A Comprehensive Guide to Downloading and Using FFmpeg on Windows 11
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Guide to Downloading and Using FFmpeg on Windows 11
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Guide to Downloading and Using FFmpeg on Windows 11. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Guide to Downloading and Using FFmpeg on Windows 11

FFmpeg is a powerful, open-source multimedia framework that provides a wide range of functionalities for manipulating and converting audio and video files. Its versatility and comprehensive feature set make it a valuable tool for professionals and enthusiasts alike, enabling tasks ranging from basic video editing to complex audio manipulation. This guide will provide a detailed understanding of FFmpeg on Windows 11, encompassing its installation, usage, and common applications.
Understanding the Significance of FFmpeg on Windows 11
FFmpeg’s relevance on Windows 11 stems from its ability to address a multitude of multimedia needs. Its core functionalities include:
- Video Conversion: Converting video files between various formats (e.g., MP4, AVI, MKV) and codecs (e.g., H.264, VP9) while maintaining or enhancing quality.
- Audio Extraction and Manipulation: Isolating audio tracks from video files, converting between audio formats (e.g., MP3, WAV, FLAC), and applying audio effects.
- Video Editing: Basic editing tasks such as trimming, joining, and adding subtitles to videos.
- Streaming: Live streaming of audio and video content.
- Screen Recording: Capturing desktop activity for tutorials or presentations.
Installing FFmpeg on Windows 11
FFmpeg is a command-line tool, requiring users to interact with it through a terminal or command prompt. The installation process on Windows 11 involves the following steps:
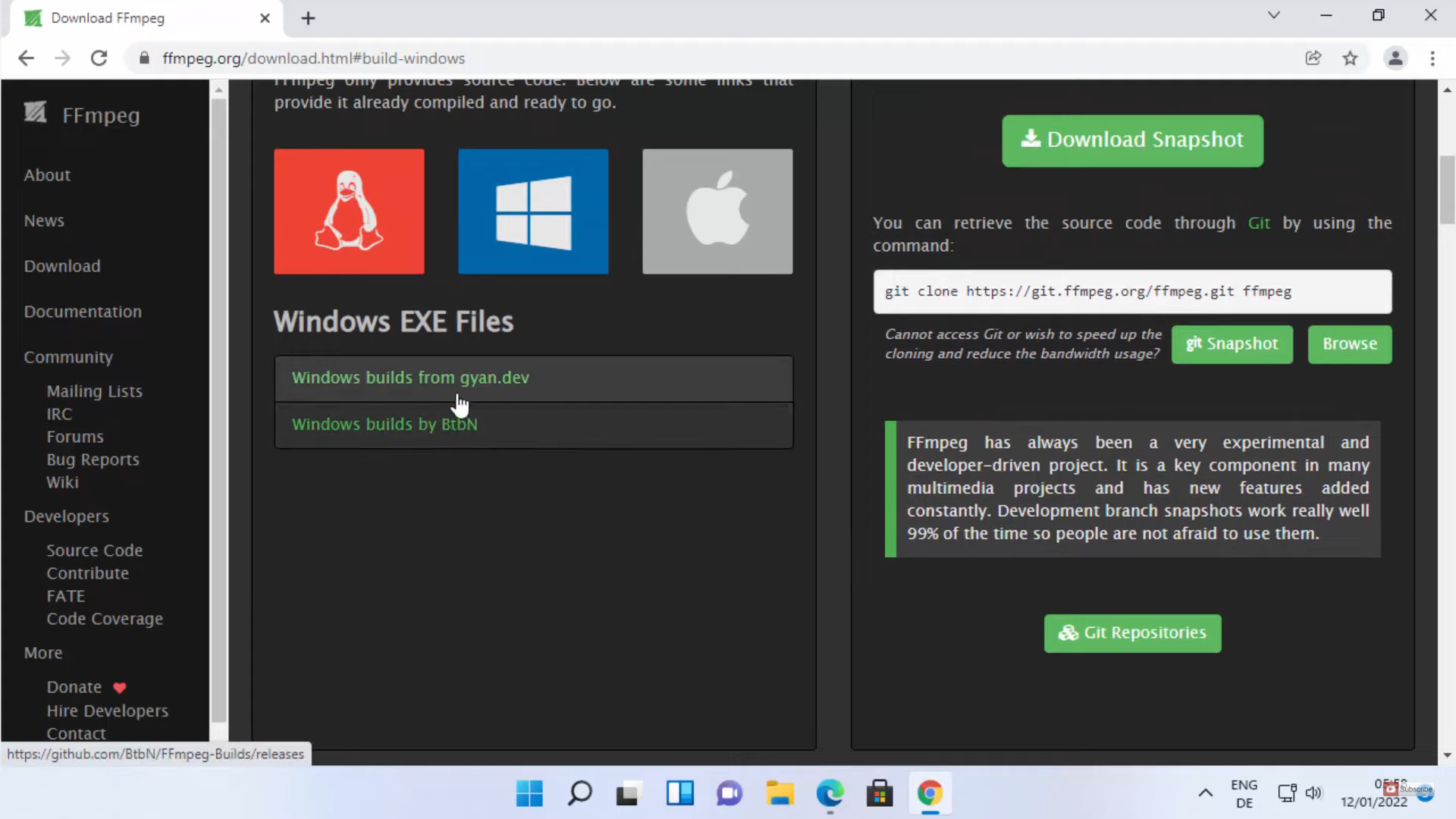
- Downloading the FFmpeg Build: The official FFmpeg website offers a comprehensive list of builds for various operating systems, including Windows. Select the appropriate build for your system architecture (32-bit or 64-bit).
