installing Windows 11 on Unsupported Hardware: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!