Creating a RAID 0 Configuration in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Creating a RAID 0 Configuration in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Creating a RAID 0 Configuration in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Creating a RAID 0 Configuration in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
RAID 0, also known as "striping," is a storage configuration that combines multiple physical hard drives into a single logical volume. This configuration offers a significant performance boost by distributing data across the drives, allowing for parallel read and write operations. This results in faster data transfer speeds, making RAID 0 an attractive option for applications demanding high performance, such as gaming, video editing, and data-intensive workloads.
However, it’s crucial to understand that RAID 0 does not provide data redundancy. If one drive fails, the entire RAID array becomes inaccessible, and all data is lost. Therefore, RAID 0 is not suitable for critical data storage where data loss is unacceptable.
This guide will provide a detailed explanation of how to create a RAID 0 configuration in Windows 11, outlining the steps, considerations, and potential pitfalls.
Prerequisites:
- Compatible Hardware: Ensure your motherboard supports RAID 0 configuration. Consult your motherboard manual or manufacturer’s website for compatibility information.
- Identical Hard Drives: RAID 0 requires using identical hard drives with the same capacity, interface (SATA, NVMe), and rotational speed (RPM). Using mismatched drives can lead to performance issues and instability.
- Windows 11 Installation: Windows 11 must be installed on the system where you intend to create the RAID 0 array.
- Backup Plan: Always create a complete backup of your data before implementing any RAID configuration. This is crucial as data loss is a significant risk with RAID 0.
Steps to Create a RAID 0 Configuration in Windows 11:
- Connect the Hard Drives: Connect the hard drives to your motherboard’s SATA or NVMe ports. Ensure the drives are connected to the appropriate ports designated for RAID configuration.
- Enter the BIOS: Restart your computer and access the BIOS setup menu by pressing the appropriate key during the boot process (usually Delete or F2). The specific key depends on your motherboard manufacturer.
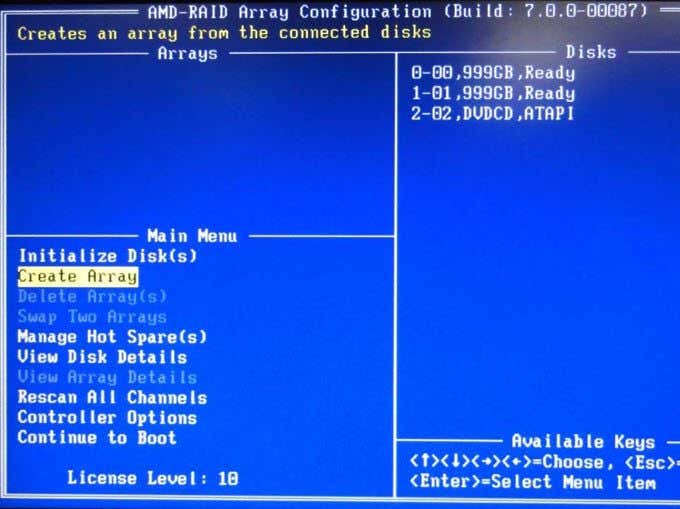
- Configure RAID Mode: Navigate to the "Advanced" or "Storage" section within the BIOS menu. Locate the RAID configuration option and enable it.
- Create a RAID Array: Select the "Create RAID Volume" option and follow the on-screen prompts.
- Select RAID Level: Choose "RAID 0" from the available RAID levels.
- Select Drives: Select the hard drives you want to include in the RAID 0 array. Ensure you select all the drives intended for the configuration.
- Assign a Drive Letter: Assign a drive letter to the new RAID 0 volume. This will be the drive letter used to access the combined volume in Windows.
- Format the RAID Volume: Once the RAID 0 volume is created, format it using the desired file system (usually NTFS) and assign a volume label.
- Install Windows 11 (Optional): If you haven’t already installed Windows 11, you can now install it on the newly created RAID 0 volume.
- Verify RAID Configuration: After completing the steps, reboot your computer and verify that the RAID 0 volume is recognized in Windows Disk Management.
Important Considerations:
- Data Loss Risk: Remember that RAID 0 offers no data redundancy. If one drive fails, the entire array becomes unusable, and all data is lost.
- Drive Failure: If a drive fails, it is critical to replace it as soon as possible. Using a new drive with the same specifications as the original is crucial to maintain the RAID 0 configuration.
- Performance Impact: While RAID 0 provides significant performance gains, it’s essential to consider the potential impact on performance if one drive fails. The remaining drive will have to handle the entire workload, leading to a noticeable decrease in performance.
- Cost: Creating a RAID 0 configuration requires multiple hard drives, increasing the overall cost compared to using a single drive.
FAQs about Creating RAID 0 in Windows 11:
Q: Can I use different types of hard drives in a RAID 0 configuration?
A: No, it’s strongly recommended to use identical hard drives with the same capacity, interface (SATA, NVMe), and rotational speed (RPM) for optimal performance and stability. Using mismatched drives can lead to performance issues and instability.
Q: Can I add or remove drives from a RAID 0 array after it’s created?
A: No, once a RAID 0 array is created, it’s not possible to add or remove drives without destroying the array and losing all data.
Q: Can I use a RAID 0 array for system boot?
A: Yes, you can install Windows 11 on a RAID 0 array, which can significantly improve boot times and system performance. However, remember that data loss is a risk if one drive fails.
Q: Can I use RAID 0 for a single drive?
A: No, RAID 0 requires at least two drives to function.
Q: How do I recover data from a failed RAID 0 array?
A: Data recovery from a failed RAID 0 array is extremely difficult and often impossible. It requires specialized data recovery software and expertise.
Tips for Creating a RAID 0 Configuration:
- Use a RAID Controller: Consider using a dedicated RAID controller card for better performance and stability.
- Monitor Drive Health: Regularly monitor the health of your drives using tools like CrystalDiskInfo or SMART. This can help identify potential problems early.
- Backup Regularly: Despite the performance benefits, RAID 0 does not provide data redundancy. Always create regular backups of your data to mitigate the risk of data loss.
Conclusion:
Creating a RAID 0 configuration in Windows 11 can significantly enhance system performance by striping data across multiple drives. However, it’s crucial to understand the inherent risks associated with this configuration, including the lack of data redundancy and the potential for complete data loss if a single drive fails. Carefully consider your needs and the potential risks before implementing a RAID 0 configuration. For critical data storage, RAID 1 or RAID 5 configurations offer better protection against data loss.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Creating a RAID 0 Configuration in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!