how to get windows 11 without tpm 2.0
Related Articles: how to get windows 11 without tpm 2.0
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to how to get windows 11 without tpm 2.0. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: how to get windows 11 without tpm 2.0
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Bypassing the TPM 2.0 Requirement for Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3.1 Understanding the TPM 2.0 Mandate
- 3.2 Exploring the Methods to Circumvent the TPM 2.0 Requirement
- 3.3 Assessing the Risks of Bypassing the TPM 2.0 Requirement
- 3.4 Recommendations for Responsible Decision-Making
- 3.5 Frequently Asked Questions
- 3.6 Tips for Avoiding the TPM 2.0 Requirement
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Bypassing the TPM 2.0 Requirement for Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide

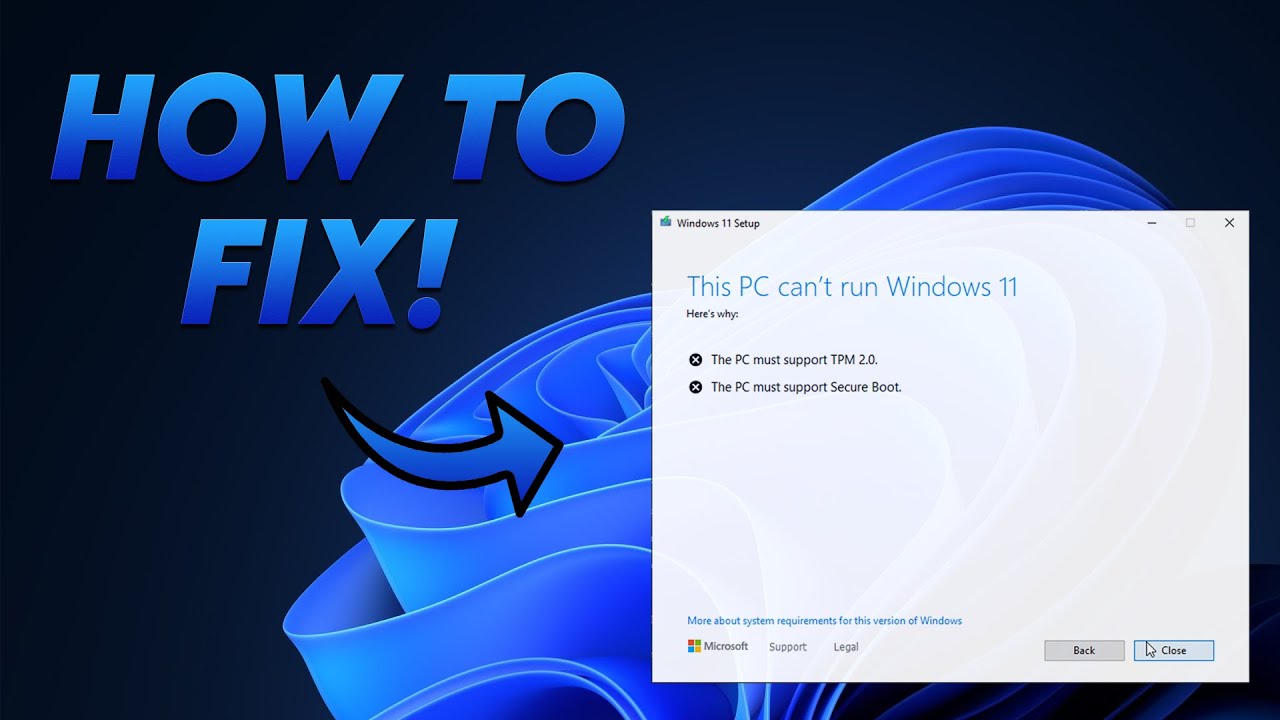
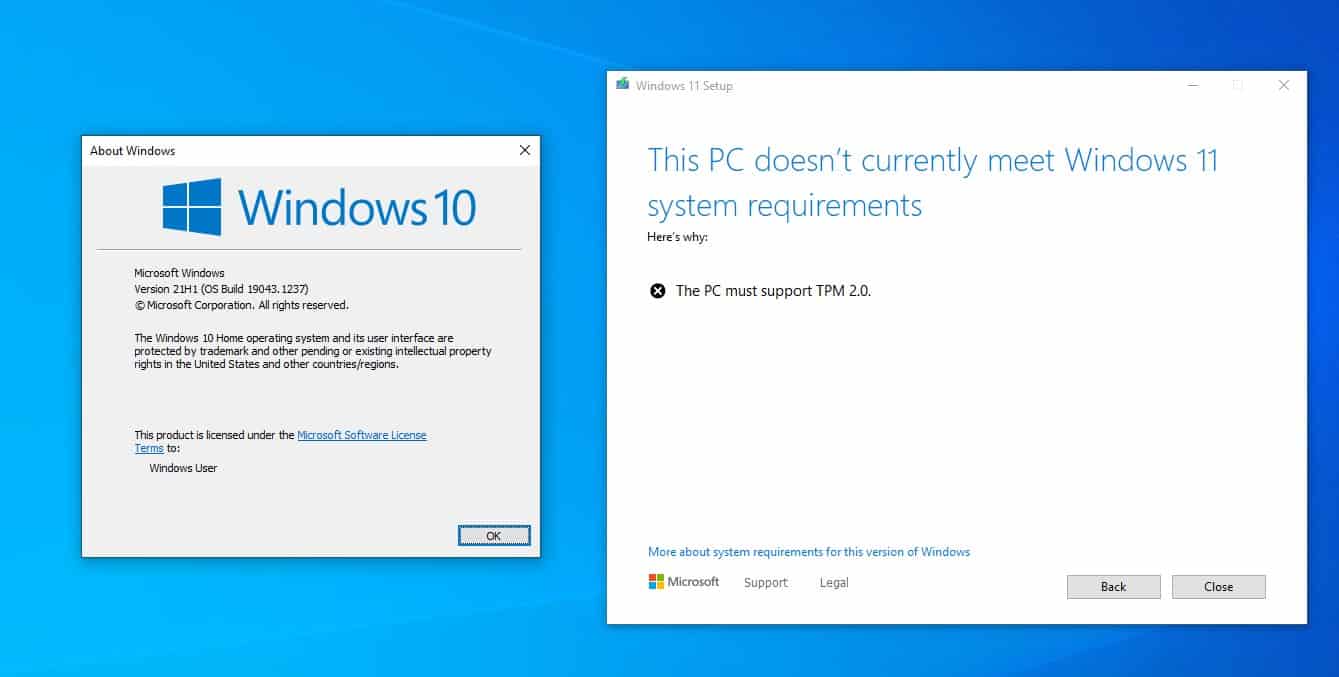
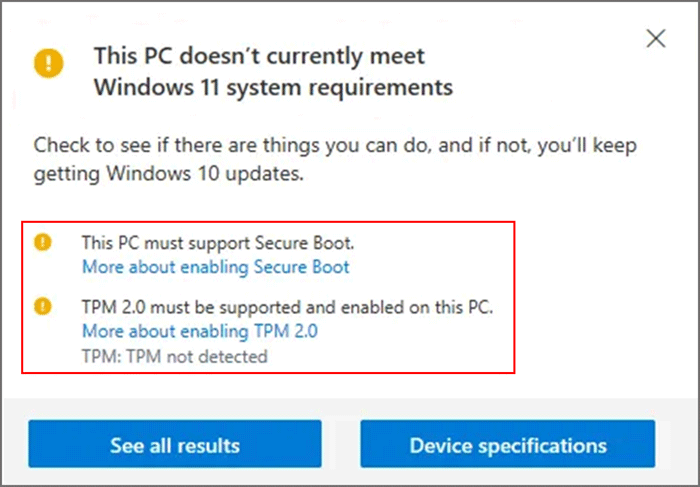
Windows 11, Microsoft’s latest operating system, boasts a range of enhancements and features designed to elevate the user experience. However, the stringent system requirements, particularly the mandatory presence of a Trusted Platform Module (TPM) 2.0, have presented a significant hurdle for many users. While the TPM 2.0 serves a crucial role in bolstering system security, its absence can prevent users from upgrading to Windows 11.
