A Deep Dive into Windows 11’s Power-Saving Feature: Understanding "Hibernate"
Related Articles: A Deep Dive into Windows 11’s Power-Saving Feature: Understanding "Hibernate"
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Deep Dive into Windows 11’s Power-Saving Feature: Understanding "Hibernate". Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Deep Dive into Windows 11’s Power-Saving Feature: Understanding "Hibernate"
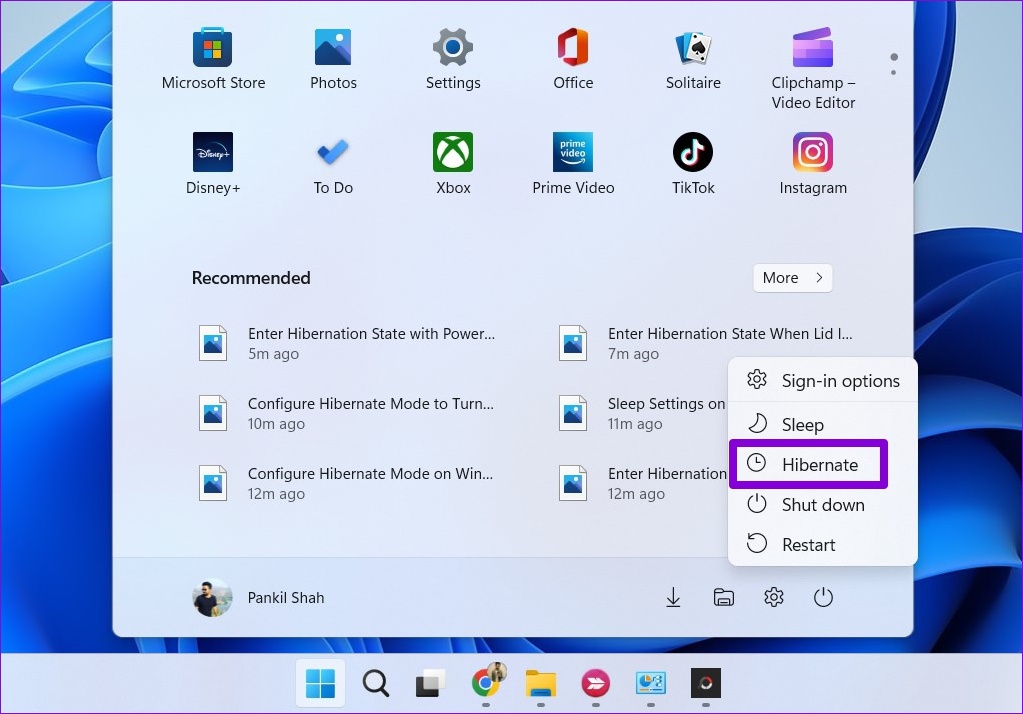
Windows 11, the latest iteration of Microsoft’s operating system, offers a variety of features designed to enhance user experience and system performance. One such feature, often overlooked but highly valuable, is the "Hibernate" option. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of this power-saving mode, exploring its intricacies, benefits, and potential applications.
Understanding the Mechanics of Hibernation
When a computer enters "Hibernate" mode, it essentially saves the entire state of the system to the hard drive. This includes all open applications, documents, and system settings. Upon restarting, the computer retrieves this saved data, restoring the system to its exact state before entering hibernation.
Key Differences: Hibernate vs. Sleep
While "Hibernate" is often confused with "Sleep," these two power-saving modes differ significantly.
- Sleep: This mode puts the computer into a low-power state, suspending all active processes but keeping the RAM powered. This allows for a quicker resume, as the system does not need to reload data from the hard drive. However, sleep mode consumes a small amount of power, and the system remains vulnerable to power outages.
- Hibernate: This mode saves the entire system state to the hard drive, effectively shutting down the computer while preserving all open data. This mode consumes no power and ensures data integrity in case of power outages. However, the resume process takes longer, as the system needs to load data from the hard drive.
Benefits of Utilizing Hibernate
Hibernate mode offers several advantages, making it a valuable tool for users seeking to optimize system performance and ensure data security.
- Power Conservation: Hibernate mode offers significant power savings compared to sleep mode. This is particularly beneficial for laptops and other portable devices, extending battery life and reducing energy consumption.
- Data Integrity: Hibernate mode provides a robust safeguard against data loss in case of power outages. Since the system state is saved to the hard drive, the computer can be safely restarted without losing any unsaved work.
- System Stability: Hibernate mode can help improve system stability by allowing for a clean restart. This can be beneficial in cases where the system is experiencing performance issues or software glitches.