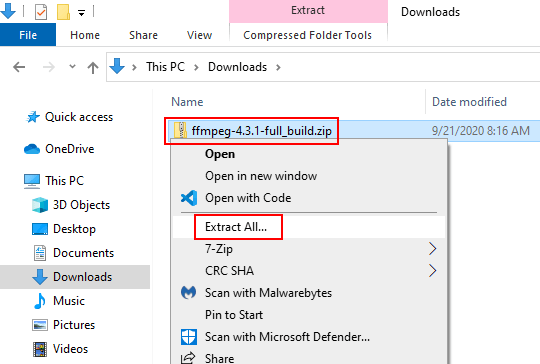
- Extracting the Archive: Once downloaded, extract the FFmpeg archive (usually a ZIP file) to a desired location on your system.
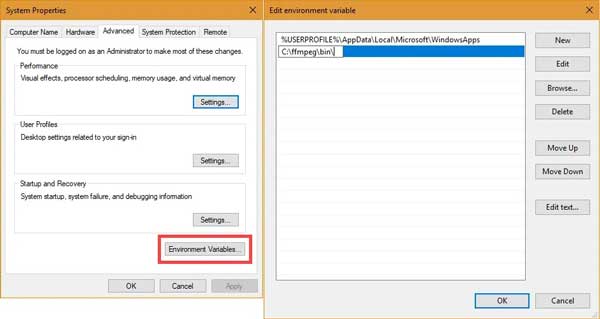
- Adding FFmpeg to the System Path: To access FFmpeg from any location on your system, you need to add its installation directory to the system’s environment variables. This allows the command prompt to locate the FFmpeg executable file.
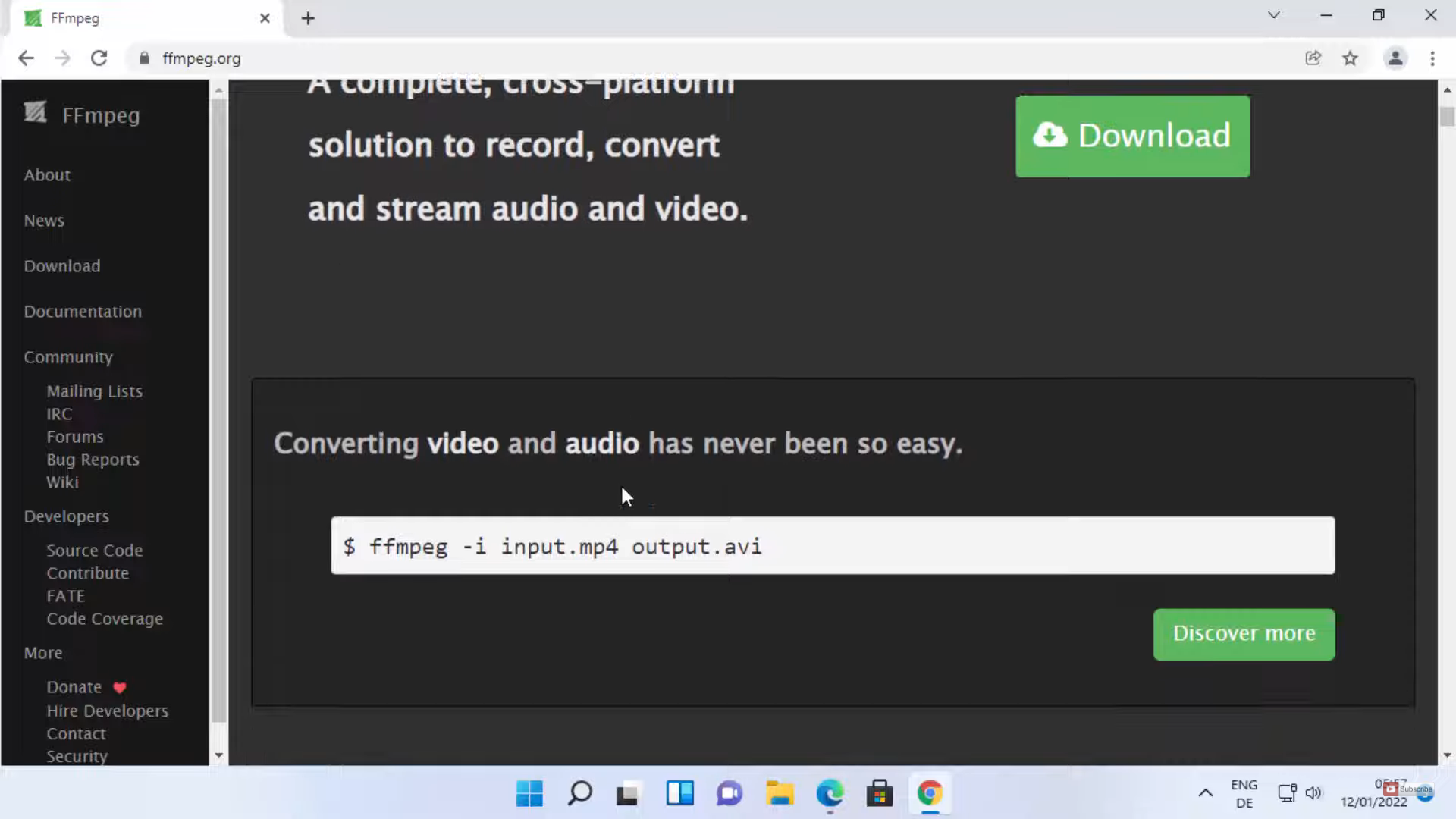
- Verifying Installation: Open a command prompt and type "ffmpeg -version." If the installation was successful, you should see the version information of your FFmpeg build.