This article provides a comprehensive guide to circumventing the TPM 2.0 requirement, exploring various methods and their associated risks. It delves into the rationale behind the TPM 2.0 mandate, highlighting its importance in safeguarding sensitive data and enhancing system integrity. The article further explores the potential consequences of bypassing this security measure, emphasizing the importance of responsible and informed decision-making.
Understanding the TPM 2.0 Mandate
The Trusted Platform Module (TPM) 2.0 is a specialized chip integrated into the motherboard of modern computers. It acts as a hardware-based security component, responsible for generating and storing cryptographic keys, securing boot processes, and protecting sensitive data. In essence, it serves as a digital fortress, safeguarding the system against unauthorized access and malicious attacks.
Microsoft’s decision to mandate TPM 2.0 for Windows 11 reflects a growing emphasis on robust security measures. This move aims to create a more secure computing environment, deterring malware and unauthorized access. By requiring TPM 2.0, Microsoft seeks to ensure that Windows 11 runs on devices equipped with the necessary security foundation, promoting a more secure and trustworthy computing experience.
Exploring the Methods to Circumvent the TPM 2.0 Requirement
While TPM 2.0 is a crucial security component, its absence can hinder users from upgrading to Windows 11. Several methods have emerged to bypass this requirement, each with its own implications and risks. Understanding these methods and their associated consequences is crucial for making informed decisions.
1. Enabling TPM Emulation:
Certain motherboard manufacturers have implemented software-based TPM emulation, effectively creating a virtual TPM environment. This approach allows users to bypass the hardware requirement while maintaining a semblance of security. However, it’s crucial to note that emulated TPMs offer a significantly lower level of security compared to their hardware counterparts.
2. Modifying the Registry:
Modifying the Windows registry can temporarily disable the TPM 2.0 requirement, allowing users to install Windows 11. This method involves altering specific registry keys, effectively tricking the installation process into bypassing the TPM 2.0 check. However, tampering with the registry can lead to system instability and potential data loss. It is strongly advised to proceed with caution and only if you have a thorough understanding of registry manipulation.
3. Using Third-Party Tools:
Several third-party tools claim to bypass the TPM 2.0 requirement. These tools often involve modifying system files or exploiting vulnerabilities in the Windows installation process. However, using such tools can expose your system to security risks, as they may contain malicious code or compromise your system’s integrity.
4. Upgrading to a Newer Motherboard:
The most straightforward solution is to upgrade to a motherboard that includes a TPM 2.0 chip. This ensures genuine hardware-based security, eliminating the need for workarounds. However, this solution requires a significant investment and may not be feasible for all users.
Assessing the Risks of Bypassing the TPM 2.0 Requirement
While bypassing the TPM 2.0 requirement might seem appealing, it’s crucial to acknowledge the associated risks. These methods compromise the system’s security, potentially leaving it vulnerable to malware and unauthorized access.
1. Increased Vulnerability to Malware:
Without the protection of a TPM 2.0 chip, your system becomes more susceptible to malware attacks. Malware can exploit vulnerabilities in the operating system or applications, potentially stealing sensitive data or causing system instability.
2. Compromised System Integrity:
Bypassing the TPM 2.0 requirement can compromise the integrity of your system. Malicious actors might gain unauthorized access, potentially altering system files or installing malicious software.
3. Reduced Security Features:
Windows 11 relies on the TPM 2.0 chip for several security features, including secure boot and BitLocker encryption. Bypassing the requirement disables these features, leaving your system vulnerable to attacks.