- Extended Downtime: Hibernate mode offers a more secure shutdown than sleep mode, as it completely shuts down the system, minimizing the risk of unauthorized access. This is particularly useful for users who leave their computers unattended for extended periods.
When to Use Hibernate
Hibernate mode is ideal for specific scenarios where its benefits outweigh those of other power-saving options.
- Long Downtime: If you plan to leave your computer unattended for an extended period, hibernation ensures data safety and minimizes power consumption.
- Power Outages: Hibernate mode provides a reliable safeguard against data loss during power outages.
- Performance Issues: If your system is experiencing performance issues, hibernation can offer a clean restart, potentially resolving the problem.
Considerations and Limitations
While Hibernate mode offers numerous advantages, it’s important to acknowledge potential drawbacks and limitations:
- Slower Resume: Hibernate mode requires the system to load data from the hard drive, making the resume process slower than waking up from sleep mode.
- Hard Drive Wear: Repeatedly saving the system state to the hard drive can potentially contribute to wear and tear. However, modern hard drives are designed to withstand this level of activity.
- Limited Availability: Some systems may not support hibernation mode, particularly older computers with limited hardware capabilities.
Enabling and Disabling Hibernate
Enabling or disabling hibernation mode in Windows 11 is a straightforward process.
To Enable Hibernate:
- Open the Control Panel.
- Select Power Options.
- Click on Choose what the power buttons do.
- Click on Change settings that are currently unavailable.
- Check the box next to Hibernate.
- Click on Save Changes.
To Disable Hibernate:
- Follow the same steps as above.
- Uncheck the box next to Hibernate.
- Click on Save Changes.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about Hibernate
Q: What happens to open applications when I hibernate?
A: All open applications, documents, and system settings are saved to the hard drive. Upon restarting, the system will restore everything to the exact state it was in before entering hibernation.
Q: Does hibernation consume any power?
A: No, hibernation consumes no power. The system is completely shut down, and all power is disconnected.
Q: Is hibernation safe for my hard drive?
A: Modern hard drives are designed to withstand the wear and tear associated with frequent hibernation. However, if you are concerned, you can limit the frequency of hibernation usage.
Q: Can I use hibernation on a tablet or smartphone?
A: Hibernate mode is typically not available on tablets or smartphones. These devices use different power-saving mechanisms, such as sleep mode and standby.
Q: What are the differences between hibernate and sleep mode?
A: Sleep mode suspends the system while keeping the RAM powered, allowing for a quick resume. Hibernate saves the system state to the hard drive, consuming no power but requiring a longer resume process.
Tips for Effective Hibernate Utilization
- Regular Maintenance: Ensure your hard drive is properly maintained to minimize the risk of data loss or system instability.
- Backup Strategy: Implement a regular backup strategy to safeguard your data, regardless of the power-saving mode used.
- Understand System Requirements: Confirm that your system supports hibernation mode before enabling it.
- Optimize Power Settings: Adjust your power settings to ensure optimal battery life and system performance.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Hibernate
Hibernate mode, while often overlooked, offers a powerful and versatile tool for optimizing system performance and ensuring data security. By understanding its mechanics, benefits, and limitations, users can effectively leverage this feature to maximize their computing experience. Whether it’s conserving battery life, protecting against data loss, or simply enjoying a clean system restart, hibernation provides a valuable solution for a variety of computing needs.


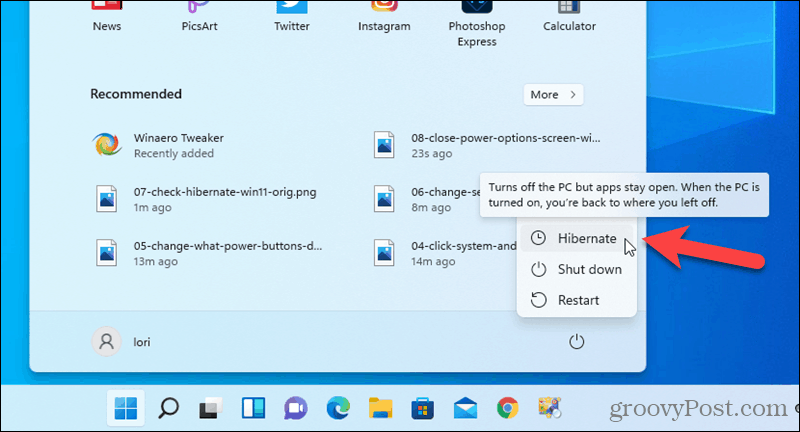




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Deep Dive into Windows 11’s Power-Saving Feature: Understanding "Hibernate". We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!