Using FFmpeg on Windows 11
FFmpeg operates through a set of commands that specify the desired actions on media files. The basic syntax for using FFmpeg is:
ffmpeg [options] [input file] [output file]The "options" parameter defines the specific actions to be performed, while "input file" and "output file" refer to the source and destination files, respectively.
Here are some common examples of FFmpeg commands:
- Converting a video file from MP4 to AVI:
ffmpeg -i input.mp4 output.avi- Extracting the audio track from a video file:
ffmpeg -i input.mp4 output.mp3- Joining two video files:
ffmpeg -i input1.mp4 -i input2.mp4 -c copy output.mp4- Adding subtitles to a video file:
ffmpeg -i input.mp4 -vf subtitles=subtitles.srt output.mp4Advanced FFmpeg Usage
Beyond basic functionalities, FFmpeg offers advanced features for complex multimedia tasks:
- Video Encoding and Decoding: FFmpeg supports a wide array of video codecs, allowing for optimal compression and quality control.
- Audio Manipulation: FFmpeg enables advanced audio manipulation, including mixing, equalization, and filtering.
- Custom Filters: FFmpeg’s extensive filter library provides options for manipulating video and audio streams in various ways, such as adding effects, applying transformations, and altering metadata.
- Scripting: FFmpeg can be integrated into scripts for automated media processing tasks.
Common FFmpeg Applications
FFmpeg finds widespread application in various fields:
- Video Editing: Professional and amateur video editors use FFmpeg for basic editing tasks, conversion, and advanced effects.
- Content Creation: Content creators rely on FFmpeg for video and audio editing, as well as for creating and manipulating multimedia assets.
- Web Development: FFmpeg is utilized for video and audio streaming on websites and web applications.
- Software Development: Developers use FFmpeg for integrating multimedia functionalities into their applications.
- Research and Development: Researchers use FFmpeg for analyzing and manipulating multimedia data for various research purposes.
FFmpeg FAQs on Windows 11
Q: Is FFmpeg compatible with Windows 11?
A: Yes, FFmpeg is fully compatible with Windows 11. You can download and install it without any compatibility issues.
Q: What are the system requirements for running FFmpeg on Windows 11?
A: FFmpeg does not have stringent system requirements. It can run on most Windows 11 systems with minimal resource consumption.
Q: How do I find the right FFmpeg build for my Windows 11 system?
A: The official FFmpeg website offers builds for both 32-bit and 64-bit systems. Ensure you download the build compatible with your Windows 11 system architecture.
Q: Can I use FFmpeg without a command prompt?
A: While FFmpeg is primarily a command-line tool, there are graphical user interfaces (GUIs) available that provide a more user-friendly interface for interacting with FFmpeg.
Q: Where can I find resources and documentation for learning FFmpeg?
A: The official FFmpeg website provides comprehensive documentation, tutorials, and examples for learning FFmpeg. There are also numerous online resources and communities dedicated to FFmpeg.
Tips for Using FFmpeg on Windows 11
- Start with basic commands: Begin by experimenting with simple commands to understand FFmpeg’s functionalities.
- Utilize online resources: Refer to online tutorials, documentation, and forums for help with specific tasks and troubleshooting.
- Experiment with filters: Explore FFmpeg’s filter library to discover creative ways to manipulate video and audio.
- Utilize scripting for automation: Automate repetitive tasks by integrating FFmpeg into scripts.
Conclusion
FFmpeg is a powerful and versatile multimedia framework that provides a comprehensive set of tools for manipulating and converting audio and video files. Its compatibility with Windows 11 makes it a valuable asset for professionals and enthusiasts alike. Understanding FFmpeg’s functionalities, mastering its command-line interface, and utilizing its advanced features can empower users to perform a wide range of multimedia tasks with ease and efficiency. The open-source nature of FFmpeg ensures its continued development and support, making it a reliable and powerful tool for multimedia manipulation on Windows 11 and beyond.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Guide to Downloading and Using FFmpeg on Windows 11. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!