4. Potential for System Instability:
Modifying the registry or using third-party tools can destabilize your system, leading to crashes, errors, and data loss. It’s crucial to understand the potential consequences before attempting these methods.
Recommendations for Responsible Decision-Making
Given the inherent risks, it’s important to approach bypassing the TPM 2.0 requirement with caution and responsibility.
1. Assess the Need:
Consider the potential benefits of upgrading to Windows 11 and weigh them against the risks of bypassing the TPM 2.0 requirement. If your system’s security is paramount, it’s advisable to avoid these methods and explore alternative solutions.
2. Understand the Risks:
Thoroughly research the consequences of each method before proceeding. Be aware of potential vulnerabilities and data loss risks associated with modifying the registry or using third-party tools.
3. Consider Alternatives:
If possible, explore alternative solutions like upgrading to a newer motherboard with TPM 2.0 support. This ensures genuine hardware-based security, eliminating the need for workarounds.
4. Exercise Caution:
Proceed with caution when modifying the registry or using third-party tools. Ensure you have backups of your data and understand the potential consequences of your actions.
5. Seek Professional Guidance:
If you’re unsure about the risks or complexities involved, seek professional guidance from a qualified technician or IT specialist. They can provide informed advice and assist you in making informed decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Can I upgrade to Windows 11 without a TPM 2.0 chip?
A: While Windows 11 officially requires a TPM 2.0 chip, there are methods to bypass this requirement. However, these methods compromise the security of your system and are not recommended for all users.
Q: Is it safe to bypass the TPM 2.0 requirement?
A: No, bypassing the TPM 2.0 requirement compromises the security of your system, making it more vulnerable to malware and unauthorized access.
Q: What are the consequences of bypassing the TPM 2.0 requirement?
A: Bypassing the TPM 2.0 requirement can increase vulnerability to malware, compromise system integrity, disable security features, and potentially lead to system instability.
Q: What are the alternatives to bypassing the TPM 2.0 requirement?
A: Alternatives include upgrading to a newer motherboard with TPM 2.0 support or considering other operating systems that do not require TPM 2.0.
Q: What should I do if I have already bypassed the TPM 2.0 requirement?
A: If you have already bypassed the TPM 2.0 requirement, it’s advisable to revert to the original settings or consider upgrading to a newer motherboard with TPM 2.0 support to enhance your system’s security.
Tips for Avoiding the TPM 2.0 Requirement
1. Upgrade to a Newer Motherboard:
Consider upgrading to a newer motherboard that includes a TPM 2.0 chip. This ensures genuine hardware-based security and eliminates the need for workarounds.
2. Utilize a Virtual Machine:
Install Windows 11 within a virtual machine on your existing system. Virtual machines often have built-in TPM emulation, allowing you to run Windows 11 without a physical TPM 2.0 chip.
3. Explore Alternative Operating Systems:
Consider exploring alternative operating systems, such as Linux distributions, that do not require a TPM 2.0 chip.
4. Stay Informed:
Stay informed about security best practices and emerging technologies related to TPM 2.0. This will help you make informed decisions about your system’s security.
5. Consult with Experts:
If you’re unsure about the best course of action, consult with a qualified technician or IT specialist. They can provide expert advice and guidance.
Conclusion
While bypassing the TPM 2.0 requirement for Windows 11 might seem appealing, it’s crucial to understand the associated risks. These methods compromise the system’s security, leaving it vulnerable to malware and unauthorized access. It’s essential to prioritize system security and consider alternatives like upgrading to a newer motherboard or exploring other operating systems.
The decision to bypass the TPM 2.0 requirement should be made with careful consideration, taking into account the risks and potential consequences. Remember, security is paramount, and compromising it for the sake of convenience can have significant and potentially irreversible repercussions.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into how to get windows 11 without tpm 2.0. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!